+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6q0j | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
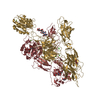
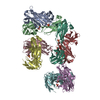
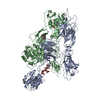
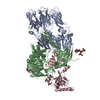
| Title | Structure of a MAPK pathway complex | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Transferase/PROTEIN BINDING / TRANSFERASE / Transferase-PROTEIN BINDING complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationepithelial cell proliferation involved in lung morphogenesis / positive regulation of endodermal cell differentiation / negative regulation of homotypic cell-cell adhesion / negative regulation of hypoxia-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle contraction / CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation / positive regulation of axon regeneration / regulation of axon regeneration / mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase / CD4-positive or CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell lineage commitment ...epithelial cell proliferation involved in lung morphogenesis / positive regulation of endodermal cell differentiation / negative regulation of homotypic cell-cell adhesion / negative regulation of hypoxia-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle contraction / CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation / positive regulation of axon regeneration / regulation of axon regeneration / mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase / CD4-positive or CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell lineage commitment / negative regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis / positive regulation of muscle contraction / Golgi inheritance / placenta blood vessel development / MAP-kinase scaffold activity / Signalling to p38 via RIT and RIN / cerebellar cortex formation / labyrinthine layer development / head morphogenesis / ARMS-mediated activation / melanosome transport / endothelial cell apoptotic process / myeloid progenitor cell differentiation / type B pancreatic cell proliferation / Signaling by MAP2K mutants / SHOC2 M1731 mutant abolishes MRAS complex function / Gain-of-function MRAS complexes activate RAF signaling / negative regulation of fibroblast migration / positive regulation of D-glucose transmembrane transport / establishment of protein localization to membrane / vesicle transport along microtubule / positive regulation of Ras protein signal transduction / regulation of Golgi inheritance / central nervous system neuron differentiation / mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase binding / regulation of T cell differentiation / positive regulation of axonogenesis / trachea formation / triglyceride homeostasis / Negative feedback regulation of MAPK pathway / regulation of early endosome to late endosome transport / regulation of stress-activated MAPK cascade / Frs2-mediated activation / stress fiber assembly / MAPK3 (ERK1) activation / ERBB2-ERBB3 signaling pathway / regulation of neurotransmitter receptor localization to postsynaptic specialization membrane / face development / endodermal cell differentiation / MAP kinase kinase activity / Bergmann glial cell differentiation / positive regulation of ATP biosynthetic process / thyroid gland development / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity / synaptic vesicle exocytosis / somatic stem cell population maintenance / positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / MAP kinase kinase kinase activity / protein kinase activator activity / negative regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process / Schwann cell development / response to axon injury / postsynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / keratinocyte differentiation / neuron projection morphogenesis / positive regulation of stress fiber assembly / sperm end piece / ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / myelination / positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity / positive regulation of autophagy / substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway / dendrite cytoplasm / cellular response to calcium ion / response to glucocorticoid / sperm principal piece / thymus development / animal organ morphogenesis / MAP3K8 (TPL2)-dependent MAPK1/3 activation / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / Signal transduction by L1 / cell motility / positive regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / RAF activation / Spry regulation of FGF signaling / Signaling by high-kinase activity BRAF mutants / MAP2K and MAPK activation / visual learning / small GTPase binding / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus / epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway / centriolar satellite / chemotaxis / neuron differentiation / Negative regulation of MAPK pathway / Signaling by RAF1 mutants / Signaling by moderate kinase activity BRAF mutants Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) Spodoptera exigua (beet armyworm) Spodoptera exigua (beet armyworm) | |||||||||
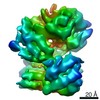
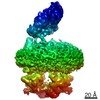
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Park, E. / Rawson, S. / Jeon, H. / Eck, M.J. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2019 Journal: Nature / Year: 2019Title: Architecture of autoinhibited and active BRAF-MEK1-14-3-3 complexes. Authors: Eunyoung Park / Shaun Rawson / Kunhua Li / Byeong-Won Kim / Scott B Ficarro / Gonzalo Gonzalez-Del Pino / Humayun Sharif / Jarrod A Marto / Hyesung Jeon / Michael J Eck /  Abstract: RAF family kinases are RAS-activated switches that initiate signalling through the MAP kinase cascade to control cellular proliferation, differentiation and survival. RAF activity is tightly ...RAF family kinases are RAS-activated switches that initiate signalling through the MAP kinase cascade to control cellular proliferation, differentiation and survival. RAF activity is tightly regulated and inappropriate activation is a frequent cause of cancer; however, the structural basis for RAF regulation is poorly understood at present. Here we use cryo-electron microscopy to determine autoinhibited and active-state structures of full-length BRAF in complexes with MEK1 and a 14-3-3 dimer. The reconstruction reveals an inactive BRAF-MEK1 complex restrained in a cradle formed by the 14-3-3 dimer, which binds the phosphorylated S365 and S729 sites that flank the BRAF kinase domain. The BRAF cysteine-rich domain occupies a central position that stabilizes this assembly, but the adjacent RAS-binding domain is poorly ordered and peripheral. The 14-3-3 cradle maintains autoinhibition by sequestering the membrane-binding cysteine-rich domain and blocking dimerization of the BRAF kinase domain. In the active state, these inhibitory interactions are released and a single 14-3-3 dimer rearranges to bridge the C-terminal pS729 binding sites of two BRAFs, which drives the formation of an active, back-to-back BRAF dimer. Our structural snapshots provide a foundation for understanding normal RAF regulation and its mutational disruption in cancer and developmental syndromes. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6q0j.cif.gz 6q0j.cif.gz | 277.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6q0j.ent.gz pdb6q0j.ent.gz | 178.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6q0j.json.gz 6q0j.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q0/6q0j https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q0/6q0j ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q0/6q0j ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q0/6q0j | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  20550MC  0541C  6nybC  6pp9C 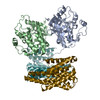 6q0kC 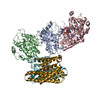 6q0tC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 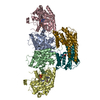
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
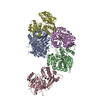
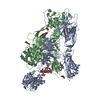
-Protein , 3 types, 6 molecules ABCDXY
| #1: Protein | Mass: 89306.812 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: S365A Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: BRAF, BRAF1, RAFB1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: BRAF, BRAF1, RAFB1 / Production host:  References: UniProt: P15056, non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase #2: Protein | Mass: 45934.543 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: S218A, S222A Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MAP2K1, MEK1, PRKMK1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MAP2K1, MEK1, PRKMK1 / Production host:  References: UniProt: Q02750, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase #3: Protein | Mass: 28108.514 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Spodoptera exigua (beet armyworm) / References: UniProt: V9P4T4 Spodoptera exigua (beet armyworm) / References: UniProt: V9P4T4 |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 6 molecules 
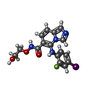



| #4: Chemical | | #5: Chemical | #6: Chemical | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: ERK pathway complex / Type: COMPLEX Details: insect cell endogenous 14-3-3 co-purified with human BRAF and MEK Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 325 kDa/nm / Experimental value: YES |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: OTHER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 53 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: NONE |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 425135 / Symmetry type: POINT |
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj












