+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9cq6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
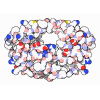
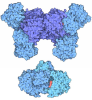
| Title | The ligation complex in the NHEJ pathway | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | LIGASE/TRANSFERASE/DNA / NHEJ / ligation / XLF / PAXX / DNA repair / Ligase IV / LIGASE-TRANSFERASE-DNA complex | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationFHA domain binding / positive regulation of chromosome organization / positive regulation of ligase activity / DNA ligase IV complex / DNA ligase activity / DN2 thymocyte differentiation / DNA ligase (ATP) / Ku70:Ku80 complex / T cell receptor V(D)J recombination / negative regulation of t-circle formation ...FHA domain binding / positive regulation of chromosome organization / positive regulation of ligase activity / DNA ligase IV complex / DNA ligase activity / DN2 thymocyte differentiation / DNA ligase (ATP) / Ku70:Ku80 complex / T cell receptor V(D)J recombination / negative regulation of t-circle formation / pro-B cell differentiation / DNA end binding / DNA ligase (ATP) activity / small-subunit processome assembly / positive regulation of lymphocyte differentiation / DNA-dependent protein kinase complex / DNA-dependent protein kinase-DNA ligase 4 complex / immunoglobulin V(D)J recombination / nonhomologous end joining complex / nucleotide-excision repair, DNA gap filling / single strand break repair / V(D)J recombination / regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation / cellular response to X-ray / isotype switching / double-strand break repair via classical nonhomologous end joining / protein localization to site of double-strand break / nuclear telomere cap complex / Cytosolic sensors of pathogen-associated DNA / IRF3-mediated induction of type I IFN / recombinational repair / positive regulation of neurogenesis / regulation of telomere maintenance / U3 snoRNA binding / DNA biosynthetic process / protein localization to chromosome, telomeric region / cellular response to lithium ion / cellular hyperosmotic salinity response / response to ionizing radiation / 2-LTR circle formation / hematopoietic stem cell proliferation / ligase activity / telomeric DNA binding / positive regulation of protein kinase activity / Lyases; Carbon-oxygen lyases; Other carbon-oxygen lyases / site of DNA damage / T cell differentiation / somatic stem cell population maintenance / 5'-deoxyribose-5-phosphate lyase activity / hematopoietic stem cell differentiation / response to X-ray / chromosome organization / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / telomere maintenance via telomerase / SUMOylation of DNA damage response and repair proteins / condensed chromosome / DNA polymerase binding / neurogenesis / activation of innate immune response / DNA helicase activity / telomere maintenance / B cell differentiation / cyclin binding / central nervous system development / stem cell proliferation / cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor / cellular response to ionizing radiation / response to gamma radiation / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / small-subunit processome / enzyme activator activity / protein-DNA complex / cellular response to gamma radiation / base-excision repair / double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / establishment of integrated proviral latency / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / fibrillar center / positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation / T cell differentiation in thymus / double-strand break repair / site of double-strand break / neuron apoptotic process / double-stranded DNA binding / scaffold protein binding / fibroblast proliferation / secretory granule lumen / DNA recombination / transcription regulator complex / ficolin-1-rich granule lumen / in utero embryonic development / molecular adaptor activity / negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process / damaged DNA binding / chromosome, telomeric region / cell population proliferation / transcription cis-regulatory region binding / ribonucleoprotein complex / innate immune response / cell division Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Li, J. / Liu, L. / Gellert, M. / Yang, W. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2025 Journal: Nature / Year: 2025Title: Dynamic assemblies and coordinated reactions of non-homologous end joining. Authors: Lan Liu / Jun Li / Metztli Cisneros-Aguirre / Arianna Merkell / Jeremy M Stark / Martin Gellert / Wei Yang /  Abstract: Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) is the main repair pathway of double-strand DNA breaks in higher eukaryotes. Here we report reconstitution of the final steps of NHEJ and structures of DNA ...Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) is the main repair pathway of double-strand DNA breaks in higher eukaryotes. Here we report reconstitution of the final steps of NHEJ and structures of DNA polymerase μ and ligase IV (LIG4) engaged in gap filling and end joining. These reactions take place in a flexible ω-shaped framework composed of XRCC4 and XLF. Two broken DNA ends, each encircled by Ku70-Ku80 internally, are docked onto the ω frame, mediated by LIG4. DNA polymerase and ligase attached to each ω arm repair only one broken strand of a defined polarity; the final steps of NHEJ requires coordination and toggling of a pair of such enzymes. The facilitators XLF and PAXX additively stimulate NHEJ reactions. As DNA-end sensor and protector, LIG4 replaces DNA-PKcs for end joining and bridges the two DNA ends for polymerase to fill remaining gaps. These assemblies present new targets for NHEJ inhibition to enhance efficacy of radiotherapy and accuracy of gene editing. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9cq6.cif.gz 9cq6.cif.gz | 1 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9cq6.ent.gz pdb9cq6.ent.gz | 795.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9cq6.json.gz 9cq6.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cq/9cq6 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cq/9cq6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cq/9cq6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cq/9cq6 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  45809MC  9cq3C  9cqcC  9n81C  9n82C  9n83C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-X-ray repair cross-complementing protein ... , 2 types, 4 molecules AaBb
| #1: Protein | Mass: 70198.336 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: XRCC6, G22P1 / Cell line (production host): HEK293T / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: XRCC6, G22P1 / Cell line (production host): HEK293T / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)References: UniProt: P12956, Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement, Lyases; Carbon-oxygen lyases; Other carbon-oxygen lyases #2: Protein | Mass: 82812.438 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line (production host): HEK293T / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line (production host): HEK293T / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P13010 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P13010 |
|---|
-Protein , 4 types, 10 molecules CcDEdeFfGH
| #3: Protein | Mass: 33625.535 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NHEJ1, XLF / Cell line (production host): HEK293T / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NHEJ1, XLF / Cell line (production host): HEK293T / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9H9Q4 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9H9Q4#4: Protein | Mass: 38337.703 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: XRCC4 / Cell line (production host): HEK293T / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: XRCC4 / Cell line (production host): HEK293T / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q13426 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q13426#5: Protein | Mass: 104378.250 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: LIG4 / Cell line (production host): HEK293T / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: LIG4 / Cell line (production host): HEK293T / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P49917, DNA ligase (ATP) Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P49917, DNA ligase (ATP)#6: Protein | Mass: 23282.197 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PAXX, C9orf142, XLS / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PAXX, C9orf142, XLS / Production host:  |
|---|
-DNA chain , 4 types, 4 molecules IJKL
| #7: DNA chain | Mass: 20722.289 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
|---|---|
| #8: DNA chain | Mass: 20811.352 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| #9: DNA chain | Mass: 15865.188 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| #10: DNA chain | Mass: 15807.135 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Non-polymers , 1 types, 1 molecules 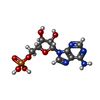
| #11: Chemical | ChemComp-AMP / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Ligation complex in the NHEJ pathway / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#10 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.854 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.9 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.35 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 42.2 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: SerialEM / Category: image acquisition |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 500830 Details: The resolution is reported by the postprocess in RELION based on the composite half maps generated by phenix.combine_focused_maps. Symmetry type: POINT |
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


















































 PDBj
PDBj