[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-4169: N terminal region of dynein tail domains in complex with dynactin... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-4169 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
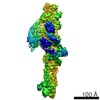
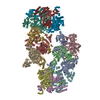
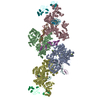
| Title | N terminal region of dynein tail domains in complex with dynactin filament and BICDR-1 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Map of the N-terminal half of two dynein tail domains bound to dynactin and BICDR1. This map was generated after particle signal subtraction from the overall map (separate deposition) | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Cryo-EM / Complex / MOTOR PROTEIN / Cargo adaptor | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationGolgi to secretory granule transport / : / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / RHOF GTPase cycle / dynactin complex / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / AURKA Activation by TPX2 ...Golgi to secretory granule transport / : / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / RHOF GTPase cycle / dynactin complex / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / transport along microtubule / F-actin capping protein complex / WASH complex / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / dynein light chain binding / dynein heavy chain binding / positive regulation of intracellular transport / regulation of metaphase plate congression / positive regulation of spindle assembly / barbed-end actin filament capping / establishment of spindle localization / regulation of cell morphogenesis / dynein complex / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / retrograde axonal transport / P-body assembly / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / MHC class II antigen presentation / microtubule motor activity / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / dynein light intermediate chain binding / cytoplasmic dynein complex / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / microtubule-based movement / nuclear migration / cortical cytoskeleton / dynein intermediate chain binding / dynactin binding / microtubule-based process / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / cytoplasmic microtubule / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / axon cytoplasm / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / cytoskeleton organization / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / MHC class II antigen presentation / Mitotic Prometaphase / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / stress granule assembly / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / regulation of mitotic spindle organization / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / sarcomere / mitotic spindle organization / filopodium / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / small GTPase binding / neuron projection development / HCMV Early Events / Aggrephagy / azurophil granule lumen / actin filament binding / Separation of Sister Chromatids / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis / actin binding / actin cytoskeleton organization / cell cortex / vesicle / microtubule / cell division / Neutrophil degranulation / centrosome / ATP hydrolysis activity / RNA binding / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / ATP binding / identical protein binding / membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Urnavicius L / Lau CK | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 2 items United Kingdom, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2018 Journal: Nature / Year: 2018Title: Cryo-EM shows how dynactin recruits two dyneins for faster movement. Authors: Linas Urnavicius / Clinton K Lau / Mohamed M Elshenawy / Edgar Morales-Rios / Carina Motz / Ahmet Yildiz / Andrew P Carter /    Abstract: Dynein and its cofactor dynactin form a highly processive microtubule motor in the presence of an activating adaptor, such as BICD2. Different adaptors link dynein and dynactin to distinct cargoes. ...Dynein and its cofactor dynactin form a highly processive microtubule motor in the presence of an activating adaptor, such as BICD2. Different adaptors link dynein and dynactin to distinct cargoes. Here we use electron microscopy and single-molecule studies to show that adaptors can recruit a second dynein to dynactin. Whereas BICD2 is biased towards recruiting a single dynein, the adaptors BICDR1 and HOOK3 predominantly recruit two dyneins. We find that the shift towards a double dynein complex increases both the force and speed of the microtubule motor. Our 3.5 Å resolution cryo-electron microscopy reconstruction of a dynein tail-dynactin-BICDR1 complex reveals how dynactin can act as a scaffold to coordinate two dyneins side-by-side. Our work provides a structural basis for understanding how diverse adaptors recruit different numbers of dyneins and regulate the motile properties of the dynein-dynactin transport machine. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_4169.map.gz emd_4169.map.gz | 288.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-4169-v30.xml emd-4169-v30.xml emd-4169.xml emd-4169.xml | 32.9 KB 32.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_4169.png emd_4169.png | 139 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-4169.cif.gz emd-4169.cif.gz | 9.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_4169_additional_1.map.gz emd_4169_additional_1.map.gz emd_4169_additional_2.map.gz emd_4169_additional_2.map.gz | 1 MB 1.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4169 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4169 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4169 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4169 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6f1uMC  4168C  4170C  4171C  4172C  4177C  5owoC  6f1tC  6f1vC  6f1yC  6f1zC 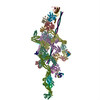 6f38C  6f3aC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_4169.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 824 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_4169.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 824 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Map of the N-terminal half of two dynein tail domains bound to dynactin and BICDR1. This map was generated after particle signal subtraction from the overall map (separate deposition) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.34 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Map of summed signal of dynein heavy chains present in main map
| File | emd_4169_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Map of summed signal of dynein heavy chains present in main map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: Map of summed signal of dynein intermediate chains...
| File | emd_4169_additional_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Map of summed signal of dynein intermediate chains present in main map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Two dynein tail domains bound to dynactin and BICDR1.
+Supramolecule #1: Two dynein tail domains bound to dynactin and BICDR1.
+Supramolecule #2: dynactin filament
+Supramolecule #3: Cytoplasmic dynein
+Supramolecule #4: BICDR1
+Macromolecule #1: ARP1 actin related protein 1 homolog A
+Macromolecule #2: Capping protein (Actin filament) muscle Z-line, alpha 1
+Macromolecule #3: F-actin capping protein beta subunit
+Macromolecule #4: Dynactin subunit 2
+Macromolecule #5: Dynactin subunit 2
+Macromolecule #6: Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1
+Macromolecule #7: Cytoplasmic dynein 1 intermediate chain 2
+Macromolecule #8: BICD family-like cargo adapter 1
+Macromolecule #9: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 52.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Target criteria: Cross-correlation coefficient |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-6f1u: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)