+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
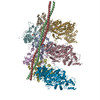
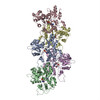
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 2w49 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | ISOMETRICALLY CONTRACTING INSECT ASYNCHRONOUS FLIGHT MUSCLE | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CONTRACTILE PROTEIN / ISOMETRIC CONTRACTION | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationtroponin C binding / Striated Muscle Contraction / troponin complex / regulation of muscle contraction / cytoskeletal motor activator activity / myosin heavy chain binding / tropomyosin binding / actin filament bundle / troponin I binding / filamentous actin ...troponin C binding / Striated Muscle Contraction / troponin complex / regulation of muscle contraction / cytoskeletal motor activator activity / myosin heavy chain binding / tropomyosin binding / actin filament bundle / troponin I binding / filamentous actin / mesenchyme migration / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin filament bundle assembly / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / actin monomer binding / skeletal muscle contraction / skeletal muscle fiber development / cardiac muscle contraction / stress fiber / titin binding / actin filament polymerization / actin filament / filopodium / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / calcium-dependent protein binding / actin filament binding / actin cytoskeleton / lamellipodium / actin binding / cell body / protein heterodimerization activity / protein domain specific binding / hydrolase activity / calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / magnesium ion binding / protein homodimerization activity / ATP binding / identical protein binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / Resolution: 35 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Wu, S. / Liu, J. / Reedy, M.C. / Tregear, R.T. / Winkler, H. / Franzini-Armstrong, C. / Sasaki, H. / Lucaveche, C. / Goldman, Y.E. / Reedy, M.K. / Taylor, K.A. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: PLoS One / Year: 2010 Journal: PLoS One / Year: 2010Title: Electron tomography of cryofixed, isometrically contracting insect flight muscle reveals novel actin-myosin interactions. Authors: Shenping Wu / Jun Liu / Mary C Reedy / Richard T Tregear / Hanspeter Winkler / Clara Franzini-Armstrong / Hiroyuki Sasaki / Carmen Lucaveche / Yale E Goldman / Michael K Reedy / Kenneth A Taylor /  Abstract: BACKGROUND: Isometric muscle contraction, where force is generated without muscle shortening, is a molecular traffic jam in which the number of actin-attached motors is maximized and all states of ...BACKGROUND: Isometric muscle contraction, where force is generated without muscle shortening, is a molecular traffic jam in which the number of actin-attached motors is maximized and all states of motor action are trapped with consequently high heterogeneity. This heterogeneity is a major limitation to deciphering myosin conformational changes in situ. METHODOLOGY: We used multivariate data analysis to group repeat segments in electron tomograms of isometrically contracting insect flight muscle, mechanically monitored, rapidly frozen, freeze ...METHODOLOGY: We used multivariate data analysis to group repeat segments in electron tomograms of isometrically contracting insect flight muscle, mechanically monitored, rapidly frozen, freeze substituted, and thin sectioned. Improved resolution reveals the helical arrangement of F-actin subunits in the thin filament enabling an atomic model to be built into the thin filament density independent of the myosin. Actin-myosin attachments can now be assigned as weak or strong by their motor domain orientation relative to actin. Myosin attachments were quantified everywhere along the thin filament including troponin. Strong binding myosin attachments are found on only four F-actin subunits, the "target zone", situated exactly midway between successive troponin complexes. They show an axial lever arm range of 77°/12.9 nm. The lever arm azimuthal range of strong binding attachments has a highly skewed, 127° range compared with X-ray crystallographic structures. Two types of weak actin attachments are described. One type, found exclusively in the target zone, appears to represent pre-working-stroke intermediates. The other, which contacts tropomyosin rather than actin, is positioned M-ward of the target zone, i.e. the position toward which thin filaments slide during shortening. CONCLUSION: We present a model for the weak to strong transition in the myosin ATPase cycle that incorporates azimuthal movements of the motor domain on actin. Stress/strain in the S2 domain may ...CONCLUSION: We present a model for the weak to strong transition in the myosin ATPase cycle that incorporates azimuthal movements of the motor domain on actin. Stress/strain in the S2 domain may explain azimuthal lever arm changes in the strong binding attachments. The results support previous conclusions that the weak attachments preceding force generation are very different from strong binding attachments. #1: Journal: J Struct Biol / Year: 2009 Title: Methods for identifying and averaging variable molecular conformations in tomograms of actively contracting insect flight muscle. Authors: Shenping Wu / Jun Liu / Mary C Reedy / Hanspeter Winkler / Michael K Reedy / Kenneth A Taylor /  Abstract: During active muscle contraction, tension is generated through many simultaneous, independent interactions between the molecular motor myosin and the actin filaments. The ensemble of myosin motors ...During active muscle contraction, tension is generated through many simultaneous, independent interactions between the molecular motor myosin and the actin filaments. The ensemble of myosin motors displays heterogeneous conformations reflecting different mechanochemical steps of the ATPase pathway. We used electron tomography of actively contracting insect flight muscle fast-frozen, freeze substituted, Araldite embedded, thin-sectioned and stained, to obtain 3D snapshots of the multiplicity of actin-attached myosin structures. We describe procedures for alignment of the repeating lattice of sub-volumes (38.7 nm cross-bridge repeats bounded by troponin) and multivariate data analysis to identify self-similar repeats for computing class averages. Improvements in alignment and classification of repeat sub-volumes reveals (for the first time in active muscle images) the helix of actin subunits in the thin filament and the troponin density with sufficient clarity that a quasiatomic model of the thin filament can be built into the class averages independent of the myosin cross-bridges. We show how quasiatomic model building can identify both strong and weak myosin attachments to actin. We evaluate the accuracy of image classification to enumerate the different types of actin-myosin attachments. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  2w49.cif.gz 2w49.cif.gz | 1.6 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb2w49.ent.gz pdb2w49.ent.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  2w49.json.gz 2w49.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/w4/2w49 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/w4/2w49 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/w4/2w49 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/w4/2w49 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  1561MPC  2w4aC  2w4gC  2w4tC 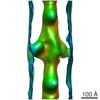 1584F M: map data used to model this data P: unfit; worng pairing?*YM C: citing same article ( F: fitted*YM |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 5 types, 36 molecules 0369147Y258ZABCTUVWXDEFGHIJKLM...
| #1: Protein | Mass: 17971.836 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Fragment: RESIDUES 5-163 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #2: Protein | Mass: 10976.568 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Fragment: RESIDUES 148-237 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #3: Protein | Mass: 16304.978 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Fragment: RESIDUES 4-144 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #4: Protein | Mass: 31917.555 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 / Fragment: RESIDUES 8-284 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #5: Protein | Mass: 41483.117 Da / Num. of mol.: 16 / Fragment: RESIDUES 3-374 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 1 types, 16 molecules 
| #6: Chemical | ChemComp-CA / |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: INSECT FIBRILLAR FLIGHT MUSCLE / Type: COMPLEX Details: THIS SPECIMEN IS OBTAINED FROM A QUICK FROZEN, ISOMETRICALLY CONTRACTING ASYNCHRONOUS INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE THAT HAS BEEN FREEZE SUBSTITUTED, PLASTIC EMBEDDED, AND THIN SECTIONED. THE FIBERS ...Details: THIS SPECIMEN IS OBTAINED FROM A QUICK FROZEN, ISOMETRICALLY CONTRACTING ASYNCHRONOUS INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE THAT HAS BEEN FREEZE SUBSTITUTED, PLASTIC EMBEDDED, AND THIN SECTIONED. THE FIBERS FOR THIS STUDY WERE SUBJECTED TO MECHANICAL TRANSIENTS. FOR THE QUICK STRETCH, THE FIBER WAS STRETCHED 6 NM PER HALF-SARCOMERE IN 2 MS AND LENGTH WAS HELD CONSTANT AFTER THE LENGTH STEP. THE FREEZING IMPACT OCCURRED 6-7 MS LATER. |
|---|---|
| Buffer solution | Name: 20 MM MOPS BUFFER, 5 MM NAN3, AND MGCL2, ATP, CACL2, AND EGTA IN VARYING MILLIMOLAR CONCENTRATIONS Details: 20 MM MOPS BUFFER, 5 MM NAN3, AND MGCL2, ATP, CACL2, AND EGTA IN VARYING MILLIMOLAR CONCENTRATIONS |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: YES / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: NO |
| Specimen support | Details: CARBON |
| Vitrification | Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER / Cryogen name: HELIUM Details: SMASH AGAINST A LIQUID HELIUM COOLED GOLD COATED COPPER MIRROR |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: FEI/PHILIPS CM300FEG/T / Details: NONE |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2 mm |
| Specimen holder | Tilt angle max: 72 ° / Tilt angle min: -72 ° |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: TVIPS TEMCAM-F224 (2k x 2k) |
| Radiation wavelength | Relative weight: 1 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Method: MARKER FREE ALIGNMENT / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF Details: NOTE THAT OUR LOWEST RESOLUTION DATA IS AT INVERSE 1 MICRON. NUMBER OF FOURIER COEFFICIENTS IS ALMOST A HALF MILLION. THESE COORDINATES WERE FIT TO AVERAGED SUBVOLUMES OBTAINED FROM A DUAL ...Details: NOTE THAT OUR LOWEST RESOLUTION DATA IS AT INVERSE 1 MICRON. NUMBER OF FOURIER COEFFICIENTS IS ALMOST A HALF MILLION. THESE COORDINATES WERE FIT TO AVERAGED SUBVOLUMES OBTAINED FROM A DUAL AXIS TOMOGRAM. THE ACTIN FILAMENT WAS GENERATED TO HAVE THE HELICAL SYMMETRY OF 28 SUBUNITS IN 13 TURNS OF THE 5.9 NM HELIX. THE FITTING WAS DONE MANUALLY USING THE CRYSTALLOGRAPHIC MODEL FITTING PROGRAM O. Symmetry type: HELICAL | ||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 35 Å | ||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Highest resolution: 35 Å
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



























































 PDBj
PDBj




