[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-3706: Human cytoplasmic dynein-1 bound to dynactin and an N-terminal co... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-3706 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Human cytoplasmic dynein-1 bound to dynactin and an N-terminal construct of BICD2 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | 3D reconstruction of DDB. Motor domains has The stable portion of the dynein tail is visible, whereas the motor domains are disordered. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Motor protein / dynein / dynactin / BICD | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationretrograde axonal transport of mitochondrion / dynactin complex / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / F-actin capping protein complex / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / barbed-end actin filament capping ...retrograde axonal transport of mitochondrion / dynactin complex / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / F-actin capping protein complex / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / barbed-end actin filament capping / dense body / Neutrophil degranulation / coronary vasculature development / dynein complex / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / MHC class II antigen presentation / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / ventricular septum development / aorta development / cortical cytoskeleton / dynein complex binding / microtubule-based process / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / axon cytoplasm / MHC class II antigen presentation / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / mitotic spindle organization / kinetochore / actin filament binding / actin binding / actin cytoskeleton organization / cell cortex / nuclear membrane / cytoskeleton / focal adhesion / centrosome / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / plasma membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||
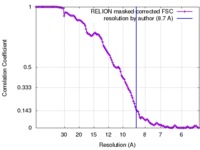
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 8.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhang K / Foster HE | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 2 items United Kingdom, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2017 Journal: Cell / Year: 2017Title: Cryo-EM Reveals How Human Cytoplasmic Dynein Is Auto-inhibited and Activated. Authors: Kai Zhang / Helen E Foster / Arnaud Rondelet / Samuel E Lacey / Nadia Bahi-Buisson / Alexander W Bird / Andrew P Carter /    Abstract: Cytoplasmic dynein-1 binds dynactin and cargo adaptor proteins to form a transport machine capable of long-distance processive movement along microtubules. However, it is unclear why dynein-1 moves ...Cytoplasmic dynein-1 binds dynactin and cargo adaptor proteins to form a transport machine capable of long-distance processive movement along microtubules. However, it is unclear why dynein-1 moves poorly on its own or how it is activated by dynactin. Here, we present a cryoelectron microscopy structure of the complete 1.4-megadalton human dynein-1 complex in an inhibited state known as the phi-particle. We reveal the 3D structure of the cargo binding dynein tail and show how self-dimerization of the motor domains locks them in a conformation with low microtubule affinity. Disrupting motor dimerization with structure-based mutagenesis drives dynein-1 into an open form with higher affinity for both microtubules and dynactin. We find the open form is also inhibited for movement and that dynactin relieves this by reorienting the motor domains to interact correctly with microtubules. Our model explains how dynactin binding to the dynein-1 tail directly stimulates its motor activity. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_3706.map.gz emd_3706.map.gz | 9.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-3706-v30.xml emd-3706-v30.xml emd-3706.xml emd-3706.xml | 67.4 KB 67.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_3706_fsc.xml emd_3706_fsc.xml | 12.7 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_3706.png emd_3706.png | 124.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-3706.cif.gz emd-3706.cif.gz | 8.2 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3706 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3706 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3706 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3706 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5nw4MC  3698C  3703C  3704C  3705C  3707C  5nugC  5nvsC  5nvuC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_3706.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_3706.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | 3D reconstruction of DDB. Motor domains has The stable portion of the dynein tail is visible, whereas the motor domains are disordered. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 2.68 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Human cytoplasmic dynein-1 bound to dynactin and an N-terminal co...
+Supramolecule #1: Human cytoplasmic dynein-1 bound to dynactin and an N-terminal co...
+Supramolecule #2: dynein-1
+Supramolecule #3: dynactin
+Supramolecule #4: BICD2
+Macromolecule #1: dynein heavy chain
+Macromolecule #2: dynein intermediate chain
+Macromolecule #3: dynein intermediate chain
+Macromolecule #4: dynein heavy chain
+Macromolecule #5: dynein N-terminal dimerization domain
+Macromolecule #6: dynein N-terminal dimerization domain
+Macromolecule #7: Robl
+Macromolecule #8: dynein light intermediate chain
+Macromolecule #9: dynein light intermediate chain
+Macromolecule #10: Arp1
+Macromolecule #11: beta-actin
+Macromolecule #12: Arp11
+Macromolecule #13: Capping protein (Actin filament) muscle Z-line, alpha 1
+Macromolecule #14: F-actin capping protein beta subunit variant II
+Macromolecule #15: dynactin shoulder complex
+Macromolecule #16: dynactin shoulder complex
+Macromolecule #17: dynactin shoulder complex
+Macromolecule #18: dynactin shoulder complex
+Macromolecule #19: Dynactin 6
+Macromolecule #20: Dynactin subunit 5
+Macromolecule #21: dynactin pointed end p62
+Macromolecule #22: p150
+Macromolecule #23: Dynactin
+Macromolecule #24: Dynactin
+Macromolecule #25: Dynactin
+Macromolecule #26: Dynactin
+Macromolecule #27: dynactin p150
+Macromolecule #28: BICD2N
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 1.6 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)