+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6nmi | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
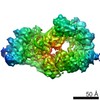
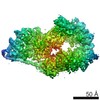
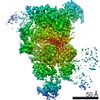
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the human TFIIH core complex | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION / DNA repair / helicase / multiprotein complex | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationMMXD complex / core TFIIH complex portion of holo TFIIH complex / Cytosolic iron-sulfur cluster assembly / central nervous system myelin formation / positive regulation of mitotic recombination / hair cell differentiation / hair follicle maturation / nucleotide-excision repair factor 3 complex / nucleotide-excision repair, preincision complex assembly / ventricular system development ...MMXD complex / core TFIIH complex portion of holo TFIIH complex / Cytosolic iron-sulfur cluster assembly / central nervous system myelin formation / positive regulation of mitotic recombination / hair cell differentiation / hair follicle maturation / nucleotide-excision repair factor 3 complex / nucleotide-excision repair, preincision complex assembly / ventricular system development / transcription factor TFIIK complex / CAK-ERCC2 complex / embryonic cleavage / UV protection / regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / DNA 5'-3' helicase / adult heart development / transcription factor TFIIH core complex / transcription factor TFIIH holo complex / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / G protein-coupled receptor internalization / nuclear thyroid hormone receptor binding / transcription preinitiation complex / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Termination / transcription factor TFIID complex / regulation of mitotic cell cycle phase transition / RNA polymerase II general transcription initiation factor activity / erythrocyte maturation / hematopoietic stem cell proliferation / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE during HIV infection / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE / spinal cord development / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex / Formation of the HIV-1 Early Elongation Complex / mRNA Capping / bone mineralization / HIV Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II HIV Promoter Escape / Transcription of the HIV genome / RNA Polymerase II Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Pre-Initiation And Promoter Opening / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation And Promoter Clearance / DNA 3'-5' helicase / 3'-5' DNA helicase activity / ATPase activator activity / DNA topological change / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / embryonic organ development / hematopoietic stem cell differentiation / Tat-mediated elongation of the HIV-1 transcript / Formation of HIV-1 elongation complex containing HIV-1 Tat / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase I / Cyclin E associated events during G1/S transition / Formation of HIV elongation complex in the absence of HIV Tat / Cyclin A:Cdk2-associated events at S phase entry / response to UV / Cyclin A/B1/B2 associated events during G2/M transition / cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex / transcription by RNA polymerase I / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Elongation / Formation of RNA Pol II elongation complex / transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair / hormone-mediated signaling pathway / extracellular matrix organization / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events / positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation / insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway / DNA helicase activity / determination of adult lifespan / post-embryonic development / maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / nucleotide-excision repair / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase II promoter / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / chromosome segregation / promoter-specific chromatin binding / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / cellular response to gamma radiation / response to calcium ion / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / multicellular organism growth / Dual Incision in GG-NER / Transcription-Coupled Nucleotide Excision Repair (TC-NER) / spindle / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / Formation of Incision Complex in GG-NER / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / Cyclin D associated events in G1 / intracellular protein localization / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding / response to oxidative stress / double-stranded DNA binding / 5'-3' DNA helicase activity Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Greber, B.J. / Toso, D. / Fang, J. / Nogales, E. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, United States,  Switzerland, 4items Switzerland, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2019 Journal: Elife / Year: 2019Title: The complete structure of the human TFIIH core complex. Authors: Basil J Greber / Daniel B Toso / Jie Fang / Eva Nogales /  Abstract: Transcription factor IIH (TFIIH) is a heterodecameric protein complex critical for transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II and nucleotide excision DNA repair. The TFIIH core complex is ...Transcription factor IIH (TFIIH) is a heterodecameric protein complex critical for transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II and nucleotide excision DNA repair. The TFIIH core complex is sufficient for its repair functions and harbors the XPB and XPD DNA-dependent ATPase/helicase subunits, which are affected by human disease mutations. Transcription initiation additionally requires the CdK activating kinase subcomplex. Previous structural work has provided only partial insight into the architecture of TFIIH and its interactions within transcription pre-initiation complexes. Here, we present the complete structure of the human TFIIH core complex, determined by phase-plate cryo-electron microscopy at 3.7 Å resolution. The structure uncovers the molecular basis of TFIIH assembly, revealing how the recruitment of XPB by p52 depends on a pseudo-symmetric dimer of homologous domains in these two proteins. The structure also suggests a function for p62 in the regulation of XPD, and allows the mapping of previously unresolved human disease mutations. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6nmi.cif.gz 6nmi.cif.gz | 558.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6nmi.ent.gz pdb6nmi.ent.gz | 445.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6nmi.json.gz 6nmi.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nm/6nmi https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nm/6nmi ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nm/6nmi ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nm/6nmi | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 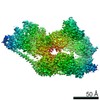 0452MC 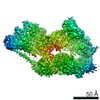 0587C  0588C  0589C  0602C  0603C  0604C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10430 (Title: Phase-plate cryo-EM of human TFIIH / Data size: 9.2 TB EMPIAR-10430 (Title: Phase-plate cryo-EM of human TFIIH / Data size: 9.2 TBData #1: Unaligned movies of human TFIIH, using the Volta phase plate, dataset 1 [micrographs - multiframe] Data #2: Unaligned movies of human TFIIH, using the Volta phase plate, dataset 2 [micrographs - multiframe] Data #3: Unaligned movies of human TFIIH, using the Volta phase plate, dataset 3 [micrographs - multiframe] Data #4: Unaligned movies of human TFIIH, using the Volta phase plate, dataset 4 [micrographs - multiframe] Data #5: Unaligned movies of human TFIIH, using the Volta phase plate, dataset 5 [micrographs - multiframe] Data #6: Unaligned movies of human TFIIH, using the Volta phase plate, dataset 6 [micrographs - multiframe]) |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-General transcription and DNA repair factor IIH helicase subunit ... , 2 types, 2 molecules AB
| #1: Protein | Mass: 74233.492 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: HeLa / References: UniProt: P19447*PLUS, DNA helicase Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: HeLa / References: UniProt: P19447*PLUS, DNA helicase |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 86417.766 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: HeLa / References: UniProt: P18074*PLUS Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: HeLa / References: UniProt: P18074*PLUS |
-General transcription factor IIH subunit ... , 5 types, 5 molecules CDEFG
| #3: Protein | Mass: 57789.000 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: HeLa / References: UniProt: P32780*PLUS Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: HeLa / References: UniProt: P32780*PLUS |
|---|---|
| #4: Protein | Mass: 52245.156 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: HeLa / References: UniProt: Q92759 Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: HeLa / References: UniProt: Q92759 |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 39609.098 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: HeLa / References: UniProt: Q13888*PLUS Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: HeLa / References: UniProt: Q13888*PLUS |
| #6: Protein | Mass: 34416.008 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: HeLa / References: UniProt: Q13889 Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: HeLa / References: UniProt: Q13889 |
| #7: Protein | Mass: 8060.362 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: HeLa / References: UniProt: Q6ZYL4 Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: HeLa / References: UniProt: Q6ZYL4 |
-Protein , 1 types, 1 molecules H
| #8: Protein | Mass: 35873.965 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: HeLa / References: UniProt: P51948 Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: HeLa / References: UniProt: P51948 |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 7 molecules 


| #9: Chemical | ChemComp-SF4 / |
|---|---|
| #10: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / |
-Details
| Has protein modification | Y |
|---|---|
| Sequence details | The full sequence for General transcription factor IIH subunit 1, p62 ...The full sequence for General transcription factor IIH subunit 1, p62 MATSSEEVLL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 UCSF Chimera
UCSF Chimera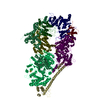

 PDBj
PDBj



















