+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-11902 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Staphylococcus aureus 70S after 30 minutes incubation at 37C | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Ribosome / H68 / translation / protein synthesis | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationribosome biogenesis / ribosomal small subunit assembly / ribosomal small subunit biogenesis / ribosomal large subunit assembly / small ribosomal subunit / small ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic small ribosomal subunit / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation ...ribosome biogenesis / ribosomal small subunit assembly / ribosomal small subunit biogenesis / ribosomal large subunit assembly / small ribosomal subunit / small ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic small ribosomal subunit / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / tRNA binding / negative regulation of translation / rRNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / translation / ribonucleoprotein complex / mRNA binding / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.11 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Cimicata G / Bashan A / Yonath A | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: mBio / Year: 2022 Journal: mBio / Year: 2022Title: Structural Studies Reveal the Role of Helix 68 in the Elongation Step of Protein Biosynthesis. Authors: Giuseppe Cimicata / Gil Fridkin / Tanaya Bose / Zohar Eyal / Yehuda Halfon / Elinor Breiner-Goldstein / Tara Fox / Ella Zimmerman / Anat Bashan / Natalia de Val / Alexander Wlodawer / Ada Yonath /   Abstract: The ribosome, a multicomponent assembly consisting of RNA and proteins, is a pivotal macromolecular machine that translates the genetic code into proteins. The large ribosomal subunit rRNA helix 68 ...The ribosome, a multicomponent assembly consisting of RNA and proteins, is a pivotal macromolecular machine that translates the genetic code into proteins. The large ribosomal subunit rRNA helix 68 (H68) is a key element in the protein synthesis process, as it coordinates the coupled movements of the actors involved in translocation, including the tRNAs and L1 stalk. Examination of cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of ribosomes incubated for various time durations at physiological temperatures led to the identification of functionally relevant H68 movements. These movements assist the transition of the L1 stalk between its open and closed states. H68 spatial flexibility and its significance to the protein synthesis process were confirmed through its effective targeting with antisense PNA oligomers. Our results suggest that H68 is actively involved in ribosome movements that are central to the elongation process. The mechanism that regulates the translocation step in ribosomes during protein synthesis is not fully understood. In this work, cryo-EM techniques used to image ribosomes from Staphylococcus aureus after incubation at physiological temperature allowed the identification of a conformation of the helix 68 that has never been observed so far. We then propose a mechanism in which such helix, switching between two different conformations, actively coordinates the translocation step, shedding light on the dynamics of ribosomal components. In addition, the relevance of helix 68 to ribosome function and its potential as an antibiotic target was proved by inhibiting Staphylococcus aureus ribosomes activity using oligomers with sequence complementarity. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_11902.map.gz emd_11902.map.gz | 224.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-11902-v30.xml emd-11902-v30.xml emd-11902.xml emd-11902.xml | 75.2 KB 75.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_11902.png emd_11902.png | 51 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-11902.cif.gz emd-11902.cif.gz | 28.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_11902_additional_1.map.gz emd_11902_additional_1.map.gz | 264.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11902 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11902 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11902 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11902 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7asoMC  0243C  6hmaC  7asmC  7asnC  7aspC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_11902.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 282.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_11902.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 282.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.86 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
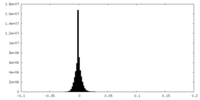
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: #1
| File | emd_11902_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
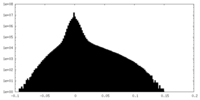
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : 70S
+Supramolecule #1: 70S
+Macromolecule #1: 5S
+Macromolecule #20: 16S
+Macromolecule #47: 23S
+Macromolecule #2: 30S ribosomal protein S3
+Macromolecule #3: 30S ribosomal protein S4
+Macromolecule #4: 30S ribosomal protein S5
+Macromolecule #5: 30S ribosomal protein S6
+Macromolecule #6: 30S ribosomal protein S7
+Macromolecule #7: 30S ribosomal protein S8
+Macromolecule #8: 30S ribosomal protein S9
+Macromolecule #9: 30S ribosomal protein S10
+Macromolecule #10: 30S ribosomal protein S11
+Macromolecule #11: 30S ribosomal protein S12
+Macromolecule #12: 30S ribosomal protein S13
+Macromolecule #13: 30S ribosomal protein S14 type Z
+Macromolecule #14: 30S ribosomal protein S15
+Macromolecule #15: 30S ribosomal protein S16
+Macromolecule #16: 30S ribosomal protein S17
+Macromolecule #17: 30S ribosomal protein S18
+Macromolecule #18: 30S ribosomal protein S19
+Macromolecule #19: 30S ribosomal protein S20
+Macromolecule #21: 50S ribosomal protein L3
+Macromolecule #22: 50S ribosomal protein L4
+Macromolecule #23: 50S ribosomal protein L5
+Macromolecule #24: 50S ribosomal protein L6
+Macromolecule #25: 50S ribosomal protein L13
+Macromolecule #26: 50S ribosomal protein L14
+Macromolecule #27: 50S ribosomal protein L15
+Macromolecule #28: 50S ribosomal protein L16
+Macromolecule #29: 50S ribosomal protein L17
+Macromolecule #30: 50S ribosomal protein L18
+Macromolecule #31: 50S ribosomal protein L20
+Macromolecule #32: 50S ribosomal protein L21
+Macromolecule #33: 50S ribosomal protein L22
+Macromolecule #34: 50S ribosomal protein L23
+Macromolecule #35: 50S ribosomal protein L24
+Macromolecule #36: 50S ribosomal protein L25
+Macromolecule #37: 50S ribosomal protein L27
+Macromolecule #38: 50S ribosomal protein L28
+Macromolecule #39: 50S ribosomal protein L29
+Macromolecule #40: 50S ribosomal protein L30
+Macromolecule #41: 50S ribosomalprotein L32p
+Macromolecule #42: 50S ribosomal protein L33
+Macromolecule #43: 50S ribosomal protein L34
+Macromolecule #44: 50S ribosomal protein L35
+Macromolecule #45: 50S ribosomal protein L36
+Macromolecule #46: 50S ribosomal protein L31 type B
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.6 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 200 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 47.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







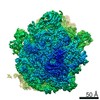
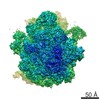
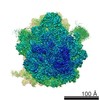







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)