+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 | データベース: EMDB / ID: EMD-3703 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| タイトル | Human cytoplasmic dynein-1 tail in the twisted state | |||||||||
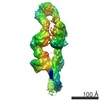
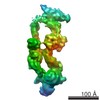
 マップデータ マップデータ | Tail region particles were recentered and extracted from the complete human dynein-1 complex. Particles predominantly contain the dynein heavy chain N-terminus in a twisted conformation. | |||||||||
 試料 試料 |
| |||||||||
 キーワード キーワード | Motor protein / dynein / tail complex | |||||||||
| 生物種 |  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) | |||||||||
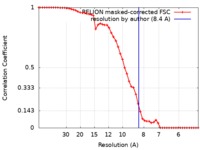
| 手法 | 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 8.4 Å | |||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Zhang K | |||||||||
| 資金援助 |  英国, 2件 英国, 2件
| |||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Cell / 年: 2017 ジャーナル: Cell / 年: 2017タイトル: Cryo-EM Reveals How Human Cytoplasmic Dynein Is Auto-inhibited and Activated. 著者: Kai Zhang / Helen E Foster / Arnaud Rondelet / Samuel E Lacey / Nadia Bahi-Buisson / Alexander W Bird / Andrew P Carter /    要旨: Cytoplasmic dynein-1 binds dynactin and cargo adaptor proteins to form a transport machine capable of long-distance processive movement along microtubules. However, it is unclear why dynein-1 moves ...Cytoplasmic dynein-1 binds dynactin and cargo adaptor proteins to form a transport machine capable of long-distance processive movement along microtubules. However, it is unclear why dynein-1 moves poorly on its own or how it is activated by dynactin. Here, we present a cryoelectron microscopy structure of the complete 1.4-megadalton human dynein-1 complex in an inhibited state known as the phi-particle. We reveal the 3D structure of the cargo binding dynein tail and show how self-dimerization of the motor domains locks them in a conformation with low microtubule affinity. Disrupting motor dimerization with structure-based mutagenesis drives dynein-1 into an open form with higher affinity for both microtubules and dynactin. We find the open form is also inhibited for movement and that dynactin relieves this by reorienting the motor domains to interact correctly with microtubules. Our model explains how dynactin binding to the dynein-1 tail directly stimulates its motor activity. | |||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| ムービー |
 ムービービューア ムービービューア |
|---|---|
| 構造ビューア | EMマップ:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| 添付画像 |
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
-EMDBアーカイブ
| マップデータ |  emd_3703.map.gz emd_3703.map.gz | 649.8 KB |  EMDBマップデータ形式 EMDBマップデータ形式 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ヘッダ (付随情報) |  emd-3703-v30.xml emd-3703-v30.xml emd-3703.xml emd-3703.xml | 38.6 KB 38.6 KB | 表示 表示 |  EMDBヘッダ EMDBヘッダ |
| FSC (解像度算出) |  emd_3703_fsc.xml emd_3703_fsc.xml | 5 KB | 表示 |  FSCデータファイル FSCデータファイル |
| 画像 |  emd_3703.png emd_3703.png | 72.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-3703.cif.gz emd-3703.cif.gz | 5.1 KB | ||
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3703 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3703 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3703 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3703 | HTTPS FTP |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  emd_3703_validation.pdf.gz emd_3703_validation.pdf.gz | 390.1 KB | 表示 |  EMDB検証レポート EMDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  emd_3703_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_3703_full_validation.pdf.gz | 389.7 KB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  emd_3703_validation.xml.gz emd_3703_validation.xml.gz | 8.3 KB | 表示 | |
| CIF形式データ |  emd_3703_validation.cif.gz emd_3703_validation.cif.gz | 10.4 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-3703 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-3703 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-3703 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-3703 | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
- リンク
リンク
| EMDBのページ |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- マップ
マップ
| ファイル |  ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_3703.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 11.4 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_3703.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 11.4 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 注釈 | Tail region particles were recentered and extracted from the complete human dynein-1 complex. Particles predominantly contain the dynein heavy chain N-terminus in a twisted conformation. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 投影像・断面図 | 画像のコントロール
画像は Spider により作成 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ボクセルのサイズ | X=Y=Z: 2.64 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
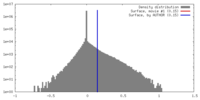
| 密度 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 空間群: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 詳細 | EMDB XML:
CCP4マップ ヘッダ情報:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-添付データ
- 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素
+全体 : Human cytoplasmic dynein-1 tail in the twisted N-terminus state
+超分子 #1: Human cytoplasmic dynein-1 tail in the twisted N-terminus state
+分子 #1: dynein heavy chain
+分子 #2: dynein intermediate chain
+分子 #3: dynein heavy chain
+分子 #4: dynein light intermediate chain
+分子 #5: dynein light intermediate chain
+分子 #6: N-terminal dimerization domain
+分子 #7: N-terminal dimerization domain
+分子 #8: LC8
+分子 #9: Tctex
+分子 #10: Tctex
+分子 #11: intermediate chain
+分子 #12: intermediate chain
+分子 #13: Robl
-実験情報
-構造解析
| 手法 | クライオ電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
 解析 解析 | 単粒子再構成法 |
| 試料の集合状態 | particle |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 濃度 | 0.15 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 緩衝液 | pH: 7.4 |
| 凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE |
- 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法
| 顕微鏡 | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| 撮影 | フィルム・検出器のモデル: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) 平均電子線量: 1.6 e/Å2 |
| 電子線 | 加速電圧: 300 kV / 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| 電子光学系 | 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM / 撮影モード: BRIGHT FIELD |
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー













 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)