+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-20552 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
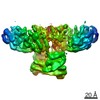
| Title | Structure of a MAPK pathway complex | |||||||||
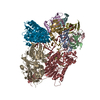
 Map data Map data | Structure of a MAPK pathway complex | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSFERASE / TRANSFERASE-PROTEIN BINDING complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationepithelial cell proliferation involved in lung morphogenesis / positive regulation of endodermal cell differentiation / negative regulation of homotypic cell-cell adhesion / negative regulation of hypoxia-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle contraction / CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation / positive regulation of axon regeneration / regulation of axon regeneration / mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase / CD4-positive or CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell lineage commitment ...epithelial cell proliferation involved in lung morphogenesis / positive regulation of endodermal cell differentiation / negative regulation of homotypic cell-cell adhesion / negative regulation of hypoxia-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle contraction / CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation / positive regulation of axon regeneration / regulation of axon regeneration / mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase / CD4-positive or CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell lineage commitment / negative regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis / positive regulation of muscle contraction / Golgi inheritance / placenta blood vessel development / MAP-kinase scaffold activity / Signalling to p38 via RIT and RIN / cerebellar cortex formation / labyrinthine layer development / head morphogenesis / melanosome transport / ARMS-mediated activation / type B pancreatic cell proliferation / myeloid progenitor cell differentiation / endothelial cell apoptotic process / Signaling by MAP2K mutants / SHOC2 M1731 mutant abolishes MRAS complex function / Gain-of-function MRAS complexes activate RAF signaling / negative regulation of fibroblast migration / positive regulation of D-glucose transmembrane transport / establishment of protein localization to membrane / positive regulation of axonogenesis / vesicle transport along microtubule / positive regulation of Ras protein signal transduction / regulation of Golgi inheritance / mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase binding / central nervous system neuron differentiation / regulation of T cell differentiation / trachea formation / triglyceride homeostasis / Negative feedback regulation of MAPK pathway / regulation of early endosome to late endosome transport / regulation of stress-activated MAPK cascade / Frs2-mediated activation / stress fiber assembly / MAPK3 (ERK1) activation / ERBB2-ERBB3 signaling pathway / regulation of neurotransmitter receptor localization to postsynaptic specialization membrane / face development / endodermal cell differentiation / MAP kinase kinase activity / Bergmann glial cell differentiation / positive regulation of ATP biosynthetic process / thyroid gland development / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity / synaptic vesicle exocytosis / somatic stem cell population maintenance / positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / MAP kinase kinase kinase activity / protein kinase activator activity / negative regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process / Schwann cell development / response to axon injury / postsynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / keratinocyte differentiation / neuron projection morphogenesis / positive regulation of stress fiber assembly / ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / myelination / positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / positive regulation of autophagy / protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity / substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / dendrite cytoplasm / insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway / cellular response to calcium ion / response to glucocorticoid / thymus development / animal organ morphogenesis / MAP3K8 (TPL2)-dependent MAPK1/3 activation / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / Signal transduction by L1 / cell motility / positive regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / RAF activation / Spry regulation of FGF signaling / Signaling by high-kinase activity BRAF mutants / MAP2K and MAPK activation / visual learning / small GTPase binding / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus / epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway / centriolar satellite / chemotaxis / neuron differentiation / Signaling by RAF1 mutants / Negative regulation of MAPK pathway / Signaling by moderate kinase activity BRAF mutants / Paradoxical activation of RAF signaling by kinase inactive BRAF / Signaling downstream of RAS mutants Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  Spodoptera exigua (beet armyworm) Spodoptera exigua (beet armyworm) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 5.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Park E / Rawson S | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2019 Journal: Nature / Year: 2019Title: Architecture of autoinhibited and active BRAF-MEK1-14-3-3 complexes. Authors: Eunyoung Park / Shaun Rawson / Kunhua Li / Byeong-Won Kim / Scott B Ficarro / Gonzalo Gonzalez-Del Pino / Humayun Sharif / Jarrod A Marto / Hyesung Jeon / Michael J Eck /  Abstract: RAF family kinases are RAS-activated switches that initiate signalling through the MAP kinase cascade to control cellular proliferation, differentiation and survival. RAF activity is tightly ...RAF family kinases are RAS-activated switches that initiate signalling through the MAP kinase cascade to control cellular proliferation, differentiation and survival. RAF activity is tightly regulated and inappropriate activation is a frequent cause of cancer; however, the structural basis for RAF regulation is poorly understood at present. Here we use cryo-electron microscopy to determine autoinhibited and active-state structures of full-length BRAF in complexes with MEK1 and a 14-3-3 dimer. The reconstruction reveals an inactive BRAF-MEK1 complex restrained in a cradle formed by the 14-3-3 dimer, which binds the phosphorylated S365 and S729 sites that flank the BRAF kinase domain. The BRAF cysteine-rich domain occupies a central position that stabilizes this assembly, but the adjacent RAS-binding domain is poorly ordered and peripheral. The 14-3-3 cradle maintains autoinhibition by sequestering the membrane-binding cysteine-rich domain and blocking dimerization of the BRAF kinase domain. In the active state, these inhibitory interactions are released and a single 14-3-3 dimer rearranges to bridge the C-terminal pS729 binding sites of two BRAFs, which drives the formation of an active, back-to-back BRAF dimer. Our structural snapshots provide a foundation for understanding normal RAF regulation and its mutational disruption in cancer and developmental syndromes. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_20552.map.gz emd_20552.map.gz | 5.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-20552-v30.xml emd-20552-v30.xml emd-20552.xml emd-20552.xml | 14 KB 14 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_20552.png emd_20552.png | 60.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-20552.cif.gz emd-20552.cif.gz | 6.6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20552 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20552 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20552 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20552 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6q0tMC  0541C  6nybC  6pp9C  6q0jC  6q0kC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_20552.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_20552.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Structure of a MAPK pathway complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.11 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : ERK pathway complex
| Entire | Name: ERK pathway complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: ERK pathway complex
| Supramolecule | Name: ERK pathway complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 280 kDa/nm |
-Macromolecule #1: Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf
| Macromolecule | Name: Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 89.306812 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSYYHHHHHH HHDIPTTENL YFQGAMDMAA LSGGGGGGAE PGQALFNGDM EPEAGAGAGA AASSAADPAI PEEVWNIKQM IKLTQEHIE ALLDKFGGEH NPPSIYLEAY EEYTSKLDAL QQREQQLLES LGNGTDFSVS SSASMDTVTS SSSSSLSVLP S SLSVFQNP ...String: MSYYHHHHHH HHDIPTTENL YFQGAMDMAA LSGGGGGGAE PGQALFNGDM EPEAGAGAGA AASSAADPAI PEEVWNIKQM IKLTQEHIE ALLDKFGGEH NPPSIYLEAY EEYTSKLDAL QQREQQLLES LGNGTDFSVS SSASMDTVTS SSSSSLSVLP S SLSVFQNP TDVARSNPKS PQKPIVRVFL PNKQRTVVPA RCGVTVRDSL KKALMMRGLI PECCAVYRIQ DGEKKPIGWD TD ISWLTGE ELHVEVLENV PLTTHNFVRK TFFTLAFCDF CRKLLFQGFR CQTCGYKFHQ RCSTEVPLMC VNYDQLDLLF VSK FFEHHP IPQEEASLAE TALTSGSSPS APASDSIGPQ ILTSPSPSKS IPIPQPFRPA DEDHRNQFGQ RDRSSAAPNV HINT IEPVN IDDLIRDQGF RGDGGSTTGL SATPPASLPG SLTNVKALQK SPGPQRERKS SSSSEDRNRM KTLGRRDSSD DWEIP DGQI TVGQRIGSGS FGTVYKGKWH GDVAVKMLNV TAPTPQQLQA FKNEVGVLRK TRHVNILLFM GYSTKPQLAI VTQWCE GSS LYHHLHIIET KFEMIKLIDI ARQTAQGMDY LHAKSIIHRD LKSNNIFLHE DLTVKIGDFG LATVKSRWSG SHQFEQL SG SILWMAPEVI RMQDKNPYSF QSDVYAFGIV LYELMTGQLP YSNINNRDQI IFMVGRGYLS PDLSKVRSNC PKAMKRLM A ECLKKKRDER PLFPQILASI ELLARSLPKI HRSA(SEP)EPSLN RAGFQTEDFS LYACASPKTP IQAGGYGAFP VHGTS AWSH PQFEK UniProtKB: Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf |
-Macromolecule #2: Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 45.835414 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGSSHHHHHH SAVDENLYFQ GGMPKKKPTP IQLNPAPDGS AVNGTSSAET NLEALQKKLE ELELDEQQRK RLEAFLTQKQ KVGELKDDD FEKISELGAG NGGVVFKVSH KPSGLVMARK LIHLEIKPAI RNQIIRELQV LHECNSPYIV GFYGAFYSDG E ISICMEHM ...String: MGSSHHHHHH SAVDENLYFQ GGMPKKKPTP IQLNPAPDGS AVNGTSSAET NLEALQKKLE ELELDEQQRK RLEAFLTQKQ KVGELKDDD FEKISELGAG NGGVVFKVSH KPSGLVMARK LIHLEIKPAI RNQIIRELQV LHECNSPYIV GFYGAFYSDG E ISICMEHM DGGSLDQVLK KAGRIPEQIL GKVSIAVIKG LTYLREKHKI MHRDVKPSNI LVNSRGEIKL CDFGVSGQLI DA MANAFVG TRSYMSPERL QGTHYSVQSD IWSMGLSLVE MAVGRYPIPP PDAKELELMF GCQVEGDAAE TPPRPRTPGR PLS SYGMDS RPPMAIFELL DYIVNEPPPK LPSGVFSLEF QDFVNKCLIK NPAERADLKQ LMVHAFIKRS DAEEVDFAGW LCST IGLNQ PSTPTHAAG UniProtKB: Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 |
-Macromolecule #3: 14-3-3 protein zeta
| Macromolecule | Name: 14-3-3 protein zeta / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Spodoptera exigua (beet armyworm) Spodoptera exigua (beet armyworm) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 28.108514 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MSVDKEELVQ RAKLAEQAER YDDMAAAMKE VTETGVELSN EERNLLSVAY KNVVGARRSS WRVISSIEQK TEGSERKQQM AKEYRVKVE KELREICYDV LGLLDKHLIP KASNPESKVF YLKMKGDYYR YLAEVATGET RNSVVEDSQK AYQDAFEISK A KMQPTHPI ...String: MSVDKEELVQ RAKLAEQAER YDDMAAAMKE VTETGVELSN EERNLLSVAY KNVVGARRSS WRVISSIEQK TEGSERKQQM AKEYRVKVE KELREICYDV LGLLDKHLIP KASNPESKVF YLKMKGDYYR YLAEVATGET RNSVVEDSQK AYQDAFEISK A KMQPTHPI RLGLALNFSV FYYEILNSPD KACQLAKQAF DDAIAELDTL NEDSYKDSTL IMQLLRDNLT LWTSDTQGDG DE PAEGGDN UniProtKB: 14-3-3 protein zeta |
-Macromolecule #4: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: 5-[(2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino]-N-(2-hydroxyethoxy)imidazo[1,5-a...
| Macromolecule | Name: 5-[(2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino]-N-(2-hydroxyethoxy)imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-6-carboxamide type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: LCJ |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 456.21 Da |
| Chemical component information | 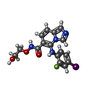 ChemComp-LCJ: |
-Macromolecule #6: PHOSPHOTHIOPHOSPHORIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHOTHIOPHOSPHORIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: AGS |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 523.247 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-AGS: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 53.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: OTHER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 5.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 595672 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-6q0t: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




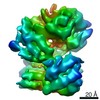

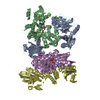
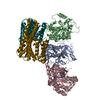


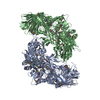
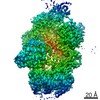









 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















