[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
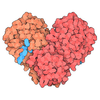
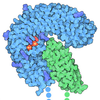
Yorodumi- PDB-9fmd: Integrative model of the human post-catalytic spliceosome (P-complex) -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9fmd | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Integrative model of the human post-catalytic spliceosome (P-complex) | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SPLICING / P-complex / spliceosome | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of homologous chromosome segregation / second spliceosomal transesterification activity / endoplasmic reticulum membrane organization / exon-exon junction subcomplex mago-y14 / negative regulation of selenocysteine incorporation / negative regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity / regulation of nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, nonsense-mediated decay / cellular response to selenite ion / post-spliceosomal complex / selenocysteine insertion sequence binding ...regulation of homologous chromosome segregation / second spliceosomal transesterification activity / endoplasmic reticulum membrane organization / exon-exon junction subcomplex mago-y14 / negative regulation of selenocysteine incorporation / negative regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity / regulation of nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, nonsense-mediated decay / cellular response to selenite ion / post-spliceosomal complex / selenocysteine insertion sequence binding / exon-exon junction complex / pre-mRNA 3'-splice site binding / protein exit from endoplasmic reticulum / negative regulation of catalytic activity / NOSIP mediated eNOS trafficking / regulation of translation at postsynapse, modulating synaptic transmission / regulation of retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway / granulocyte differentiation / post-mRNA release spliceosomal complex / renal system process / 3'-5' RNA helicase activity / U2 snRNP binding / U7 snRNA binding / histone pre-mRNA DCP binding / generation of catalytic spliceosome for first transesterification step / U7 snRNP / negative regulation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway / Z-decay: degradation of maternal mRNAs by zygotically expressed factors / cis assembly of pre-catalytic spliceosome / histone pre-mRNA 3'end processing complex / regulation of vitamin D receptor signaling pathway / endonucleolytic cleavage of tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / regulation of mRNA processing / negative regulation of lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway / SLBP independent Processing of Histone Pre-mRNAs / SLBP Dependent Processing of Replication-Dependent Histone Pre-mRNAs / spliceosome conformational change to release U4 (or U4atac) and U1 (or U11) / Deadenylation of mRNA / negative regulation of interleukin-8 production / negative regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential / nuclear retinoic acid receptor binding / embryonic cranial skeleton morphogenesis / oocyte development / embryonic brain development / alternative mRNA splicing, via spliceosome / U12-type spliceosomal complex / protein methylation / poly(A) binding / 7-methylguanosine cap hypermethylation / U1 snRNP binding / negative regulation of interferon-beta production / M-decay: degradation of maternal mRNAs by maternally stored factors / RNA splicing, via transesterification reactions / U2-type catalytic step 1 spliceosome / methylosome / pre-mRNA binding / C2H2 zinc finger domain binding / pICln-Sm protein complex / positive regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome / ATP-dependent activity, acting on RNA / snRNP binding / mRNA 3'-end processing / regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome / sno(s)RNA-containing ribonucleoprotein complex / small nuclear ribonucleoprotein complex / Notch binding / SMN-Sm protein complex / spliceosomal tri-snRNP complex / host-mediated activation of viral transcription / mRNA cis splicing, via spliceosome / U2-type precatalytic spliceosome / P granule / positive regulation of vitamin D receptor signaling pathway / commitment complex / telomerase holoenzyme complex / regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process / nuclear vitamin D receptor binding / U2-type prespliceosome assembly / U2-type spliceosomal complex / Regulation of gene expression in late stage (branching morphogenesis) pancreatic bud precursor cells / positive regulation of alpha-beta T cell differentiation / Transport of Mature mRNA derived from an Intron-Containing Transcript / telomerase RNA binding / RUNX3 regulates NOTCH signaling / U2-type catalytic step 2 spliceosome / NOTCH4 Intracellular Domain Regulates Transcription / U2 snRNP / U1 snRNP / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Termination / U4 snRNP / NOTCH3 Intracellular Domain Regulates Transcription / nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, nonsense-mediated decay / U2-type prespliceosome / negative regulation of type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway / positive regulation of neurogenesis / protein peptidyl-prolyl isomerization / K63-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / inner cell mass cell proliferation / ubiquitin-ubiquitin ligase activity / nuclear androgen receptor binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)  Human adenovirus 2 Human adenovirus 2 | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Rothe, P. / Plaschka, C. / Vorlaender, M.K. | |||||||||
| Funding support | European Union, 1items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: Mechanism for the initiation of spliceosome disassembly. Authors: Matthias K Vorländer / Patricia Rothe / Justus Kleifeld / Eric D Cormack / Lalitha Veleti / Daria Riabov-Bassat / Laura Fin / Alex W Phillips / Luisa Cochella / Clemens Plaschka /   Abstract: Precursor-mRNA (pre-mRNA) splicing requires the assembly, remodelling and disassembly of the multi-megadalton ribonucleoprotein complex called the spliceosome. Recent studies have shed light on ...Precursor-mRNA (pre-mRNA) splicing requires the assembly, remodelling and disassembly of the multi-megadalton ribonucleoprotein complex called the spliceosome. Recent studies have shed light on spliceosome assembly and remodelling for catalysis, but the mechanism of disassembly remains unclear. Here we report cryo-electron microscopy structures of nematode and human terminal intron lariat spliceosomes along with biochemical and genetic data. Our results uncover how four disassembly factors and the conserved RNA helicase DHX15 initiate spliceosome disassembly. The disassembly factors probe large inner and outer spliceosome surfaces to detect the release of ligated mRNA. Two of these factors, TFIP11 and C19L1, and three general spliceosome subunits, SYF1, SYF2 and SDE2, then dock and activate DHX15 on the catalytic U6 snRNA to initiate disassembly. U6 therefore controls both the start and end of pre-mRNA splicing. Taken together, our results explain the molecular basis of the initiation of canonical spliceosome disassembly and provide a framework to understand general spliceosomal RNA helicase control and the discard of aberrant spliceosomes. #1:  Journal: Science / Year: 2019 Journal: Science / Year: 2019Title: A human postcatalytic spliceosome structure reveals essential roles of metazoan factors for exon ligation. Authors: Sebastian M Fica / Chris Oubridge / Max E Wilkinson / Andrew J Newman / Kiyoshi Nagai /  Abstract: During exon ligation, the spliceosome recognizes the 3'-splice site (3'SS) of precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) through non-Watson-Crick pairing with the 5'SS and the branch adenosine, in a ...During exon ligation, the spliceosome recognizes the 3'-splice site (3'SS) of precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) through non-Watson-Crick pairing with the 5'SS and the branch adenosine, in a conformation stabilized by Prp18 and Prp8. Here we present the 3.3-angstrom cryo-electron microscopy structure of a human postcatalytic spliceosome just after exon ligation. The 3'SS docks at the active site through conserved RNA interactions in the absence of Prp18. Unexpectedly, the metazoan-specific FAM32A directly bridges the 5'-exon and intron 3'SS of pre-mRNA and promotes exon ligation, as shown by functional assays. CACTIN, SDE2, and NKAP-factors implicated in alternative splicing-further stabilize the catalytic conformation of the spliceosome during exon ligation. Together these four proteins act as exon ligation factors. Our study reveals how the human spliceosome has co-opted additional proteins to modulate a conserved RNA-based mechanism for 3'SS selection and to potentially fine-tune alternative splicing at the exon ligation stage. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9fmd.cif.gz 9fmd.cif.gz | 3.2 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9fmd.ent.gz pdb9fmd.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9fmd.json.gz 9fmd.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fm/9fmd https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fm/9fmd ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fm/9fmd ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fm/9fmd | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
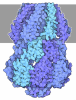
| Related structure data |  4525M  8ro0C 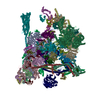 8ro1C  8ro2C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
+Protein , 24 types, 25 molecules 1325056789ACJLNNOPQRSRTVXZbiwz
+RNA chain , 5 types, 5 molecules 256EXIN
+Splicing factor ... , 3 types, 3 molecules 3Fx
+U5 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein ... , 2 types, 2 molecules BE
+Pre-mRNA-splicing factor ... , 7 types, 7 molecules DHIKMOU
+Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans ... , 2 types, 2 molecules Sy
+Pre-mRNA-processing factor ... , 2 types, 5 molecules Wqrst
+Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein ... , 6 types, 12 molecules ahcjdkelfmgn
+U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein ... , 2 types, 2 molecules op
+Non-polymers , 6 types, 16 molecules 









+Details
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 53 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 103860 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










































 PDBj
PDBj