[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
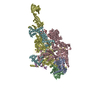
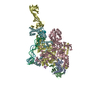
Yorodumi- PDB-5nug: Motor domains from human cytoplasmic dynein-1 in the phi-particle... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5nug | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Motor domains from human cytoplasmic dynein-1 in the phi-particle conformation | |||||||||
 Components Components | Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1 | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MOTOR PROTEIN / dynein / motor domain / AAA+ | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of intracellular transport / regulation of metaphase plate congression / positive regulation of spindle assembly / establishment of spindle localization / dynein complex / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / retrograde axonal transport / P-body assembly / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / dynein light intermediate chain binding ...positive regulation of intracellular transport / regulation of metaphase plate congression / positive regulation of spindle assembly / establishment of spindle localization / dynein complex / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / retrograde axonal transport / P-body assembly / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / dynein light intermediate chain binding / cytoplasmic dynein complex / nuclear migration / dynein intermediate chain binding / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / cytoplasmic microtubule / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / axon cytoplasm / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / MHC class II antigen presentation / Mitotic Prometaphase / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / stress granule assembly / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / regulation of mitotic spindle organization / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / mitotic spindle organization / filopodium / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / HCMV Early Events / Aggrephagy / azurophil granule lumen / Separation of Sister Chromatids / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis / cell cortex / microtubule / cell division / Neutrophil degranulation / centrosome / ATP hydrolysis activity / RNA binding / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / ATP binding / identical protein binding / membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhang, K. / Foster, H.E. / Carter, A.P. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 2items United Kingdom, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2017 Journal: Cell / Year: 2017Title: Cryo-EM Reveals How Human Cytoplasmic Dynein Is Auto-inhibited and Activated. Authors: Kai Zhang / Helen E Foster / Arnaud Rondelet / Samuel E Lacey / Nadia Bahi-Buisson / Alexander W Bird / Andrew P Carter /    Abstract: Cytoplasmic dynein-1 binds dynactin and cargo adaptor proteins to form a transport machine capable of long-distance processive movement along microtubules. However, it is unclear why dynein-1 moves ...Cytoplasmic dynein-1 binds dynactin and cargo adaptor proteins to form a transport machine capable of long-distance processive movement along microtubules. However, it is unclear why dynein-1 moves poorly on its own or how it is activated by dynactin. Here, we present a cryoelectron microscopy structure of the complete 1.4-megadalton human dynein-1 complex in an inhibited state known as the phi-particle. We reveal the 3D structure of the cargo binding dynein tail and show how self-dimerization of the motor domains locks them in a conformation with low microtubule affinity. Disrupting motor dimerization with structure-based mutagenesis drives dynein-1 into an open form with higher affinity for both microtubules and dynactin. We find the open form is also inhibited for movement and that dynactin relieves this by reorienting the motor domains to interact correctly with microtubules. Our model explains how dynactin binding to the dynein-1 tail directly stimulates its motor activity. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5nug.cif.gz 5nug.cif.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5nug.ent.gz pdb5nug.ent.gz | 955.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5nug.json.gz 5nug.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nu/5nug https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nu/5nug ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nu/5nug ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nu/5nug | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  3698MC  3703C  3704C  3705C  3706C  3707C  5nvsC  5nvuC  5nw4C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | 
|
| 2 | 
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 533083.250 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DYNC1H1, DHC1, DNCH1, DNCL, DNECL, DYHC, KIAA0325 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DYNC1H1, DHC1, DNCH1, DNCL, DNECL, DYHC, KIAA0325 / Production host:  #2: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / #3: Chemical | #4: Chemical | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Motor domains from human cytoplasmic dynein-1 in the phi-particle conformation Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 Details: 20mM HEPES pH7.4, 150 mM KCl, 1mM MgCl2, 5 mM DTT, 0.1 mM ATP |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.15 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: vitrification was performed immediately after gel filtration. |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 59000 X / Calibrated magnification: 106061 X / Nominal defocus max: 5000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 1500 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 5000 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Temperature (max): 100 K / Temperature (min): 90 K |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 2 sec. / Electron dose: 1.6 e/Å2 / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 6746 / Num. of real images: 312198 Details: Images were also collected using K2 summit detetor in counting mode |
| Image scans | Sampling size: 14 µm / Width: 4096 / Height: 4096 / Movie frames/image: 34 / Used frames/image: 3-34 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: REFMAC / Version: 5.8.0166 / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Image processing | Details: Negative stain dataset was processed as | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1 Details: Negative stain dataset was processed to generate templates. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C2 (2 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 233227 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 145 / Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: RECIPROCAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Resolution: 3.8→232.32 Å / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc: 0.865 / SU B: 59.043 / SU ML: 0.777 / ESU R: 0.879 Stereochemistry target values: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD WITH PHASES Details: HYDROGENS HAVE BEEN ADDED IN THE RIDING POSITIONS
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Solvent model: PARAMETERS FOR MASK CACLULATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 145.21 Å2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: 1 / Total: 46232 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj























