+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
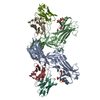
| Title | Structure of beta-arrestin1 in complex with mouse C5aR1pp | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GPCR / G protein / SIGNALING PROTEIN / beta-arrestin | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcomplement component C5a binding / cell proliferation in hindbrain / V2 vasopressin receptor binding / alpha-1A adrenergic receptor binding / follicle-stimulating hormone receptor binding / TGFBR3 regulates TGF-beta signaling / sensory perception of touch / G alpha (s) signalling events / presynapse organization / complement component C5a signaling pathway ...complement component C5a binding / cell proliferation in hindbrain / V2 vasopressin receptor binding / alpha-1A adrenergic receptor binding / follicle-stimulating hormone receptor binding / TGFBR3 regulates TGF-beta signaling / sensory perception of touch / G alpha (s) signalling events / presynapse organization / complement component C5a signaling pathway / follicle-stimulating hormone signaling pathway / regulation of inositol trisphosphate biosynthetic process / protein phosphorylated amino acid binding / alpha-1B adrenergic receptor binding / Lysosome Vesicle Biogenesis / complement component C5a receptor activity / Regulation of Complement cascade / Peptide ligand-binding receptors / AP-2 adaptor complex binding / response to peptidoglycan / Ub-specific processing proteases / angiotensin receptor binding / MAP2K and MAPK activation / Golgi Associated Vesicle Biogenesis / Cargo recognition for clathrin-mediated endocytosis / clathrin-cargo adaptor activity / Clathrin-mediated endocytosis / G alpha (i) signalling events / negative regulation of interleukin-8 production / regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / complement receptor mediated signaling pathway / cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity involved in apoptotic process / arrestin family protein binding / G protein-coupled receptor internalization / mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase binding / positive regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis / Thrombin signalling through proteinase activated receptors (PARs) / clathrin binding / response to morphine / stress fiber assembly / positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction / positive regulation of macrophage chemotaxis / pseudopodium / amyloid-beta clearance / negative regulation of interleukin-6 production / positive regulation of receptor internalization / positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production / negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway / phototransduction / positive regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / insulin-like growth factor receptor binding / Neutrophil degranulation / neutrophil chemotaxis / clathrin-coated pit / astrocyte activation / negative regulation of protein ubiquitination / GTPase activator activity / positive regulation of protein ubiquitination / nuclear estrogen receptor binding / positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation / phosphoprotein binding / microglial cell activation / G protein-coupled receptor binding / negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II / G protein-coupled receptor activity / adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / cognition / adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / endocytosis / apical part of cell / positive regulation of protein phosphorylation / positive regulation of angiogenesis / protein transport / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / cytoplasmic vesicle / regulation of apoptotic process / basolateral plasma membrane / phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / dendritic spine / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process / molecular adaptor activity / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / transmembrane transporter binding / postsynaptic membrane / transcription coactivator activity / positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / positive regulation of MAPK cascade / endosome / postsynaptic density / defense response to Gram-positive bacterium / protein ubiquitination / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / response to xenobiotic stimulus / inflammatory response / signaling receptor binding / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |   | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.72 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Banerjee R / Yadav R / Yadav MK / Ganguly M / Mishra S / Dalal A / Gati C / Shukla AK | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  India, India,  United Kingdom, 3 items United Kingdom, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2025 Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2025Title: Molecular fingerprints of a convergent mechanism orchestrating diverse ligand recognition and species-specific pharmacology at the complement anaphylatoxin receptors. Authors: Sudha Mishra / Manish K Yadav / Annu Dalal / Manisankar Ganguly / Ravi Yadav / Kazuhiro Sawada / Divyanshu Tiwari / Nabarun Roy / Nilanjana Banerjee / Jenny N Fung / Jianina Marallag / ...Authors: Sudha Mishra / Manish K Yadav / Annu Dalal / Manisankar Ganguly / Ravi Yadav / Kazuhiro Sawada / Divyanshu Tiwari / Nabarun Roy / Nilanjana Banerjee / Jenny N Fung / Jianina Marallag / Cedric S Cui / Xaria X Li / John D Lee / Calvin Aaron Dsouza / Shirsha Saha / Parishmita Sarma / Ganita Rawat / Houming Zhu / Htet A Khant / Richard J Clark / Fumiya K Sano / Ramanuj Banerjee / Trent M Woodruff / Osamu Nureki / Cornelius Gati / Arun K Shukla /     Abstract: Complement anaphylatoxin receptors (C3aR and C5aR1) are prototypical G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) playing crucial physiological roles in innate immunity by combating pathogenic infections and ...Complement anaphylatoxin receptors (C3aR and C5aR1) are prototypical G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) playing crucial physiological roles in innate immunity by combating pathogenic infections and orchestrating inflammatory responses. They continue to be important therapeutic targets for multiple disorders including autoimmune diseases, acute and chronic inflammation, and allergy-related conditions. Recent structural coverage has provided important insights into their activation and signaling, however, confounding observations in the literature related to ligand efficacy and functional responses, especially in different model systems, present a major challenge for drug discovery efforts. Here, we systematically and comprehensively profile a broad set of natural and synthetic ligands at C3aR and C5aR1 and discover a previously unanticipated level of functional specialization in terms of species-specific pharmacology and receptor activation. Taking a lead from this, we determine seventeen cryo-EM structures of different ligand-receptor-G-protein complexes and uncover distinct orientation of agonists between the human and mouse receptors despite an overlapping positioning in the orthosteric binding pocket. Combined with extensive mutagenesis and functional assays, these structural snapshots allow us to decode and validate a convergent molecular mechanism involving a "Five-Point-Switch" in these receptors that orchestrates the recognition and efficacy of diverse agonists. We also identify species-specific differences at the level of phosphorylation patterns encoded in the carboxyl-terminus of these receptors and directly visualize their impact on βarr binding and activation using cryo-EM structures. Interestingly, we observe that βarrs engage with the mouse C5aR1 using a variation of previously discovered P-X-P-P phosphorylation motif via a "Sliding-Mechanism" and also exhibit distinct oligomeric state for the human vs. mouse receptors. Taken together, this study elucidates functional specialization at the complement anaphylatoxin receptors and underlying molecular mechanisms, offering a previously lacking framework with direct and immediate implications for the development of novel therapeutics. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_62649.map.gz emd_62649.map.gz | 181.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-62649-v30.xml emd-62649-v30.xml emd-62649.xml emd-62649.xml | 22.2 KB 22.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_62649_fsc.xml emd_62649_fsc.xml | 12.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_62649.png emd_62649.png | 98.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-62649.cif.gz emd-62649.cif.gz | 6.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_62649_half_map_1.map.gz emd_62649_half_map_1.map.gz emd_62649_half_map_2.map.gz emd_62649_half_map_2.map.gz | 200.2 MB 200.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-62649 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-62649 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-62649 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-62649 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9kyuMC  9kugC  9kutC  9kv6C  9kv8C  9kvpC  9kwgC  9kwxC  9kx6C  9kxsC  9ky2C  9kz2C  9kz8C  9kzkC  9l0hC  9umjC  9umrC  9umxC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_62649.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_62649.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.0109 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_62649_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_62649_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : beta-arrestin1 in complex with mouse C5aR1pp
| Entire | Name: beta-arrestin1 in complex with mouse C5aR1pp |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: beta-arrestin1 in complex with mouse C5aR1pp
| Supramolecule | Name: beta-arrestin1 in complex with mouse C5aR1pp / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: Beta-arrestin-1
| Supramolecule | Name: Beta-arrestin-1 / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: Fab30 Heavy Chain and Light chain
| Supramolecule | Name: Fab30 Heavy Chain and Light chain / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #3-#4 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #4: mouse C5aR1 phosphopeptide
| Supramolecule | Name: mouse C5aR1 phosphopeptide / type: complex / ID: 4 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: Beta-arrestin-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Beta-arrestin-1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 47.088508 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGDKGTRVFK KASPNGKLTV YLGKRDFVDH IDLVDPVDGV VLVDPEYLKE RRVYVTLTCA FRYGREDLDV LGLTFRKDLF VANVQSFPP APEDKKPLTR LQERLIKKLG EHAYPFTFEI PPNLPCSVTL QPGPEDTGKA CGVDYEVKAF CAENLEEKIH K RNSVRLVI ...String: MGDKGTRVFK KASPNGKLTV YLGKRDFVDH IDLVDPVDGV VLVDPEYLKE RRVYVTLTCA FRYGREDLDV LGLTFRKDLF VANVQSFPP APEDKKPLTR LQERLIKKLG EHAYPFTFEI PPNLPCSVTL QPGPEDTGKA CGVDYEVKAF CAENLEEKIH K RNSVRLVI RKVQYAPERP GPQPTAETTR QFLMSDKPLH LEASLDKEIY YHGEPISVNV HVTNNTNKTV KKIKISVRQY AD ICLFNTA QYKCPVAMEE ADDTVAPSST FCKVYTLTPF LANNREKRGL ALDGKLKHED TNLASSTLLR EGANREILGI IVS YKVKVK LVVSRGGLLG DLASSDVAVE LPFTLMHPKP KEEPPHREVP ESETPVDTNL IELDTNDDDI VFEDFARQRL KGMK DDKDE EDDGTGSPHL NNR UniProtKB: Beta-arrestin-1 |
-Macromolecule #2: C5aR1 phosphopeptide
| Macromolecule | Name: C5aR1 phosphopeptide / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 2.972297 KDa |
| Sequence | String: GGGD(SEP)K(TPO)F(TPO)P (SEP)(TPO)(TPO)D(TPO)(SEP)TRKS QAV UniProtKB: C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor 1 |
-Macromolecule #3: Fab30 Heavy Chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Fab30 Heavy Chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 25.512354 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: EISEVQLVES GGGLVQPGGS LRLSCAASGF NVYSSSIHWV RQAPGKGLEW VASISSYYGY TYYADSVKGR FTISADTSKN TAYLQMNSL RAEDTAVYYC ARSRQFWYSG LDYWGQGTLV TVSSASTKGP SVFPLAPSSK STSGGTAALG CLVKDYFPEP V TVSWNSGA ...String: EISEVQLVES GGGLVQPGGS LRLSCAASGF NVYSSSIHWV RQAPGKGLEW VASISSYYGY TYYADSVKGR FTISADTSKN TAYLQMNSL RAEDTAVYYC ARSRQFWYSG LDYWGQGTLV TVSSASTKGP SVFPLAPSSK STSGGTAALG CLVKDYFPEP V TVSWNSGA LTSGVHTFPA VLQSSGLYSL SSVVTVPSSS LGTQTYICNV NHKPSNTKVD KKVEPKSCDK THHHHHHHH |
-Macromolecule #4: Fab30 Light Chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Fab30 Light Chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 23.435064 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SDIQMTQSPS SLSASVGDRV TITCRASQSV SSAVAWYQQK PGKAPKLLIY SASSLYSGVP SRFSGSRSGT DFTLTISSLQ PEDFATYYC QQYKYVPVTF GQGTKVEIKR TVAAPSVFIF PPSDSQLKSG TASVVCLLNN FYPREAKVQW KVDNALQSGN S QESVTEQD ...String: SDIQMTQSPS SLSASVGDRV TITCRASQSV SSAVAWYQQK PGKAPKLLIY SASSLYSGVP SRFSGSRSGT DFTLTISSLQ PEDFATYYC QQYKYVPVTF GQGTKVEIKR TVAAPSVFIF PPSDSQLKSG TASVVCLLNN FYPREAKVQW KVDNALQSGN S QESVTEQD SKDSTYSLSS TLTLSKADYE KHKVYACEVT HQGLSSPVTK SFNRGEC |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Average electron dose: 53.7 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-9kyu: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)