+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-11320 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
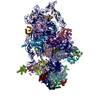
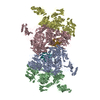
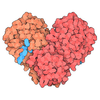
| Title | SARS-CoV-2-Nsp1-40S complex, composite map | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | inhibitor / mRNA channel / 40S ribosomal subunit / TRANSLATION | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response / oxidized pyrimidine DNA binding / response to TNF agonist / positive regulation of base-excision repair / positive regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response / positive regulation of gastrulation / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage / protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor activity / positive regulation of endodeoxyribonuclease activity / nucleolus organization ...negative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response / oxidized pyrimidine DNA binding / response to TNF agonist / positive regulation of base-excision repair / positive regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response / positive regulation of gastrulation / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage / protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor activity / positive regulation of endodeoxyribonuclease activity / nucleolus organization / IRE1-RACK1-PP2A complex / positive regulation of Golgi to plasma membrane protein transport / TNFR1-mediated ceramide production / negative regulation of RNA splicing / negative regulation of DNA repair / supercoiled DNA binding / NF-kappaB complex / cysteine-type endopeptidase activator activity involved in apoptotic process / neural crest cell differentiation / oxidized purine DNA binding / positive regulation of ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to hydrogen peroxide / negative regulation of bicellular tight junction assembly / regulation of establishment of cell polarity / ubiquitin-like protein conjugating enzyme binding / rRNA modification in the nucleus and cytosol / erythrocyte homeostasis / negative regulation of phagocytosis / Formation of the ternary complex, and subsequently, the 43S complex / cytoplasmic side of rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane / negative regulation of ubiquitin protein ligase activity / protein kinase A binding / ion channel inhibitor activity / laminin receptor activity / Ribosomal scanning and start codon recognition / pigmentation / Translation initiation complex formation / positive regulation of mitochondrial depolarization / fibroblast growth factor binding / positive regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / monocyte chemotaxis / negative regulation of translational frameshifting / TOR signaling / BH3 domain binding / Protein hydroxylation / positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation / SARS-CoV-1 modulates host translation machinery / regulation of adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / iron-sulfur cluster binding / mTORC1-mediated signalling / regulation of cell division / Peptide chain elongation / cellular response to ethanol / positive regulation of GTPase activity / Selenocysteine synthesis / Formation of a pool of free 40S subunits / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator / endonucleolytic cleavage to generate mature 3'-end of SSU-rRNA from (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / Eukaryotic Translation Termination / protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / Response of EIF2AK4 (GCN2) to amino acid deficiency / negative regulation of ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / Viral mRNA Translation / negative regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response / ubiquitin ligase inhibitor activity / negative regulation of protein binding / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / positive regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator / GTP hydrolysis and joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit / L13a-mediated translational silencing of Ceruloplasmin expression / Major pathway of rRNA processing in the nucleolus and cytosol / regulation of translational fidelity / phagocytic cup / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / Protein methylation / spindle assembly / positive regulation of microtubule polymerization / Nuclear events stimulated by ALK signaling in cancer / endonucleolytic cleavage in ITS1 to separate SSU-rRNA from 5.8S rRNA and LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / positive regulation of cell cycle / rough endoplasmic reticulum / laminin binding / ribosomal small subunit export from nucleus / translation regulator activity / translation initiation factor binding / Maturation of protein E / gastrulation / Maturation of protein E / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) endonuclease activity / ER Quality Control Compartment (ERQC) / Myoclonic epilepsy of Lafora / MDM2/MDM4 family protein binding / FLT3 signaling by CBL mutants / signaling adaptor activity / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD Domain Mutants / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.8 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Schubert K / Karousis ED | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Switzerland, 3 items Switzerland, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2020Title: SARS-CoV-2 Nsp1 binds the ribosomal mRNA channel to inhibit translation. Authors: Katharina Schubert / Evangelos D Karousis / Ahmad Jomaa / Alain Scaiola / Blanca Echeverria / Lukas-Adrian Gurzeler / Marc Leibundgut / Volker Thiel / Oliver Mühlemann / Nenad Ban /  Abstract: The SARS-CoV-2 non-structural protein 1 (Nsp1), also referred to as the host shutoff factor, suppresses host innate immune functions. By combining cryo-electron microscopy and biochemistry, we show ...The SARS-CoV-2 non-structural protein 1 (Nsp1), also referred to as the host shutoff factor, suppresses host innate immune functions. By combining cryo-electron microscopy and biochemistry, we show that SARS-CoV-2 Nsp1 binds to the human 40S subunit in ribosomal complexes, including the 43S pre-initiation complex and the non-translating 80S ribosome. The protein inserts its C-terminal domain into the mRNA channel, where it interferes with mRNA binding. We observe translation inhibition in the presence of Nsp1 in an in vitro translation system and in human cells. Based on the high-resolution structure of the 40S-Nsp1 complex, we identify residues of Nsp1 crucial for mediating translation inhibition. We further show that the full-length 5' untranslated region of the genomic viral mRNA stimulates translation in vitro, suggesting that SARS-CoV-2 combines global inhibition of translation by Nsp1 with efficient translation of the viral mRNA to allow expression of viral genes. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_11320.map.gz emd_11320.map.gz | 633.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-11320-v30.xml emd-11320-v30.xml emd-11320.xml emd-11320.xml | 56.8 KB 56.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_11320.png emd_11320.png | 100.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-11320.cif.gz emd-11320.cif.gz | 12.4 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11320 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11320 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11320 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11320 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6zojMC  6zokC  6zolC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_11320.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 669.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_11320.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 669.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
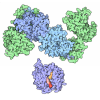
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.08 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
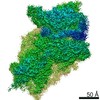
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : SARS-CoV-2-Nsp1-40S complex, composite map
+Supramolecule #1: SARS-CoV-2-Nsp1-40S complex, composite map
+Supramolecule #2: Ribosomal proteins
+Supramolecule #3: SARS-CoV-2-Nsp1
+Macromolecule #1: 18S ribosomal RNA
+Macromolecule #2: 40S ribosomal protein SA
+Macromolecule #3: 40S ribosomal protein S3a
+Macromolecule #4: 40S ribosomal protein S2
+Macromolecule #5: 40S ribosomal protein S3
+Macromolecule #6: 40S ribosomal protein S4, X isoform
+Macromolecule #7: 40S ribosomal protein S5
+Macromolecule #8: 40S ribosomal protein S6
+Macromolecule #9: 40S ribosomal protein S7
+Macromolecule #10: 40S ribosomal protein S8
+Macromolecule #11: 40S ribosomal protein S9
+Macromolecule #12: 40S ribosomal protein S10
+Macromolecule #13: 40S ribosomal protein S11
+Macromolecule #14: 40S ribosomal protein S12
+Macromolecule #15: 40S ribosomal protein S13
+Macromolecule #16: 40S ribosomal protein S14
+Macromolecule #17: 40S ribosomal protein S15
+Macromolecule #18: 40S ribosomal protein S16
+Macromolecule #19: 40S ribosomal protein S17
+Macromolecule #20: 40S ribosomal protein S18
+Macromolecule #21: 40S ribosomal protein S19
+Macromolecule #22: 40S ribosomal protein S20
+Macromolecule #23: 40S ribosomal protein S21
+Macromolecule #24: 40S ribosomal protein S15a
+Macromolecule #25: 40S ribosomal protein S23
+Macromolecule #26: 40S ribosomal protein S24
+Macromolecule #27: 40S ribosomal protein S25
+Macromolecule #28: 40S ribosomal protein S26
+Macromolecule #29: 40S ribosomal protein S27
+Macromolecule #30: 40S ribosomal protein S28
+Macromolecule #31: 40S ribosomal protein S29
+Macromolecule #32: 40S ribosomal protein S30
+Macromolecule #33: Ribosomal protein S27a
+Macromolecule #34: Receptor of activated protein C kinase 1
+Macromolecule #35: Non-structural protein 1
+Macromolecule #36: 60S ribosomal protein L41
+Macromolecule #37: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #38: ZINC ION
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.6 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








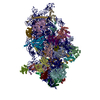




































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)