[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
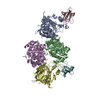
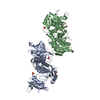
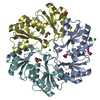
Yorodumi- PDB-7te6: Crystal structure of GluN1b-2B ATD complexed to Fab5 anti-GluN2B ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7te6 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Crystal structure of GluN1b-2B ATD complexed to Fab5 anti-GluN2B antibody | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN/IMMUNE SYSTEM / Fab fragment complexed to the receptor / SIGNALING PROTEIN-IMMUNE SYSTEM complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcellular response to curcumin / cellular response to corticosterone stimulus / cellular response to magnesium starvation / sensory organ development / regulation of cAMP/PKA signal transduction / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / Assembly and cell surface presentation of NMDA receptors / response to hydrogen sulfide / auditory behavior / sensitization ...cellular response to curcumin / cellular response to corticosterone stimulus / cellular response to magnesium starvation / sensory organ development / regulation of cAMP/PKA signal transduction / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / Assembly and cell surface presentation of NMDA receptors / response to hydrogen sulfide / auditory behavior / sensitization / response to other organism / dendritic branch / fear response / response to methylmercury / apical dendrite / regulation of ARF protein signal transduction / response to manganese ion / suckling behavior / positive regulation of inhibitory postsynaptic potential / response to carbohydrate / interleukin-1 receptor binding / cellular response to dsRNA / cellular response to lipid / response to growth hormone / negative regulation of dendritic spine maintenance / RAF/MAP kinase cascade / response to amine / heterocyclic compound binding / positive regulation of glutamate secretion / Synaptic adhesion-like molecules / regulation of monoatomic cation transmembrane transport / NMDA glutamate receptor activity / response to glycoside / NMDA selective glutamate receptor complex / glutamate binding / ligand-gated sodium channel activity / response to zinc ion / calcium ion transmembrane import into cytosol / protein heterotetramerization / small molecule binding / glycine binding / receptor clustering / startle response / parallel fiber to Purkinje cell synapse / behavioral response to pain / monoatomic cation transmembrane transport / regulation of MAPK cascade / regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / response to magnesium ion / response to electrical stimulus / action potential / extracellularly glutamate-gated ion channel activity / associative learning / regulation of neuronal synaptic plasticity / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / monoatomic cation transport / glutamate receptor binding / detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain / response to mechanical stimulus / long-term memory / neuron development / multicellular organismal response to stress / positive regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / postsynaptic density, intracellular component / monoatomic cation channel activity / behavioral fear response / response to fungicide / synaptic cleft / glutamate-gated receptor activity / cellular response to manganese ion / regulation of long-term synaptic depression / D2 dopamine receptor binding / glutamate-gated calcium ion channel activity / response to cytokine / presynaptic active zone membrane / ionotropic glutamate receptor binding / cell adhesion molecule binding / ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway / ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / cellular response to forskolin / protein tyrosine kinase binding / synaptic membrane / positive regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential / sodium ion transmembrane transport / hippocampal mossy fiber to CA3 synapse / response to amphetamine / learning / response to nicotine / response to cocaine / hippocampus development / synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / excitatory postsynaptic potential / cellular response to amino acid stimulus / regulation of membrane potential / transmitter-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / response to calcium ion / cerebral cortex development / regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / regulation of synaptic plasticity / beta-catenin binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 4.55 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 4.55 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Regan, M. / Tajima, N. / Furukawa, H. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Development and characterization of functional antibodies targeting NMDA receptors. Authors: Nami Tajima / Noriko Simorowski / Remy A Yovanno / Michael C Regan / Kevin Michalski / Ricardo Gómez / Albert Y Lau / Hiro Furukawa /  Abstract: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) are critically involved in basic brain functions and neurodegeneration as well as tumor invasiveness. Targeting specific subtypes of NMDARs with distinct ...N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) are critically involved in basic brain functions and neurodegeneration as well as tumor invasiveness. Targeting specific subtypes of NMDARs with distinct activities has been considered an effective therapeutic strategy for neurological disorders and diseases. However, complete elimination of off-target effects of small chemical compounds has been challenging and thus, there is a need to explore alternative strategies for targeting NMDAR subtypes. Here we report identification of a functional antibody that specifically targets the GluN1-GluN2B NMDAR subtype and allosterically down-regulates ion channel activity as assessed by electrophysiology. Through biochemical analysis, x-ray crystallography, single-particle electron cryomicroscopy, and molecular dynamics simulations, we show that this inhibitory antibody recognizes the amino terminal domain of the GluN2B subunit and increases the population of the non-active conformational state. The current study demonstrates that antibodies may serve as specific reagents to regulate NMDAR functions for basic research and therapeutic objectives. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7te6.cif.gz 7te6.cif.gz | 405.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7te6.ent.gz pdb7te6.ent.gz | 327.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7te6.json.gz 7te6.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/te/7te6 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/te/7te6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/te/7te6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/te/7te6 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7te4C  7te9C  7tebC  7teeC  7teqC  7terC  7tesC  7tetC  3qelS  5b3jS S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 
| ||||||||
| 2 | 
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 42932.055 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  #2: Protein | Mass: 41367.902 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #3: Antibody | Mass: 23844.684 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #4: Antibody | Mass: 23855.256 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 3.01 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 59.11 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 290 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop Details: 2.1 M sodium/potassium phosphate, 100 mM lithium sulfate, 100 mM CAPS, pH 10.5, 4% formamide |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  APS APS  / Beamline: 23-ID-B / Wavelength: 1.1 Å / Beamline: 23-ID-B / Wavelength: 1.1 Å |
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS PILATUS3 6M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Oct 10, 2018 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1.1 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 4.54→30 Å / Num. obs: 17965 / % possible obs: 97.5 % / Redundancy: 7.7 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.156 / Net I/σ(I): 6.2 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 4.54→4.66 Å / Num. unique obs: 1644 / CC1/2: 0.534 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: PDB entries 5B3J & 3QEL Resolution: 4.55→24.984 Å / SU ML: 0.77 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 1.36 / Phase error: 33.7 / Stereochemistry target values: ML
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 222.11 Å2 / Biso mean: 83.7583 Å2 / Biso min: 38.55 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: final / Resolution: 4.55→24.984 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Rfactor Rfree error: 0
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 PDBj
PDBj





