[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
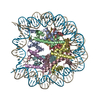
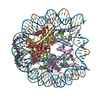
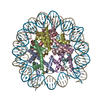
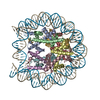
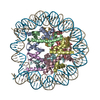
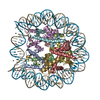
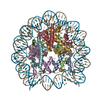
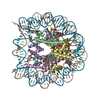
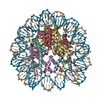
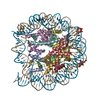
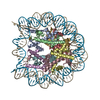
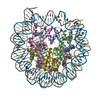
Yorodumi- PDB-5b40: The nucleosome structure containing H2B-K120 and H4-K31 monoubiqu... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5b40 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | The nucleosome structure containing H2B-K120 and H4-K31 monoubiquitinations | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | STRUCTURAL PROTEIN/DNA / nucleosome / ubiquitin / histone modification / chromatin / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN-DNA complex | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere ...negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / telomere organization / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Interleukin-7 signaling / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Meiotic synapsis / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / innate immune response in mucosa / Defective pyroptosis / Negative Regulation of CDH1 Gene Transcription / HDACs deacetylate histones / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / lipopolysaccharide binding / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / HDMs demethylate histones / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Meiotic recombination / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / Metalloprotease DUBs / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / RMTs methylate histone arginines / HCMV Early Events / structural constituent of chromatin / UCH proteinases / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / nucleosome assembly / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / antibacterial humoral response / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / HATs acetylate histones / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / chromatin organization / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / gene expression / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / killing of cells of another organism / defense response to Gram-negative bacterium / chromosome, telomeric region / Ub-specific processing proteases / defense response to Gram-positive bacterium / Amyloid fiber formation / protein heterodimerization activity / negative regulation of cell population proliferation / chromatin binding / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / protein-containing complex / extracellular space / DNA binding / RNA binding / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / nucleoplasm / membrane / nucleus / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 3.33 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 3.33 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Machida, S. / Sekine, S. / Nishiyama, Y. / Horikoshi, N. / Kurumizaka, H. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 3items Japan, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: To Be Published Journal: To Be PublishedTitle: Monoubiquitination of histones H2B and H4 changes the nucleosome stability without affecting the nucleosome structure Authors: Machida, S. / Sekine, S. / Nishiyama, Y. / Horikoshi, N. / Kurumizaka, H. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5b40.cif.gz 5b40.cif.gz | 317.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5b40.ent.gz pdb5b40.ent.gz | 240.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5b40.json.gz 5b40.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b4/5b40 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b4/5b40 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b4/5b40 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b4/5b40 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 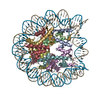 3av1S S: Starting model for refinement |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 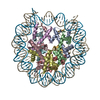
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 15671.314 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: C110A Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST2H3A, HIST2H3C, H3F2, H3FM, HIST2H3D / Plasmid: pET15b / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST2H3A, HIST2H3C, H3F2, H3FM, HIST2H3D / Plasmid: pET15b / Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 11650.667 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: K31C Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: HIST1H4A, H4/A, H4FA, HIST1H4B, H4/I, H4FI, HIST1H4C, H4/G, H4FG, HIST1H4D, H4/B, H4FB, HIST1H4E, H4/J, H4FJ, HIST1H4F, H4/C, H4FC, HIST1H4H, H4/H, H4FH, HIST1H4I, H4/M, H4FM, HIST1H4J, H4/E, ...Gene: HIST1H4A, H4/A, H4FA, HIST1H4B, H4/I, H4FI, HIST1H4C, H4/G, H4FG, HIST1H4D, H4/B, H4FB, HIST1H4E, H4/J, H4FJ, HIST1H4F, H4/C, H4FC, HIST1H4H, H4/H, H4FH, HIST1H4I, H4/M, H4FM, HIST1H4J, H4/E, H4FE, HIST1H4K, H4/D, H4FD, HIST1H4L, H4/K, H4FK, HIST2H4A, H4/N, H4F2, H4FN, HIST2H4, HIST2H4B, H4/O, H4FO, HIST4H4 Plasmid: pET15b / Production host:  #3: Protein | Mass: 14447.825 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2AB, H2AFM, HIST1H2AE, H2AFA / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2AB, H2AFM, HIST1H2AE, H2AFA / Production host:  #4: Protein | Mass: 14191.479 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: K121C Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2BJ, H2BFR / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2BJ, H2BFR / Production host:  #5: DNA chain | Mass: 45053.855 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.68 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 54.11 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 293 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop Details: 90mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.8), 3.6% PGA-LM, 25.2% PEG 400, 2-6% Pentaerythritol ethoxylate (3/4 EO/OH) |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  Photon Factory Photon Factory  / Beamline: BL-1A / Wavelength: 1.1 Å / Beamline: BL-1A / Wavelength: 1.1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS PILATUS 2M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Dec 17, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1.1 Å / Relative weight: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection | Resolution: 3.33→50 Å / Num. obs: 30012 / % possible obs: 97.7 % / Redundancy: 6.2 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 101.38 Å2 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.07 / Net I/av σ(I): 18.667 / Net I/σ(I): 11.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection shell |
|
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 3AV1 Resolution: 3.33→39.391 Å / SU ML: 0.51 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 2.08 / Phase error: 28.16
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 253.54 Å2 / Biso mean: 122.03 Å2 / Biso min: 42.34 Å2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: final / Resolution: 3.33→39.391 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Total num. of bins used: 14
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj











































