+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Human Tip60 complex | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Overall structure | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Eukaryotic transcription / Histone acetyltransferase / chromatin remodeling / Complex / TRANSCRIPTION | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpiccolo histone acetyltransferase complex / promoter-enhancer loop anchoring activity / telomerase RNA localization to Cajal body / sperm DNA condensation / regulation of DNA strand elongation / positive regulation of telomere maintenance in response to DNA damage / histone chaperone activity / positive regulation of norepinephrine uptake / Regulation of CDH1 Function / establishment of protein localization to chromatin ...piccolo histone acetyltransferase complex / promoter-enhancer loop anchoring activity / telomerase RNA localization to Cajal body / sperm DNA condensation / regulation of DNA strand elongation / positive regulation of telomere maintenance in response to DNA damage / histone chaperone activity / positive regulation of norepinephrine uptake / Regulation of CDH1 Function / establishment of protein localization to chromatin / Formation of the polybromo-BAF (pBAF) complex / Formation of the non-canonical BAF (ncBAF) complex / Formation of the canonical BAF (cBAF) complex / Formation of the embryonic stem cell BAF (esBAF) complex / Formation of neuronal progenitor and neuronal BAF (npBAF and nBAF) / R2TP complex / dynein axonemal particle / bBAF complex / cellular response to cytochalasin B / neural retina development / npBAF complex / nBAF complex / brahma complex / regulation of transepithelial transport / RPAP3/R2TP/prefoldin-like complex / Swr1 complex / morphogenesis of a polarized epithelium / Formation of annular gap junctions / Formation of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC) / structural constituent of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / GBAF complex / Gap junction degradation / Folding of actin by CCT/TriC / regulation of G0 to G1 transition / Cell-extracellular matrix interactions / protein localization to adherens junction / protein antigen binding / dense body / Tat protein binding / postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / Ino80 complex / Prefoldin mediated transfer of substrate to CCT/TriC / RSC-type complex / blastocyst formation / regulation of double-strand break repair / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / Adherens junctions interactions / chromatin-protein adaptor activity / RHOF GTPase cycle / adherens junction assembly / box C/D snoRNP assembly / apical protein localization / Sensory processing of sound by inner hair cells of the cochlea / Sensory processing of sound by outer hair cells of the cochlea / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / tight junction / regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / SWI/SNF complex / positive regulation of T cell differentiation / Formation of Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci (SAHF) / apical junction complex / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / spinal cord development / negative regulation of gene expression, epigenetic / maintenance of blood-brain barrier / regulation of norepinephrine uptake / regulation of chromosome organization / transporter regulator activity / nitric-oxide synthase binding / Transcriptional Regulation by E2F6 / cortical cytoskeleton / positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance / NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / RUNX1 interacts with co-factors whose precise effect on RUNX1 targets is not known / Recycling pathway of L1 / TFIID-class transcription factor complex binding / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in pigmentation / regulation of DNA replication / MLL1 complex / brush border / regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / regulation of embryonic development / somatic stem cell population maintenance / EPH-ephrin mediated repulsion of cells / Telomere Extension By Telomerase / negative regulation of cell differentiation / spermatid development / protein folding chaperone complex / kinesin binding / enzyme-substrate adaptor activity / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / positive regulation of myoblast differentiation / RNA polymerase II core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / regulation of DNA repair / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / EPHB-mediated forward signaling Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.52 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Li C / Smirnova E / Schnitzler C / Crucifix C / Concordet JP / Brion A / Poterszman A / Schultz P / Papai G / Ben-Shem A | |||||||||
| Funding support |  France, 1 items France, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: Structure of the human TIP60-C histone exchange and acetyltransferase complex. Authors: Changqing Li / Ekaterina Smirnova / Charlotte Schnitzler / Corinne Crucifix / Jean Paul Concordet / Alice Brion / Arnaud Poterszman / Patrick Schultz / Gabor Papai / Adam Ben-Shem /  Abstract: Chromatin structure is a key regulator of DNA transcription, replication and repair. In humans, the TIP60-EP400 complex (TIP60-C) is a 20-subunit assembly that affects chromatin structure through two ...Chromatin structure is a key regulator of DNA transcription, replication and repair. In humans, the TIP60-EP400 complex (TIP60-C) is a 20-subunit assembly that affects chromatin structure through two enzymatic activities: ATP-dependent exchange of histone H2A-H2B for H2A.Z-H2B, and histone acetylation. In yeast, however, these activities are performed by two independent complexes-SWR1 and NuA4, respectively. How the activities of the two complexes are merged into one supercomplex in humans, and what this association entails for the structure and mechanism of the proteins and their recruitment to chromatin, are unknown. Here we describe the structure of the endogenous human TIP60-C. We find a three-lobed architecture composed of SWR1-like (SWR1L) and NuA4-like (NuA4L) parts, which associate with a TRRAP activator-binding module. The huge EP400 subunit contains the ATPase motor, traverses the junction between SWR1L and NuA4L twice and constitutes the scaffold of the three-lobed architecture. NuA4L is completely rearranged compared with its yeast counterpart. TRRAP is flexibly tethered to NuA4L-in stark contrast to its robust connection to the completely opposite side of NuA4 in yeast. A modelled nucleosome bound to SWR1L, supported by tests of TIP60-C activity, suggests that some aspects of the histone exchange mechanism diverge from what is seen in yeast. Furthermore, a fixed actin module (as opposed to the mobile actin subcomplex in SWR1; ref. ), the flexibility of TRRAP and the weak effect of extranucleosomal DNA on exchange activity lead to a different, activator-based mode of enlisting TIP60-C to chromatin. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_18581.map.gz emd_18581.map.gz | 616.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-18581-v30.xml emd-18581-v30.xml emd-18581.xml emd-18581.xml | 27 KB 27 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_18581_fsc.xml emd_18581_fsc.xml | 22.7 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_18581.png emd_18581.png | 78.8 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_18581_msk_1.map emd_18581_msk_1.map | 1.2 GB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-18581.cif.gz emd-18581.cif.gz | 9.2 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_18581_half_map_1.map.gz emd_18581_half_map_1.map.gz emd_18581_half_map_2.map.gz emd_18581_half_map_2.map.gz | 1.1 GB 1.1 GB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18581 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18581 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18581 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18581 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 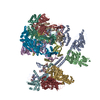 8qr1C  8qriC C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_18581.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 1.2 GB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_18581.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 1.2 GB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Overall structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.73 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_18581_msk_1.map emd_18581_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map A
| File | emd_18581_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map B
| File | emd_18581_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Tip60 complex
| Entire | Name: Tip60 complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Tip60 complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Tip60 complex / type: cell / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Strain: K562 Homo sapiens (human) / Strain: K562 |
-Macromolecule #1: EP400
| Macromolecule | Name: EP400 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MHHGTGPQNV QHQLQRSRAC PGSEGEEQPA HPNPPPSPAA PFAPSASPSA PQSPSYQIQQ LMNRSPATG QNVNITLQSV GPVVGGNQQI TLAPLPLPSP TSPGFQFSAQ PRRFEHGSPS Y IQVTSPLS QQVQTQSPTQ PSPGPGQALQ NVRAGAPGPG LGLCSSSPTG ...String: MHHGTGPQNV QHQLQRSRAC PGSEGEEQPA HPNPPPSPAA PFAPSASPSA PQSPSYQIQQ LMNRSPATG QNVNITLQSV GPVVGGNQQI TLAPLPLPSP TSPGFQFSAQ PRRFEHGSPS Y IQVTSPLS QQVQTQSPTQ PSPGPGQALQ NVRAGAPGPG LGLCSSSPTG GFVDASVLVR QI SLSPSSG GHFVFQDGSG LTQIAQGAQV QLQHPGTPIT VRERRPSQPH TQSGGTIHHL GPQ SPAAAG GAGLQPLASP SHITTANLPP QISSIIQGQL VQQQQVLQGP PLPRPLGFER TPGV LLPGA GGAAGFGMTS PPPPTSPSRT AVPPGLSSLP LTSVGNTGMK KVPKKLEEIP PASPE MAQM RKQCLDYHYQ EMQALKEVFK EYLIELFFLQ HFQGNMMDFL AFKKKHYAPL QAYLRQ NDL DIEEEEEEEE EEEEKSEVIN DEVKVVTGKD GQTGTPVAIA TQLPPKVSAA FSSQQQP FQ QALAGSLVAG AGSTVETDLF KRQQAMPSTG MAEQSKRPRL EVGHQGVVFQ HPGADAGV P LQQLMPTAQG GMPPTPQAAQ LAGQRQSQQQ YDPSTGPPVQ NAASLHTPLP QLPGRLPPA GVPTAALSSA LQFAQQPQVV EAQTQLQIPV KTQQPNVPIP APPSSQLPIP PSQPAQLALH VPTPGKVQV QASQLSSLPQ MVASTRLPVD PAPPCPRPLP TSSTSSLAPV SGSGPGPSPA R SSPVNRPS SATNKALSPV TSRTPGVVAS APTKPQSPAQ NATSSQDSSQ DTLTEQITLE NQ VHQRIAE LRKAGLWSQR RLPKLQEAPR PKSHWDYLLE EMQWMATDFA QERRWKVAAA KKL VRTVVR HHEEKQLREE RGKKEEQSRL RRIAASTARE IECFWSNIEQ VVEIKLRVEL EEKR KKALN LQKVSRRGKE LRPKGFDALQ ESSLDSGMSG RKRKASISLT DDEVDDEEET IEEEE ANEG VVDHQTELSN LAKEAELPLL DLMKLYEGAF LPSSQWPRPK PDGEDTSGEE DADDCP GDR ESRKDLVLID SLFIMDQFKA AERMNIGKPN AKDIADVTAV AEAILPKGSA RVTTSVK FN APSLLYGALR DYQKIGLDWL AKLYRKNLNG ILADEAGLGK TVQIIAFFAH LACNEGNW G PHLVVVRSCN ILKWELELKR WCPGLKILSY IGSHRELKAK RQEWAEPNSF HVCITSYTQ FFRGLTAFTR VRWKCLVIDE MQRVKGMTER HWEAVFTLQS QQRLLLIDSP LHNTFLELWT MVHFLVPGI SRPYLSSPLR APSEESQDYY HKVVIRLHRV TQPFILRRTK RDVEKQLTKK Y EHVLKCRL SNRQKALYED VILQPGTQEA LKSGHFVNVL SILVRLQRIC NHPGLVEPRH PG SSYVAGP LEYPSASLIL KALERDFWKE ADLSMFDLIG LENKITRHEA ELLSKKKIPR KLM EEISTS AAPAARPAAA KLKASRLFQP VQYGQKPEGR TVAFPSTHPP RTAAPTTASA APQG PLRGR PPIATFSANP EAKAAAAPFQ TSQASASAPR HQPASASSTA ASPAHPAKLR AQTTA QAST PGQPPPQPQA PSHAAGQSAL PQRLVLPSQA QARLPSGEVV KIAQLASITG PQSRVA QPE TPVTLQFQGS KFTLSHSQLR QLTAGQPLQL QGSVLQIVSA PGQPYLRAPG PVVMQTV SQ AGAVHGALGS KPPAGGPSPA PLTPQVGVPG RVAVNALAVG EPGTASKPAS PIGGPTQE E KTRLLKERLD QIYLVNERRC SQAPVYGRDL LRICALPSHG RVQWRGSLDG RRGKEAGPA HSYTSSSESP SELMLTLCRC GESLQDVIDR VAFVIPPVVA APPSLRVPRP PPLYSHRMRI LRQGLREHA APYFQQLRQT TAPRLLQFPE LRLVQFDSGK LEALAILLQK LKSEGRRVLI L SQMILMLD ILEMFLNFHY LTYVRIDENA SSEQRQELMR SFNRDRRIFC AILSTHSRTT GI NLVEADT VVFYDNDLNP VMDAKAQEWC DRIGRCKDIH IYRLVSGNSI EEKLLKNGTK DLI REVAAQ GNDYSMAFLT QRTIQELFEV YSPMDDAGFP VKAEEFVVLS QEPSVTETIA PKIA RPFIE ALKSIEYLEE DAQKSAQEGV LGPHTDALSS DSENMPCDEE PSQLEELADF MEQLT PIEK YALNYLELFH TSIEQEKERN SEDAVMTAVR AWEFWNLKTL QEREARLRLE QEEAEL LTY TREDAYSMEY VYEDVDGQTE VMPLWTPPTP PQDDSDIYLD SVMCLMYEAT PIPEAKL PP VYVRKERKRH KTDPSAAGRK KKQRHGEAVV PPRSLFDRAT PGLLKIRREG KEQKKNIL L KQQVPFAKPL PTFAKPTAEP GQDNPEWLIS EDWALLQAVK QLLELPLNLT IVSPAHTPN WDLVSDVVNS CSRIYRSSKQ CRNRYENVII PREEGKSKNN RPLRTSQIYA QDENATHTQL YTSHFDLMK MTAGKRSPPI KPLLGMNPFQ KNPKHASVLA ESGINYDKPL PPIQVASLRA E RIAKEKKA LADQQKAQQP AVAQPPPPQP QPPPPPQQPP PPLPQPQAAG SQPPAGPPAV QP QPQPQPQ TQPQPVQAPA KAQPAITTGG SAAVLAGTIK TSVTGTSMPT GAVSGNVIVN TIA GVPAAT FQSINKRLAS PVAPGALTTP GGSAPAQVVH TQPPPRAVGS PATATPDLVS MATT QGVRA VTSVTASAVV TTNLTPVQTP ARSLVPQVSQ ATGVQLPGKT ITPAHFQLLR QQQQQ QQQQ QQQQQQQQQQ QQQQQQQQQQ TTTTSQVQVP QIQGQAQSPA QIKAVGKLTP EHLIKM QKQ KLQMPPQPPP PQAQSAPPQP TAQVQVQTSQ PPQQQSPQLT TVTAPRPGAL LTGTTVA NL QVARLTRVPT SQLQAQGQMQ TQAPQPAQVA LAKPPVVSVP AAVVSSPGVT TLPMNVAG I SVAIGQPQKA AGQTVVAQPV HMQQLLKLKQ QAVQQQKAIQ PQAAQGPAAV QQKITAQQI TTPGAQQKVA YAAQPALKTQ FLTTPISQAQ KLAGAQQVQT QIQVAKLPQV VQQQTPVASI QQVASASQQ ASPQTVALTQ ATAAGQQVQM IPAVTATAQV VQQKLIQQQV VTTASAPLQT P GAPNPAQV PASSDSPSQQ PKLQMRVPAV RLKTPTKPPC Q UniProtKB: E1A-binding protein p400 |
-Macromolecule #2: EPC1
| Macromolecule | Name: EPC1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MSKLSFRARA LDASKPLPVF RCEDLPDLHE YASINRAVPQ MPTGMEKEEE SEHHLQRAIS AQQVYGEKRD NMVIPVPEAE SNIAYYESIY PGEFKMPKQL IHIQPFSLDA EQPDYDLDSE DEVFVNKLKK KMDICPLQFE EMIDRLEKGS GQQPVSLQEA KLLLKEDDEL ...String: MSKLSFRARA LDASKPLPVF RCEDLPDLHE YASINRAVPQ MPTGMEKEEE SEHHLQRAIS AQQVYGEKRD NMVIPVPEAE SNIAYYESIY PGEFKMPKQL IHIQPFSLDA EQPDYDLDSE DEVFVNKLKK KMDICPLQFE EMIDRLEKGS GQQPVSLQEA KLLLKEDDEL IREVYEYWIK KRKNCRGPSL IPSVKQEKRD GSSTNDPYVA FRRRTEKMQT RKNRKNDEAS YEKMLKLRRD LSRAVTILEM IKRREKSKRE LLHLTLEIME KRYNLGDYNG EIMSEVMAQR QPMKPTYAIP IIPITNSSQF KHQEAMDVKE FKVNKQDKAD LIRPKRKYEK KPKVLPSSAA ATPQQTSPAA LPVFNAKDLN QYDFPSSDEE PLSQVLSGSS EAEEDNDPDG PFAFRRKAGC QYYAPHLDQT GNWPWTSPKD GGLGDVRYRY CLTTLTVPQR CIGFARRRVG RGGRVLLDRA HSDYDSVFHH LDLEMLSSPQ HSPVNQFANT SETNTSDKSF SKDLSQILVN IKSCRWRHFR PRTPSLHDSD NDELSCRKLY RSINRTGTAQ PGTQTCSTST QSKSSSGSAH FAFTAEQYQQ HQQQLALMQK QQLAQIQQQQ ANSNSSTNTS QNLASNQQKS GFRLNIQGLE RTLQGFVSKT LDSASAQFAA SALVTSEQLM GFKMKDDVVL GIGVNGVLPA SGVYKGLHLS STTPTALVHT SPSTAGSALL QPSNITQTSS SHSALSHQVT AANSATTQVL IGNNIRLTVP SSVATVNSIA PINARHIPRT LSAVPSSALK LAAAANCQVS KVPSSSSVDS VPRENHESEK PALNNIADNT VAMEVT UniProtKB: Enhancer of polycomb homolog 1 |
-Macromolecule #3: VPS72
| Macromolecule | Name: VPS72 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MSLAGGRAPR KTAGNRLSGL LEAEEEDEFY QTTYGGFTEE SGDDEYQGDQ SDTEDEVDSD FDIDEGDEPS SDGEAEEPRR KRRVVTKAYK EPLKSLRPRK VNTPAGSSQK AREEKALLPL ELQDDGSDSR KSMRQSTAEH TRQTFLRVQE RQGQSRRRKG PHCERPLTQE ...String: MSLAGGRAPR KTAGNRLSGL LEAEEEDEFY QTTYGGFTEE SGDDEYQGDQ SDTEDEVDSD FDIDEGDEPS SDGEAEEPRR KRRVVTKAYK EPLKSLRPRK VNTPAGSSQK AREEKALLPL ELQDDGSDSR KSMRQSTAEH TRQTFLRVQE RQGQSRRRKG PHCERPLTQE ELLREAKITE ELNLRSLETY ERLEADKKKQ VHKKRKCPGP IITYHSVTVP LVGEPGPKEE NVDIEGLDPA PSVSALTPHA GTGPVNPPAR CSRTFITFSD DATFEEWFPQ GRPPKVPVRE VCPVTHRPAL YRDPVTDIPY ATARAFKIIR EAYKKYITAH GLPPTASALG PGPPPPEPLP GSGPRALRQK IVIK UniProtKB: Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 72 homolog |
-Macromolecule #4: DMAP1
| Macromolecule | Name: DMAP1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MATGADVRDI LELGGPEGDA ASGTISKKDI INPDKKKSKK SSETLTFKRP EGMHREVYAL LYSDKKDAPP LLPSDTGQGY RTVKAKLGSK KVRPWKWMPF TNPARKDGAM FFHWRRAAEE GKDYPFARFN KTVQVPVYSE QEYQLYLHDD AWTKAETDHL FDLSRRFDLR ...String: MATGADVRDI LELGGPEGDA ASGTISKKDI INPDKKKSKK SSETLTFKRP EGMHREVYAL LYSDKKDAPP LLPSDTGQGY RTVKAKLGSK KVRPWKWMPF TNPARKDGAM FFHWRRAAEE GKDYPFARFN KTVQVPVYSE QEYQLYLHDD AWTKAETDHL FDLSRRFDLR FVVIHDRYDH QQFKKRSVED LKERYYHICA KLANVRAVPG TDLKIPVFDA GHERRRKEQL ERLYNRTPEQ VAEEEYLLQE LRKIEARKKE REKRSQDLQK LITAADTTAE QRRTERKAPK KKLPQKKEAE KPAVPETAGI KFPDFKSAGV TLRSQRMKLP SSVGQKKIKA LEQMLLELGV ELSPTPTEEL VHMFNELRSD LVLLYELKQA CANCEYELQM LRHRHEALAR AGVLGGPATP ASGPGPASAE PAVTEPGLGP DPKDTIIDVV GAPLTPNSRK RRESASSSSS VKKAKKP UniProtKB: DNA methyltransferase 1-associated protein 1 |
-Macromolecule #5: ACL6A
| Macromolecule | Name: ACL6A / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MSGGVYGGDE VGALVFDIGS YTVRAGYAGE DCPKVDFPTA IGMVVERDDG STLMEIDGDK GKQGGPTYYI DTNALRVPRE NMEAISPLKN GMVEDWDSFQ AILDHTYKMH VKSEASLHPV LMSEAPWNTR AKREKLTELM FEHYNIPAFF LCKTAVLTAF ANGRSTGLIL ...String: MSGGVYGGDE VGALVFDIGS YTVRAGYAGE DCPKVDFPTA IGMVVERDDG STLMEIDGDK GKQGGPTYYI DTNALRVPRE NMEAISPLKN GMVEDWDSFQ AILDHTYKMH VKSEASLHPV LMSEAPWNTR AKREKLTELM FEHYNIPAFF LCKTAVLTAF ANGRSTGLIL DSGATHTTAI PVHDGYVLQQ GIVKSPLAGD FITMQCRELF QEMNIELVPP YMIASKEAVR EGSPANWKRK EKLPQVTRSW HNYMCNCVIQ DFQASVLQVS DSTYDEQVAA QMPTVHYEFP NGYNCDFGAE RLKIPEGLFD PSNVKGLSGN TMLGVSHVVT TSVGMCDIDI RPGLYGSVIV AGGNTLIQSF TDRLNRELSQ KTPPSMRLKL IANNTTVERR FSSWIGGSIL ASLGTFQQMW ISKQEYEEGG KQCVERKCP UniProtKB: Actin-like protein 6A |
-Macromolecule #6: ACTIN
| Macromolecule | Name: ACTIN / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MDDDIAALVV DNGSGMCKAG FAGDDAPRAV FPSIVGRPRH QGVMVGMGQK DSYVGDEAQS KRGILTLKYP IEHGIVTNWD DMEKIWHHTF YNELRVAPEE HPVLLTEAPL NPKANREKMT QIMFETFNTP AMYVAIQAVL SLYASGRTTG IVMDSGDGVT HTVPIYEGYA ...String: MDDDIAALVV DNGSGMCKAG FAGDDAPRAV FPSIVGRPRH QGVMVGMGQK DSYVGDEAQS KRGILTLKYP IEHGIVTNWD DMEKIWHHTF YNELRVAPEE HPVLLTEAPL NPKANREKMT QIMFETFNTP AMYVAIQAVL SLYASGRTTG IVMDSGDGVT HTVPIYEGYA LPHAILRLDL AGRDLTDYLM KILTERGYSF TTTAEREIVR DIKEKLCYVA LDFEQEMATA ASSSSLEKSY ELPDGQVITI GNERFRCPEA LFQPSFLGME SCGIHETTFN SIMKCDVDIR KDLYANTVLS GGTTMYPGIA DRMQKEITAL APSTMKIKII APPERKYSVW IGGSILASLS TFQQMWISKQ EYDESGPSIV HRKCF UniProtKB: Actin, cytoplasmic 1 |
-Macromolecule #7: RUVBL1
| Macromolecule | Name: RUVBL1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 7 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MKIEEVKSTT KTQRIASHSH VKGLGLDESG LAKQAASGLV GQENAREACG VIVELIKSKK MAGRAVLLAG PPGTGKTALA LAIAQELGSK VPFCPMVGSE VYSTEIKKTE VLMENFRRAI GLRIKETKEV YEGEVTELTP CETENPMGGY GKTISHVIIG LKTAKGTKQL ...String: MKIEEVKSTT KTQRIASHSH VKGLGLDESG LAKQAASGLV GQENAREACG VIVELIKSKK MAGRAVLLAG PPGTGKTALA LAIAQELGSK VPFCPMVGSE VYSTEIKKTE VLMENFRRAI GLRIKETKEV YEGEVTELTP CETENPMGGY GKTISHVIIG LKTAKGTKQL KLDPSIFESL QKERVEAGDV IYIEANSGAV KRQGRCDTYA TEFDLEAEEY VPLPKGDVHK KKEIIQDVTL HDLDVANARP QGGQDILSMM GQLMKPKKTE ITDKLRGEIN KVVNKYIDQG IAELVPGVLF VDEVHMLDIE CFTYLHRALE SSIAPIVIFA SNRGNCVIRG TEDITSPHGI PLDLLDRVMI IRTMLYTPQE MKQIIKIRAQ TEGINISEEA LNHLGEIGTK TTLRYSVQLL TPANLLAKIN GKDSIEKEHV EEISELFYDA KSSAKILADQ QDKYMK UniProtKB: RuvB-like 1 |
-Macromolecule #8: RUVBL2
| Macromolecule | Name: RUVBL2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 8 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MATVTATTKV PEIRDVTRIE RIGAHSHIRG LGLDDALEPR QASQGMVGQL AARRAAGVVL EMIREGKIAG RAVLIAGQPG TGKTAIAMGM AQALGPDTPF TAIAGSEIFS LEMSKTEALT QAFRRSIGVR IKEETEIIEG EVVEIQIDRP ATGTGSKVGK LTLKTTEMET ...String: MATVTATTKV PEIRDVTRIE RIGAHSHIRG LGLDDALEPR QASQGMVGQL AARRAAGVVL EMIREGKIAG RAVLIAGQPG TGKTAIAMGM AQALGPDTPF TAIAGSEIFS LEMSKTEALT QAFRRSIGVR IKEETEIIEG EVVEIQIDRP ATGTGSKVGK LTLKTTEMET IYDLGTKMIE SLTKDKVQAG DVITIDKATG KISKLGRSFT RARDYDAMGS QTKFVQCPDG ELQKRKEVVH TVSLHEIDVI NSRTQGFLAL FSGDTGEIKS EVREQINAKV AEWREEGKAE IIPGVLFIDE VHMLDIESFS FLNRALESDM APVLIMATNR GITRIRGTSY QSPHGIPIDL LDRLLIVSTT PYSEKDTKQI LRIRCEEEDV EMSEDAYTVL TRIGLETSLR YAIQLITAAS LVCRKRKGTE VQVDDIKRVY SLFLDESRST QYMKEYQDAF LFNELKGETM DTS UniProtKB: RuvB-like 2 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.2 mg/mL | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
| ||||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: PLASMA CLEANING / Pretreatment - Time: 90 sec. | ||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 279 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.8000000000000003 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)