[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-5hzv: Crystal structure of the zona pellucida module of human endoglin/CD105 -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5hzv | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Crystal structure of the zona pellucida module of human endoglin/CD105 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Maltose-binding periplasmic protein,Endoglin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN / ZONA PELLUCIDA DOMAIN / ANGIOGENESIS / GLYCOPROTEIN / RECEPTOR | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationatrioventricular canal morphogenesis / detection of hypoxia / endothelial microparticle / venous blood vessel morphogenesis / dorsal aorta morphogenesis / cell migration involved in endocardial cushion formation / vascular associated smooth muscle cell development / atrial cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis / positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell differentiation / central nervous system vasculogenesis ...atrioventricular canal morphogenesis / detection of hypoxia / endothelial microparticle / venous blood vessel morphogenesis / dorsal aorta morphogenesis / cell migration involved in endocardial cushion formation / vascular associated smooth muscle cell development / atrial cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis / positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell differentiation / central nervous system vasculogenesis / epithelial to mesenchymal transition involved in endocardial cushion formation / positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition involved in endocardial cushion formation / cardiac ventricle morphogenesis / regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / galactose binding / cardiac atrium morphogenesis / smooth muscle tissue development / type II transforming growth factor beta receptor binding / activin binding / type I transforming growth factor beta receptor binding / glycosaminoglycan binding / ventricular trabecula myocardium morphogenesis / positive regulation of BMP signaling pathway / outflow tract septum morphogenesis / transforming growth factor beta binding / artery morphogenesis / endocardial cushion morphogenesis / branching involved in blood vessel morphogenesis / detection of maltose stimulus / negative regulation of endothelial cell proliferation / heart looping / maltose transport complex / negative regulation of SMAD protein signal transduction / carbohydrate transport / positive regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure / signaling receptor activator activity / positive regulation of SMAD protein signal transduction / extracellular matrix disassembly / carbohydrate transmembrane transporter activity / maltose binding / maltose transport / maltodextrin transmembrane transport / BMP signaling pathway / vasculogenesis / regulation of cell adhesion / coreceptor activity / ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter complex, substrate-binding subunit-containing / transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter complex / negative regulation of cell migration / cell chemotaxis / cell motility / wound healing / negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of angiogenesis / transmembrane signaling receptor activity / cell migration / regulation of cell population proliferation / outer membrane-bounded periplasmic space / response to hypoxia / periplasmic space / positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / signaling receptor complex / cell adhesion / nuclear body / negative regulation of gene expression / external side of plasma membrane / focal adhesion / DNA damage response / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / cell surface / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / protein homodimerization activity / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / extracellular space / membrane / identical protein binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.7 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.7 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Bokhove, M. / Saito, T. / Jovine, L. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Sweden, 7items Sweden, 7items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2017 Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2017Title: Structural Basis of the Human Endoglin-BMP9 Interaction: Insights into BMP Signaling and HHT1. Authors: Saito, T. / Bokhove, M. / Croci, R. / Zamora-Caballero, S. / Han, L. / Letarte, M. / de Sanctis, D. / Jovine, L. #1: Journal: J. Biol. Chem. / Year: 1990 Title: Primary structure of endoglin, an RGD-containing glycoprotein of human endothelial cells. Authors: Gougos, A. / Letarte, M. #2: Journal: FEBS Lett. / Year: 1992 Title: A large domain common to sperm receptors (Zp2 and Zp3) and TGF-beta type III receptor. Authors: Bork, P. / Sander, C. #3: Journal: Annu Rev Biochem / Year: 2005 Title: Zona pellucida domain proteins. Authors: Luca Jovine / Costel C Darie / Eveline S Litscher / Paul M Wassarman /  Abstract: Many eukaryotic proteins share a sequence designated as the zona pellucida (ZP) domain. This structural element, present in extracellular proteins from a wide variety of organisms, from nematodes to ...Many eukaryotic proteins share a sequence designated as the zona pellucida (ZP) domain. This structural element, present in extracellular proteins from a wide variety of organisms, from nematodes to mammals, consists of approximately 260 amino acids with eight conserved cysteine (Cys) residues and is located close to the C terminus of the polypeptide. ZP domain proteins are often glycosylated, modular structures consisting of multiple types of domains. Predictions can be made about some of the structural features of the ZP domain and ZP domain proteins. The functions of ZP domain proteins vary tremendously, from serving as structural components of egg coats, appendicularian mucous houses, and nematode dauer larvae, to serving as mechanotransducers in flies and receptors in mammals and nonmammals. Generally, ZP domain proteins are present in filaments and/or matrices, which is consistent with the role of the domain in protein polymerization. A general mechanism for assembly of ZP domain proteins has been presented. It is likely that the ZP domain plays a common role despite its presence in proteins of widely diverse functions. #4:  Journal: Cell / Year: 2010 Journal: Cell / Year: 2010Title: Insights into egg coat assembly and egg-sperm interaction from the X-ray structure of full-length ZP3. Authors: Ling Han / Magnus Monné / Hiroki Okumura / Thomas Schwend / Amy L Cherry / David Flot / Tsukasa Matsuda / Luca Jovine /  Abstract: ZP3, a major component of the zona pellucida (ZP) matrix coating mammalian eggs, is essential for fertilization by acting as sperm receptor. By retaining a propeptide that contains a polymerization- ...ZP3, a major component of the zona pellucida (ZP) matrix coating mammalian eggs, is essential for fertilization by acting as sperm receptor. By retaining a propeptide that contains a polymerization-blocking external hydrophobic patch (EHP), we determined the crystal structure of an avian homolog of ZP3 at 2.0 Å resolution. The structure unveils the fold of a complete ZP domain module in a homodimeric arrangement required for secretion and reveals how EHP prevents premature incorporation of ZP3 into the ZP. This suggests mechanisms underlying polymerization and how local structural differences, reflected by alternative disulfide patterns, control the specificity of ZP subunit interaction. Close relative positioning of a conserved O-glycan important for sperm binding and the hypervariable, positively selected C-terminal region of ZP3 suggests a concerted role in the regulation of species-restricted gamete recognition. Alternative conformations of the area around the O-glycan indicate how sperm binding could trigger downstream events via intramolecular signaling. #5:  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2016 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2016Title: A structured interdomain linker directs self-polymerization of human uromodulin. Authors: Marcel Bokhove / Kaoru Nishimura / Martina Brunati / Ling Han / Daniele de Sanctis / Luca Rampoldi / Luca Jovine /    Abstract: Uromodulin (UMOD)/Tamm-Horsfall protein, the most abundant human urinary protein, plays a key role in chronic kidney diseases and is a promising therapeutic target for hypertension. Via its bipartite ...Uromodulin (UMOD)/Tamm-Horsfall protein, the most abundant human urinary protein, plays a key role in chronic kidney diseases and is a promising therapeutic target for hypertension. Via its bipartite zona pellucida module (ZP-N/ZP-C), UMOD forms extracellular filaments that regulate kidney electrolyte balance and innate immunity, as well as protect against renal stones. Moreover, salt-dependent aggregation of UMOD filaments in the urine generates a soluble molecular net that captures uropathogenic bacteria and facilitates their clearance. Despite the functional importance of its homopolymers, no structural information is available on UMOD and how it self-assembles into filaments. Here, we report the crystal structures of polymerization regions of human UMOD and mouse ZP2, an essential sperm receptor protein that is structurally related to UMOD but forms heteropolymers. The structure of UMOD reveals that an extensive hydrophobic interface mediates ZP-N domain homodimerization. This arrangement is required for filament formation and is directed by an ordered ZP-N/ZP-C linker that is not observed in ZP2 but is conserved in the sequence of deafness/Crohn's disease-associated homopolymeric glycoproteins α-tectorin (TECTA) and glycoprotein 2 (GP2). Our data provide an example of how interdomain linker plasticity can modulate the function of structurally similar multidomain proteins. Moreover, the architecture of UMOD rationalizes numerous pathogenic mutations in both UMOD and TECTA genes. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5hzv.cif.gz 5hzv.cif.gz | 249 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5hzv.ent.gz pdb5hzv.ent.gz | 200.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5hzv.json.gz 5hzv.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hz/5hzv https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hz/5hzv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hz/5hzv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hz/5hzv | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 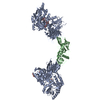 5hzwC  5i04C  5i05C  3sexS C: citing same article ( S: Starting model for refinement |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 68228.398 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Mutation: D449A, K450A, E539A, N540A, A582H, K586H, K606A, A679V, I684V, E726A, E729A, D730A AND R734N,D449A, K450A, E539A, N540A, A582H, K586H, K606A, A679V, I684V, E726A, E729A, D730A AND ...Mutation: D449A, K450A, E539A, N540A, A582H, K586H, K606A, A679V, I684V, E726A, E729A, D730A AND R734N,D449A, K450A, E539A, N540A, A582H, K586H, K606A, A679V, I684V, E726A, E729A, D730A AND R734N,D449A, K450A, E539A, N540A, A582H, K586H, K606A, A679V, I684V, E726A, E729A, D730A AND R734N,D449A, K450A, E539A, N540A, A582H, K586H, K606A, A679V, I684V, E726A, E729A, D730A AND R734N,D449A, K450A, E539A, N540A, A582H, K586H, K606A, A679V, I684V, E726A, E729A, D730A AND R734N,D449A, K450A, E539A, N540A, A582H, K586H, K606A, A679V, I684V, E726A, E729A, D730A AND R734N,D449A, K450A, E539A, N540A, A582H, K586H, K606A, A679V, I684V, E726A, E729A, D730A AND R734N,D449A, K450A, E539A, N540A, A582H, K586H, K606A, A679V, I684V, E726A, E729A, D730A AND R734N,D449A, K450A, E539A, N540A, A582H, K586H, K606A, A679V, I684V, E726A, E729A, D730A AND R734N,D449A, K450A, E539A, N540A, A582H, K586H, K606A, A679V, I684V, E726A, E729A, D730A AND R734N,D449A, K450A, E539A, N540A, A582H, K586H, K606A, A679V, I684V, E726A, E729A, D730A AND R734N,D449A, K450A, E539A, N540A, A582H, K586H, K606A, A679V, I684V, E726A, E729A, D730A AND R734N,D449A, K450A, E539A, N540A, A582H, K586H, K606A, A679V, I684V, E726A, E729A, D730A AND R734N,D449A, K450A, E539A, N540A, A582H, K586H, K606A, A679V, I684V, E726A, E729A, D730A AND R734N,D449A, K450A, E539A, N540A, A582H, K586H, K606A, A679V, I684V, E726A, E729A, D730A AND R734N,D449A, K450A, E539A, N540A, A582H, K586H, K606A, A679V, I684V, E726A, E729A, D730A AND R734N Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: THIS PROTEIN IS A CHIMERA. RESIDUES 368-734 ARE FROM E. COLI MALTOSE BINDING PROTEIN (MBP), CORRESPOND TO RESIDUES 27-393 OF SWISS-PROT DATABASE ENTRY P0AEX9 AND CONTAIN MUTATIONS D449A, ...Details: THIS PROTEIN IS A CHIMERA. RESIDUES 368-734 ARE FROM E. COLI MALTOSE BINDING PROTEIN (MBP), CORRESPOND TO RESIDUES 27-393 OF SWISS-PROT DATABASE ENTRY P0AEX9 AND CONTAIN MUTATIONS D449A, K450A, E539A, N540A, A582H, K586H, K606A, A679V, I684V, E726A, E729A, D730A AND R734N (CORRESPONDING TO D108A, K109A, E198A, N199A, A241H, K245H, K265A, A338V, I343V, E385A, E388A, D389A AND R393N IN P0AEX9). RESIDUES 738-981 ARE FROM HUMAN ENDOGLIN PROTEIN AND CORRESPOND TO RESIDUES 338-581 OF SWISS-PROT DATABASE ENTRY P17813. SUBTRACTING 400 FROM THE PDB ENTRY RESIDUE NUMBERING RESULTS IN THE NUMBERING ACCORDING TO UNIPROT ENTRY P17813. Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Strain: K12 / Cell: ENDOTHELIAL / Gene: malE, b4034, JW3994, ENG, END / Plasmid: pHLsec / Cell line (production host): HEK293T / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P0AEX9, UniProt: P17813 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P0AEX9, UniProt: P17813 |
|---|---|
| #2: Polysaccharide | alpha-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-alpha-D-glucopyranose / alpha-maltose |
| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-GOL / |
| #4: Water | ChemComp-HOH / |
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.94 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 58.2 % / Description: Hexagonal rod |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 293 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / pH: 6.5 Details: 11.5% equal mixture of MPD, PEG 1000 and PEG 3350 (1:1:1), MES/imidazole mix PH range: 5.5-7.0 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  ESRF ESRF  / Beamline: ID23-1 / Wavelength: 1 Å / Beamline: ID23-1 / Wavelength: 1 Å |
| Detector | Type: PSI PILATUS 6M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Sep 25, 2015 |
| Radiation | Monochromator: Si Single Crystal / Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.69→29.51 Å / Num. obs: 21583 / % possible obs: 97.9 % / Observed criterion σ(I): -3 / Redundancy: 3.3 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 72.174 Å2 / Rsym value: 0.062 / Net I/σ(I): 9.43 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 2.69→2.76 Å / Redundancy: 2.8 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.675 / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 0.99 / % possible all: 85.4 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 3SEX Resolution: 2.7→29.5037 Å / SU ML: 0.51 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.33 / Phase error: 36.22 / Stereochemistry target values: ML
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 2.7→29.5037 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS params. | Method: refined / Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS group |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 PDBj
PDBj