+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structure of the human TIP60-C histone exchange and acetyltransferase complex. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 635, Issue 8039, Page 764-769, Year 2024 |
| Publish date | Sep 11, 2024 |
 Authors Authors | Changqing Li / Ekaterina Smirnova / Charlotte Schnitzler / Corinne Crucifix / Jean Paul Concordet / Alice Brion / Arnaud Poterszman / Patrick Schultz / Gabor Papai / Adam Ben-Shem /  |
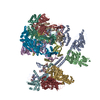
| PubMed Abstract | Chromatin structure is a key regulator of DNA transcription, replication and repair. In humans, the TIP60-EP400 complex (TIP60-C) is a 20-subunit assembly that affects chromatin structure through two ...Chromatin structure is a key regulator of DNA transcription, replication and repair. In humans, the TIP60-EP400 complex (TIP60-C) is a 20-subunit assembly that affects chromatin structure through two enzymatic activities: ATP-dependent exchange of histone H2A-H2B for H2A.Z-H2B, and histone acetylation. In yeast, however, these activities are performed by two independent complexes-SWR1 and NuA4, respectively. How the activities of the two complexes are merged into one supercomplex in humans, and what this association entails for the structure and mechanism of the proteins and their recruitment to chromatin, are unknown. Here we describe the structure of the endogenous human TIP60-C. We find a three-lobed architecture composed of SWR1-like (SWR1L) and NuA4-like (NuA4L) parts, which associate with a TRRAP activator-binding module. The huge EP400 subunit contains the ATPase motor, traverses the junction between SWR1L and NuA4L twice and constitutes the scaffold of the three-lobed architecture. NuA4L is completely rearranged compared with its yeast counterpart. TRRAP is flexibly tethered to NuA4L-in stark contrast to its robust connection to the completely opposite side of NuA4 in yeast. A modelled nucleosome bound to SWR1L, supported by tests of TIP60-C activity, suggests that some aspects of the histone exchange mechanism diverge from what is seen in yeast. Furthermore, a fixed actin module (as opposed to the mobile actin subcomplex in SWR1; ref. ), the flexibility of TRRAP and the weak effect of extranucleosomal DNA on exchange activity lead to a different, activator-based mode of enlisting TIP60-C to chromatin. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:39260417 / PubMed:39260417 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.4 - 6.2 Å |
| Structure data |  EMDB-18581: Human Tip60 complex  EMDB-18591: Human Tip60 complex locally refined on RUVBL1/2  EMDB-18597: Human Tip60 complex locally refined on ACTIN and the ATPase domain of EP400  EMDB-18598: Tip60 complex locally refined on ARP domain EMDB-18611, PDB-8qr1:  EMDB-18612: Structure of TRRAP and EP400 in the human Tip 60 complex  EMDB-18613: TRRAP in human Tip60 complex locally refined 1  EMDB-18618: TRRAP in human Tip60 complex locally refined 2 EMDB-18619: TRRAP and EP400 in the human Tip60 complex - composite map  EMDB-18794: Human Tip60 complex with bound H2A.Z/H2B |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION / Eukaryotic transcription / Histone acetyltransferase / chromatin remodeling / Complex |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers





 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)