[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-4170: C terminal region of the dynein heavy chains in the dynein tail/d... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-4170 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
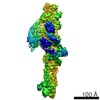
| Title | C terminal region of the dynein heavy chains in the dynein tail/dynactin/BICDR1 complex | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Map of C terminal of dynein tail domains, bound to BICDR and dynactin | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Cryo-EM / Complex / MOTOR PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of intracellular transport / regulation of metaphase plate congression / positive regulation of spindle assembly / establishment of spindle localization / dynein complex / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / retrograde axonal transport / P-body assembly / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / dynein light intermediate chain binding ...positive regulation of intracellular transport / regulation of metaphase plate congression / positive regulation of spindle assembly / establishment of spindle localization / dynein complex / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / retrograde axonal transport / P-body assembly / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / dynein light intermediate chain binding / cytoplasmic dynein complex / nuclear migration / dynein intermediate chain binding / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / cytoplasmic microtubule / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / axon cytoplasm / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / MHC class II antigen presentation / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / Mitotic Prometaphase / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / stress granule assembly / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / regulation of mitotic spindle organization / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / mitotic spindle organization / filopodium / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / HCMV Early Events / Aggrephagy / azurophil granule lumen / Separation of Sister Chromatids / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis / cell cortex / microtubule / cell division / Neutrophil degranulation / centrosome / ATP hydrolysis activity / RNA binding / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / ATP binding / identical protein binding / membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Urnavicius L / Lau CK | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 2 items United Kingdom, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2018 Journal: Nature / Year: 2018Title: Cryo-EM shows how dynactin recruits two dyneins for faster movement. Authors: Linas Urnavicius / Clinton K Lau / Mohamed M Elshenawy / Edgar Morales-Rios / Carina Motz / Ahmet Yildiz / Andrew P Carter /    Abstract: Dynein and its cofactor dynactin form a highly processive microtubule motor in the presence of an activating adaptor, such as BICD2. Different adaptors link dynein and dynactin to distinct cargoes. ...Dynein and its cofactor dynactin form a highly processive microtubule motor in the presence of an activating adaptor, such as BICD2. Different adaptors link dynein and dynactin to distinct cargoes. Here we use electron microscopy and single-molecule studies to show that adaptors can recruit a second dynein to dynactin. Whereas BICD2 is biased towards recruiting a single dynein, the adaptors BICDR1 and HOOK3 predominantly recruit two dyneins. We find that the shift towards a double dynein complex increases both the force and speed of the microtubule motor. Our 3.5 Å resolution cryo-electron microscopy reconstruction of a dynein tail-dynactin-BICDR1 complex reveals how dynactin can act as a scaffold to coordinate two dyneins side-by-side. Our work provides a structural basis for understanding how diverse adaptors recruit different numbers of dyneins and regulate the motile properties of the dynein-dynactin transport machine. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_4170.map.gz emd_4170.map.gz | 287.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-4170-v30.xml emd-4170-v30.xml emd-4170.xml emd-4170.xml | 12.3 KB 12.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_4170.png emd_4170.png | 135.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-4170.cif.gz emd-4170.cif.gz | 6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4170 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4170 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4170 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4170 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6f1vMC  4168C  4169C  4171C  4172C  4177C  5owoC  6f1tC  6f1uC  6f1yC  6f1zC  6f38C  6f3aC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_4170.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 824 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_4170.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 824 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Map of C terminal of dynein tail domains, bound to BICDR and dynactin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.34 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Two dynein tail domains bound to dynactin and BICDR1
| Entire | Name: Two dynein tail domains bound to dynactin and BICDR1 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Two dynein tail domains bound to dynactin and BICDR1
| Supramolecule | Name: Two dynein tail domains bound to dynactin and BICDR1 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 136.786094 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSEPGGGGGE DGSAGLEVSA VQNVADVSVL QKHLRKLVPL LLEDGGEAPA ALEAALEEKS ALEQMRKFLS DPQVHTVLVE RSTLKEDVG DEGEEEKEFI SYNINIDIHY GVKSNSLAFI KRTPVIDADK PVSSQLRVLT LSEDSPYETL HSFISNAVAP F FKSYIRES ...String: MSEPGGGGGE DGSAGLEVSA VQNVADVSVL QKHLRKLVPL LLEDGGEAPA ALEAALEEKS ALEQMRKFLS DPQVHTVLVE RSTLKEDVG DEGEEEKEFI SYNINIDIHY GVKSNSLAFI KRTPVIDADK PVSSQLRVLT LSEDSPYETL HSFISNAVAP F FKSYIRES GKADRDGDKM APSVEKKIAE LEMGLLHLQQ NIEIPEISLP IHPMITNVAK QCYERGEKPK VTDFGDKVED PT FLNQLQS GVNRWIREIQ KVTKLDRDPA SGTALQEISF WLNLERALYR IQEKRESPEV LLTLDILKHG KRFHATVSFD TDT GLKQAL ETVNDYNPLM KDFPLNDLLS ATELDKIRQA LVAIFTHLRK IRNTKYPIQR ALRLVEAISR DLSSQLLKVL GTRK LMHVA YEEFEKVMVA CFEVFQTWDD EYEKLQVLLR DIVKRKREEN LKMVWRINPA HRKLQARLDQ MRKFRRQHEQ LRAVI VRVL RPQVTAVAQQ NQGEVPEPQD MKVAEVLFDA ADANAIEEVN LAYENVKEVD GLDVSKEGTE AWEAAMKRYD ERIDRV ETR ITARLRDQLG TAKNANEMFR IFSRFNALFV RPHIRGAIRE YQTQLIQRVK DDIESLHDKF KVQYPQSQAC KMSHVRD LP PVSGSIIWAK QIDRQLTAYM KRVEDVLGKG WENHVEGQKL KQDGDSFRMK LNTQEIFDDW ARKVQQRNLG VSGRIFTI E STRVRGRTGN VLKLKVNFLP EIITLSKEVR NLKWLGFRVP LAIVNKAHQA NQLYPFAISL IESVRTYERT CEKVEERNT ISLLVAGLKK EVQALIAEGI ALVWESYKLD PYVQRLAETV FNFQEKVDDL LIIEEKIDLE VRSLETCMYD HKTFSEILNR VQKAVDDLN LHSYSNLPIW VNKLDMEIER ILGVRLQAGL RAWTQVLLGQ AEDKAEVDMD TDAPQVSHKP GGEPKIKNVV H ELRITNQV IYLNPPIEEC RYKLYQEMFA WKMVVLSLPR IQSQRYQVGV HYELTEEEKF YRNALTRMPD GPVALEESYS AV MGIVSEV EQYVKVWLQY QCLWDMQAEN IYNRLGEDLN KWQALLVQIR KARGTFDNAE TKKEFGPVVI DYGKVQSKVN LKY DSWHKE VLSKFGQMLG SNMTEFHSQI SKSRQELEQH SVDTASTSDA VTFITYVQSL KRKIKQFEKQ UniProtKB: Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 52.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: EMDB MAP EMDB ID: Details: Initial model low pass filtered to 50 A |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: RELION / Number images used: 86030 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING / Software - Name: RELION |
| Final angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING / Software - Name: RELION Details: Particle signal subtraction used to remove regions outside of the C terminus of the dynein tails before final 3D classification and refinement |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Target criteria: Cross-correlation coefficient |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-6f1v: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller
























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)