+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 3j6c | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
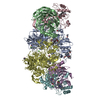
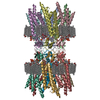
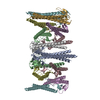
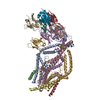
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of MAVS CARD filament | ||||||
 Components Components | Mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN / Innate immunity / helical filament | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of IP-10 production / regulation of peroxisome organization / positive regulation of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5 production / positive regulation of myeloid dendritic cell cytokine production / CARD domain binding / positive regulation of response to cytokine stimulus / NF-kB activation through FADD/RIP-1 pathway mediated by caspase-8 and -10 / protein localization to mitochondrion / positive regulation of type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway / peroxisomal membrane ...positive regulation of IP-10 production / regulation of peroxisome organization / positive regulation of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5 production / positive regulation of myeloid dendritic cell cytokine production / CARD domain binding / positive regulation of response to cytokine stimulus / NF-kB activation through FADD/RIP-1 pathway mediated by caspase-8 and -10 / protein localization to mitochondrion / positive regulation of type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway / peroxisomal membrane / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation / negative regulation of viral genome replication / type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway / cytoplasmic pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway / cellular response to exogenous dsRNA / positive regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome complex assembly / TRAF6 mediated NF-kB activation / positive regulation of interferon-alpha production / positive regulation of type I interferon production / ubiquitin ligase complex / positive regulation of defense response to virus by host / signaling adaptor activity / antiviral innate immune response / activation of innate immune response / protein serine/threonine kinase binding / positive regulation of interferon-beta production / positive regulation of interleukin-8 production / Negative regulators of DDX58/IFIH1 signaling / molecular condensate scaffold activity / PKR-mediated signaling / DDX58/IFIH1-mediated induction of interferon-alpha/beta / positive regulation of protein import into nucleus / Evasion by RSV of host interferon responses / positive regulation of interleukin-6 production / mitochondrial membrane / positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production / SARS-CoV-1 activates/modulates innate immune responses / Ovarian tumor domain proteases / TRAF3-dependent IRF activation pathway / protein-macromolecule adaptor activity / defense response to virus / DNA-binding transcription factor binding / molecular adaptor activity / mitochondrial outer membrane / positive regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / defense response to bacterium / intracellular signal transduction / innate immune response / protein kinase binding / SARS-CoV-2 activates/modulates innate and adaptive immune responses / signal transduction / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / mitochondrion / identical protein binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 9.6 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Xu, H. / He, X. / Zheng, H. / Huang, L.J. / Hou, F. / Yu, Z. / de la Cruz, M.J. / Borkowski, B. / Zhang, X. / Chen, Z.J. / Jiang, Q.-X. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2014 Journal: Elife / Year: 2014Title: Structural basis for the prion-like MAVS filaments in antiviral innate immunity. Authors: Hui Xu / Xiaojing He / Hui Zheng / Lily J Huang / Fajian Hou / Zhiheng Yu / Michael Jason de la Cruz / Brian Borkowski / Xuewu Zhang / Zhijian J Chen / Qiu-Xing Jiang /  Abstract: Mitochondrial antiviral signaling (MAVS) protein is required for innate immune responses against RNA viruses. In virus-infected cells MAVS forms prion-like aggregates to activate antiviral signaling ...Mitochondrial antiviral signaling (MAVS) protein is required for innate immune responses against RNA viruses. In virus-infected cells MAVS forms prion-like aggregates to activate antiviral signaling cascades, but the underlying structural mechanism is unknown. Here we report cryo-electron microscopic structures of the helical filaments formed by both the N-terminal caspase activation and recruitment domain (CARD) of MAVS and a truncated MAVS lacking part of the proline-rich region and the C-terminal transmembrane domain. Both structures are left-handed three-stranded helical filaments, revealing specific interfaces between individual CARD subunits that are dictated by electrostatic interactions between neighboring strands and hydrophobic interactions within each strand. Point mutations at multiple locations of these two interfaces impaired filament formation and antiviral signaling. Super-resolution imaging of virus-infected cells revealed rod-shaped MAVS clusters on mitochondria. These results elucidate the structural mechanism of MAVS polymerization, and explain how an α-helical domain uses distinct chemical interactions to form self-perpetuating filaments. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.01489.001. #1:  Journal: BMC Struct Biol / Year: 2008 Journal: BMC Struct Biol / Year: 2008Title: Crystal structure of human IPS-1/MAVS/VISA/Cardif caspase activation recruitment domain. Authors: Jane A Potter / Richard E Randall / Garry L Taylor /  Abstract: BACKGROUND: IPS-1/MAVS/VISA/Cardif is an adaptor protein that plays a crucial role in the induction of interferons in response to viral infection. In the initial stage of the intracellular antiviral ...BACKGROUND: IPS-1/MAVS/VISA/Cardif is an adaptor protein that plays a crucial role in the induction of interferons in response to viral infection. In the initial stage of the intracellular antiviral response two RNA helicases, retinoic acid inducible gene-I (RIG-I) and melanoma differentiation-association gene 5 (MDA5), are independently able to bind viral RNA in the cytoplasm. The 62 kDa protein IPS-1/MAVS/VISA/Cardif contains an N-terminal caspase activation and recruitment (CARD) domain that associates with the CARD regions of RIG-I and MDA5, ultimately leading to the induction of type I interferons. As a first step towards understanding the molecular basis of this important adaptor protein we have undertaken structural studies of the IPS-1 MAVS/VISA/Cardif CARD region. RESULTS: The crystal structure of human IPS-1/MAVS/VISA/Cardif CARD has been determined to 2.1A resolution. The protein was expressed and crystallized as a maltose-binding protein (MBP) fusion ...RESULTS: The crystal structure of human IPS-1/MAVS/VISA/Cardif CARD has been determined to 2.1A resolution. The protein was expressed and crystallized as a maltose-binding protein (MBP) fusion protein. The MBP and IPS-1 components each form a distinct domain within the structure. IPS-1/MAVS/VISA/Cardif CARD adopts a characteristic six-helix bundle with a Greek-key topology and, in common with a number of other known CARD structures, contains two major polar surfaces on opposite sides of the molecule. One face has a surface-exposed, disordered tryptophan residue that may explain the poor solubility of untagged expression constructs. CONCLUSION: The IPS-1/MAVS/VISA/Cardif CARD domain adopts the classic CARD fold with an asymmetric surface charge distribution that is typical of CARD domains involved in homotypic protein-protein ...CONCLUSION: The IPS-1/MAVS/VISA/Cardif CARD domain adopts the classic CARD fold with an asymmetric surface charge distribution that is typical of CARD domains involved in homotypic protein-protein interactions. The location of the two polar areas on IPS-1/MAVS/VISA/Cardif CARD suggest possible types of associations that this domain makes with the two CARD domains of MDA5 or RIG-I. The N-terminal CARD domains of RIG-I and MDA5 share greatest sequence similarity with IPS-1/MAVS/VISA/Cardif CARD and this has allowed modelling of their structures. These models show a very different charge profile for the equivalent surfaces compared to IPS-1/MAVS/VISA/Cardif CARD. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  3j6c.cif.gz 3j6c.cif.gz | 31.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb3j6c.ent.gz pdb3j6c.ent.gz | 20.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  3j6c.json.gz 3j6c.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j6/3j6c https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j6/3j6c ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j6/3j6c ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j6/3j6c | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5890MC  5891C  4o9fC  4o9lC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10014 (Title: MAVS CARD and DeltaProTM filaments / Data size: 35.3 / Data #1: CARD set1 micrographs [micrographs - single frame] / Data #2: CARD set2 micrographs [micrographs - single frame] / Data #3: CARD set3 micrographs [micrographs - single frame] / Data #4: CARD set4 micrographs [micrographs - single frame] EMPIAR-10014 (Title: MAVS CARD and DeltaProTM filaments / Data size: 35.3 / Data #1: CARD set1 micrographs [micrographs - single frame] / Data #2: CARD set2 micrographs [micrographs - single frame] / Data #3: CARD set3 micrographs [micrographs - single frame] / Data #4: CARD set4 micrographs [micrographs - single frame]Data #5: CARD set1 segments [picked particles - multiframe - unprocessed] Data #6: CARD set2 segments [picked particles - multiframe - unprocessed] Data #7: CARD set3 segments [picked particles - multiframe - unprocessed] Data #8: CARD set4 segments [picked particles - multiframe - unprocessed] Data #9: DeltProTM micrographs [micrographs - single frame] Data #10: DeltaProTM segments [picked particles - multiframe - unprocessed]) |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | x 24
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 | 
|
| Symmetry | Helical symmetry: (Circular symmetry: 3 / Dyad axis: no / N subunits divisor: 1 / Num. of operations: 24 / Rise per n subunits: 16.8 Å / Rotation per n subunits: -53.6 °) |
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 10826.325 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Fragment: caspase activation recruitment domain (UNP residues 3-93) Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MAVS, IPS1, KIAA1271, VISA / Plasmid: pcDNA3 / Cell line (production host): HEK293T / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MAVS, IPS1, KIAA1271, VISA / Plasmid: pcDNA3 / Cell line (production host): HEK293T / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q7Z434 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q7Z434 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: MAVS CARD filament / Type: COMPLEX / Details: polymer |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.546 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Buffer solution | Name: 20 mM Tris-HCl, 50 mM NaCl, 1 mM DTT / pH: 7.5 / Details: 20 mM Tris-HCl, 50 mM NaCl, 1 mM DTT |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Details: Quantifoil grids coated with thin carbon on top |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Details: Plunged into liquid ethane (FEI VITROBOT MARK III) |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: JEOL 2200FS / Date: Oct 20, 2011 |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 60000 X / Calibrated magnification: 61950 X / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs: 2 mm Astigmatism: Objective lens astigmatism was corrected at 100,000x magnification Camera length: 0 mm |
| Specimen holder | Specimen holder model: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN / Tilt angle max: 0 ° / Tilt angle min: 0 ° |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 20 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: FEI / Energyfilter upper: 35 eV / Energyfilter lower: 0 eV |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Relative weight: 1 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: Each filament segment | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: 53.6 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 16.8 Å / Axial symmetry: C3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Method: IHRSR / Resolution: 9.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Nominal pixel size: 2.333 Å / Actual pixel size: 2.333 Å Details: Final data were calculated from three separate datasets from three sessions of data collection. The handedness of the map was determined by cryo-electron tomography (Helical Details: IHRSR). Symmetry type: HELICAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL Details: REFINEMENT PROTOCOL--rigid body DETAILS--The docking of one X-ray model into a segmented map corresponding to one subunit was first done manually in Chimera, and then optimized using SITUS. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 2VGQ Pdb chain-ID: A / Accession code: 2VGQ / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj









