The presentation materials from the 11th Japan-Korea-China Bioinformatics Training Course Symposium (June 17-18, 2013) are available for download .
Celebrating 10 Years of the wwPDB
Celebrating 10 Years of the wwPDB

Click on the birthday cake for a slideshow of wwPDB milestones through the years.
July 1st 2013 marks the 10-year anniversary of the founding of the wwPDB, the international collaboration that manages the PDB archive.
From modest beginnings
Starting from just 7 protein crystal structures in 1971, the PDB archive has grown rapidly over the past 42 years. Last year alone, 9,972 new structures were deposited, more than in the first 25 years of the PDB combined. Today, the archive contains over 90,000 structures and at its current rate of growth will reach the 100,000 structure mark in 2014, the International Year of Crystallography.
On July 1st 2003, the way in which the PDB archive was managed was transformed by the founding of the Worldwide Protein Data Bank organization. From its inception, the PDB has been an international archive and the establishment of the wwPDB ensured that these valuable data will continue to be stored, managed and kept freely available for the benefit of scientists worldwide.
The wwPDB organization nowadays consists of four partners: Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics Protein Data Bank (RCSB PDB) and BioMagResBank (BMRB) in the USA, Protein Data Bank in Europe (PDBe), and Protein Data Bank Japan (PDBj).
wwPDB activities
The wwPDB partner sites each act as deposition, processing and distribution centres for PDB data. They work together and in consultation with the wider community to define deposition and annotation policies, file formats and validation standards for structural data. This close collaboration between the member organizations is vital to guarantee that the global community of PDB users is provided with reliable and consistent data.
While working jointly on all aspects of data representation and processing, each partner site also offers independent tools and services that help make the wealth of data about biomacromolecular structure and function easily accessible to the user community.
wwPDB activities are overseen by an international advisory committee comprising of experts in X-ray crystallography, 3DEM, NMR, and bioinformatics.
Future Challenges
The increasing volume, diversity and complexity of biological data being deposited in the PDB and the emergence of hybrid techniques to obtain structural insights into biologically relevant molecules, complexes and molecular machines all present major challenges for the management and presentation of structural data.
To address these challenges, the wwPDB partners are jointly developing a software system that will allow deposition, validation and annotation of complex and diverse macromolecular structures along with the underlying experimental data using a single interface. This new system will go into full production at all the wwPDB deposition sites early in 2014 and will be able to handle depositions of structures of any size, determined using diffraction, NMR and/or EM methods.
Validation will be an integral part of the new deposition and annotation system. Assessment of coordinates, experimental data and associated meta data at the time of deposition is vital for improving the quality of the archive. In addition, it will help users with no or limited structural biology background to select the most appropriate structural models for their purposes.
Whatever new challenges the next 10 years will bring, the wwPDB will remain committed to maintain high standards of quality, integrity and consistency of the macromolecular structure archive and to make it freely available to an increasingly large, diverse and demanding global community of users.
(1) Announcing the worldwide Protein Data Bank. Berman H, Henrick K, Nakamura H. Nat. Struct. Biol. 10, 980 (2003) doi:10.1038/nsb1203-980
[ wwPDB News ]
The 11th Japan-Korea-China Bioinformatics Training Course Symposium will be held at Soochow University from June 17th to 18th, 2013.
The following seminar is finished.
The 11th Japan-Korea-China Bioinformatics Training Course & Symposium
- Period: June 17th (Mon.), 18th (Tue.)
- Venue: Soochow University, Suzhou, China
We are pleased to announce that "The 11th Japan-Korea-China Bioinformatics Training Course & Symposium" will be held at Soochow University, Suzhou, China, from June 17th to 18th, 2013. Assoc. prof.Akira R. Kinjo, a development member of PDBj, will give a lecture on a subject; On the optimal contact potential and sequence conversation modes of protein.
Tuesday, June 18th, 2013 [10:50-11:50]
Dr. KINJO Akira, Associate Professor, Institute for Protein Research, Osaka University, Osaka, Japan
"On the optimal contact potential and sequence conservation modes of proteins."
For more details, please refer to the following pages.
- Official site (http://cjk-bioinfo.scbit.org/)
- poster (pdf 1.2 MB)
The Biologically Interesting Molecule Reference Dictionary (BIRD) for Peptide-like Antibiotic and Inhibitor Molecules
The Biologically Interesting Molecule Reference Dictionary (BIRD) for Peptide-like Antibiotic and Inhibitor Molecules
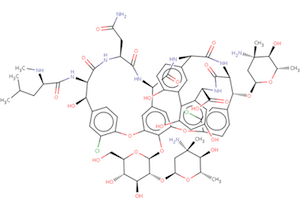 The wwPDB's Biologically Interesting molecule Reference Dictionary (BIRD) describes antibiotics, peptide inhibitors, and other complex biological ligands.
The wwPDB's Biologically Interesting molecule Reference Dictionary (BIRD) describes antibiotics, peptide inhibitors, and other complex biological ligands.
To help define and represent these biologically interesting molecules, BIRD contains chemical descriptions, sequence and linkage information, and functional and classification information as taken from the core structures and from e\ xternal resources.
All PDB entries containing these molecules have been annotated using this dictionary, with corresponding BIRD ID code contained only in the PDBx-formatted file. The use of BIRD will greatly improve the consistency of peptide-like an\ tibiotic and inhibitor molecules in the PDB.
BIRD is available on the PDBj/wwPDB FTP server adjacent to the Chemical Component Dictionary at:
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/data/bird/prd/ (PDBj FTP site) ftp://ftp.wwpdb.org/pub/pdb/data/bird/prd/ (wwPDB FTP site)It is updated as new entries are added to the PDB archive. An overview of BIRD, along with definition details, is available from wwPDB web page.
The number of structures annotated by PDBj has reached 20,000
PDBj has annotated 20,000 structures since we began annotating PDB entries in 2000. We are grateful to all depositors and wwPDB members for this great accomplishment.
Statistics for PDB entries that are deposited and processed by yearis available on wwPDB Statistics page.
The latest version of jV, jV4.3 , has been released.
The new format, v.1.9.0, for the EMDB header file (XML file associated with each map) has been released
All EMDB header files in the FTP archive have been updated to new version
(ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-/header/emd-.xml)
The EMDataBank deposition/annotation/search services will start using this new format.
The schema for 1.9.0 is available for download here:
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/doc/XML-schemas/Header-schema/current/emdb.xsd
A complete list of changes can be found at the beginning of the schema file. For more details about the schema change, see wwPDB News.
Structural Life Science - 7th International Conference on Structural Genomics (ICSG2013-SLS) will be held in Sapporo, Japan, July 29th - August 1st, 2013. PDBj will introduce activities of PDBj and wwPDB in a booth display.
The 12th AsCA will be held in Hong Kong from 7 to 10 December. Haruki Nakamura, Head of PDBj will give a poster presentation to introduce PDBj's web services and our latest activities.
The following seminar was finished.
The 12th Conference of the Asian Crystallographic Association
The 12th AsCA will be held in Hong Kong from 7 to 10 December. Genji Kurisu will give an oral presentation about "Modifications to the Protein Data Bank (PDB)". Haruki Nakamura, Head of PDBj, will give a poster presentation to introduce PDBj's web services and our latest activities.
- Oral Presentation
- Date&Time: Sunday 8 December 10:50-11:15
- Venue: Lecture Theatre J (MS-1)
- Presentation No: O1-1 (ASCA130144)
- Genji Kurisu, Atsushi Nakagawa, Haruki Nakamura (Institute for Protein Research, Osaka University)
- "Modifications to the Protein Data Bank (PDB)"
- Poster Presentation
- Date&Time: Monday 9 December 16:15-18:00
- Poster No: P-068 (ASCA130132)
- Haruki Nakamura et al. (Institute for Protein Research, Osaka University)
- "Protein Data Bank Japan (PDBj): maintaining structural data archive and integration of structure data with other life sciences data resources by semantic web technologies."
The 12th Conference of the Asian Crystallographic Association (http://asca13.ust.hk/web/asca/index.php)
- Date: 7-10 December 2013
- Venue: The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST)
The wwPDB is going to start to use a new standard format, PDBx/mmCIF in 2014, replacing the legacy \
New wwPDB service allows crystallographers to validate their own structures ( wwPDB News )
wwPDB NMR Validation Task Force Recommendations Published ( wwPDB News )
Paper Published \
New wwPDB X-ray structure validation reports support depositors, journal editors and referees
New wwPDB X-ray structure validation reports support depositors, journal editors and referees
The wwPDB partners are pleased to announce that new, considerably more informative X-ray structure validation reports are now being provided to depositors as part of the structure annotation process. The reports can be used by depositors to assess the quality of their structures, and by journal editors and referees as a useful tool in the manuscript-review process.
The new reports implement recommendations of a large group of community experts on validation [1,2]. They were originally scheduled to be introduced as part of the new wwPDB Deposition & Annotation system, which will come online in 2014. However, initial feedback on the reports has been very positive and therefore the reports are provided for all new X-ray crystal structures deposited PDBe, PDBj, and RCSB PDB as of August 1, 2013.
"Validation 'at the gate' is crucial to improving the quality and consistency of the structural archive," said Gerard Kleywegt, Head of PDBe. "The new wwPDB validation reports for X-ray crystal structures draw on a wealth of community experience in the validation of models, experimental data and the fit of the model to these data. The new style reports are a huge improvement compared to the reports previously provided by the wwPDB partners. Initial feedback from depositors, annotation staff and users alike has been very positive and this has in fact motivated us to start delivering the reports much earlier than we had planned. We strongly encourage journal editors and referees to request these reports from depositors as part of the manuscript submission and review process."
Provision of wwPDB validation reports is already required by the International Union of Crystallography (IUCr) journals as part of their submission process, and the wwPDB partners hope that the launch of the new improved reports will encourage other journals to follow suit.
The new X-ray validation reports have been prepared according to the recommendations of the wwPDB X-ray Validation Task Force [1,2], first convened in April 2008. The validation pipeline uses tried and tested software, including MolProbity, Xtriage, Mogul, EDS and various CCP4 programs. The reports include the results of geometry checks, structure factor validation, and ligand validation. They summarise the quality of the structure and highlight specific concerns by considering the coordinates of the model, the diffraction data and the fit between the two. Easily interpretable summary information that compares the quality of a model with that of other models in the archive is also provided to further support depositors, journal editors and referees.
The reports will be sent to depositors of X-ray crystal structures upon completion of the curation process by wwPDB annotation staff. Later this year, a standalone web service will be released which can be used to generate validation reports prior to deposition. Please note that the reports and the online documentation are still undergoing active development. This means that there may be a few cases where a report cannot be generated (we endeavour to fix such cases as soon as we can), and that the content and layout of the reports is subject to change. However, the wwPDB partners feel that the benefits of providing the new reports vastly outweigh these issues. Early in 2014, validation reports for all X-ray crystal structures already in the PDB archive will be made publicly available as PDF files, together with XML files that contain exhaustive validation information for each entry (e.g., complete lists of outliers for every criterion). Validation pipelines for structures determined by NMR spectroscopy [3] or 3D cryo-electron microscopy [4] are under development and will be introduced at a later stage.
Further information, including sample X-ray validation reports, is provided. We welcome your feedback on the new validation reports. If you would like to send us your comments or questions, then please contact validation@mail.wwpdb.org
[1] Read RJ, Adams PD, Arendall WB, III, Brunger AT, Emsley P, Joosten RP, Kleywegt GJ, Krissinel EB, Lutteke T, Otwinowski Z, Perrakis A, Richardson JS, Sheffler WH, Smith JL, Tickle IJ, Vriend G, Zwart PH. (2011) A new generation of crystallographic validation tools for the Protein Data Bank. Structure 19: 1395-1412. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2011.08.006
[2] Gore S., Velankar S. and Kleywegt G.J. Implementing an X-ray validation pipeline for the Protein Data Bank 2012, Acta Cryst., D68, 478-483. doi: 10.1107/S0907444911050359
[3] Montelione GT, Nilges M, Bax A, Güntert P, Herrmann T, Richardson JS, Schwieters C, Vranken WF, Vuister GW, Wishart DS, Berman HM, Kleywegt GJ, Markley JL. (in press) Recommendations of the wwPDB NMR Structure Validation Task Force. Structure.
[4] Henderson R, Sali A, Baker ML, Carragher B, Devkota B, Downing KH, Egelman EH, Feng Z, Frank J, Grigorieff N, Jiang W, Ludtke SJ, Medalia O, Penczek PA, Rosenthal PB, Rossmann MG, Schmid MF, Schroder GF, Steven AC, Stokes DL, Westbrook JD, Wriggers W, Yang H, Young J, Berman HM, Chiu W, Kleywegt GJ, Lawson CL. (2012) Outcome of the first electron microscopy validation task force meeting. Structure 20: 205-214. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2011.08.006
[ wwPDB News ]
Landmark HIV Capsid Structures Released in PDB

Two complete HIV-capsid structures, both of unprecedented size, are described in this week's issue of Nature and released in the Protein Data Bank (PDB; wwpdb.org). This represents a significant advance in the field of structural biology and a milestone for the PDB.
PDB entries 3J3Q and 3J3Y are models based on cryo-electron microscopy data and use of a molecular dynamics flexible-fitting method. They contain 1356 and 1176 protein chains, respectively, and over two million atoms each. The HIV-1 capsid is the protein envelope that encloses and protects the RNA genome of the virus. An important subject of study, the full capsid has been a difficult target for structural characterization due to its extremely large size and morphological variability.
The wwPDB has anticipated structures of increasing size and complexity that exceed the limitations of the original PDB file format. These capsid structures have been curated following the recently announced wwPDB procedures for the deposition and release of large structures. Extremely large structures can now be deposited, annotated, and released as single files in PDBx/mmCIF and PDBML/XML formats.
The intact capsid structures and the cryo-electron tomography reconstruction from which they were generated can be downloaded from the PDB archive ftp sites in the USA, Europe and Japan as follows:
- USA
-
ftp://ftp.wwpdb.org/pub/pdb/data/large_structures/mmCIF/3j3q.cif.gz
ftp://ftp.wwpdb.org/pub/pdb/data/large_structures/XML/3j3q.xml.gz
ftp://ftp.wwpdb.org/pub/pdb/data/large_structures/mmCIF/3j3y.cif.gz
ftp://ftp.wwpdb.org/pub/pdb/data/large_structures/XML/3j3y.xml.gz
ftp://ftp.wwpdb.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-5639/map/emd_5639.map.gz
- Europe
-
ftp://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/databases/pdb/data/large_structures/mmCIF/3j3q.cif.gz
ftp://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/databases/pdb/data/large_structures/XML/3j3q.xml.gz
ftp://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/databases/pdb/data/large_structures/mmCIF/3j3y.cif.gz
ftp://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/databases/pdb/data/large_structures/XML/3j3y.xml.gz
ftp://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/databases/emdb/structures/EMD-5639/map/emd_5639.map.gz
- Japan
-
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/data/large_structures/mmCIF/3j3q.cif.gz
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/data/large_structures/XML/3j3q.xml.gz
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/data/large_structures/mmCIF/3j3y.cif.gz
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/data/large_structures/XML/3j3y.xml.gz
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-5639/map/emd_5639.map.gz
Reference
Mature HIV-1 capsid structure by cryo-electron microscopy and all-atom molecular dynamics.
Gongpu Zhao, Juan R. Perilla, Ernest L. Yufenyuy, Xin Meng, Bo Chen, Jiying Ning, Jinwoo Ahn, Angela M. Gronenborn, Klaus Schulten, Christopher Aiken, & Peijun Zhang,
Nature 497, 643-646 (2013) DOI: 10.1038/nature12162
Related Entries
EMDB entry EMD-5639 is the cryo-electron tomography reconstruction from which 3J3Q and 3J3Y were generated; related entry 3J34, derived from an 8.6 Ångström reconstruction of a capsid hexameric subunit in a helical assembly (EMD-5582), was used in the construction of both 3J3Q and 3J3Y. These entries can be accessed and analysed through the websites of the wwPDB partners in Europe (pdbe.org), the USA (rcsb.org) and Japan (pdbj.org).
Deposition and Release of PDB Entries Containing Large Structures
In order to meet the challenges of ever greater numbers of PDB depositions, involving ever larger and more complex structures, often determined using multiple methods, the Worldwide Protein Data Bank partners (wwPDB: http://wwpdb.org/) are developing a completely new system for deposition and annotation of PDB entries.
This new system will go into full production at all the wwPDB deposition sites early in 2014 and will then be able to handle depositions of structures of any size, determined using diffraction, NMR and/or EM methods. Large structures will also be processed and released intact so that "split entries" become a thing of the past.
For more details, please see wwPDB News.







