[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8txx: Cryo-EM structure of the human nucleosome core particle ubiquityl... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8txx | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
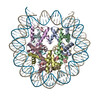
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the human nucleosome core particle ubiquitylated at histone H2A K15 in complex with RNF168 (Class 3) | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSFERASE / Nucleosome core particle / chromatin / RNF168 / MIU2-LRM domains / DNA repair / DNA double-strand break / Homologous recombination / BRCA1-BARD1 / 53BP1 / ubiquitin / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN-DNA-TRANSFERASE complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationhistone H2AK15 ubiquitin ligase activity / histone ubiquitin ligase activity / double-strand break repair via classical nonhomologous end joining / isotype switching / hypothalamus gonadotrophin-releasing hormone neuron development / female meiosis I / positive regulation of protein monoubiquitination / fat pad development / mitochondrion transport along microtubule / K63-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding ...histone H2AK15 ubiquitin ligase activity / histone ubiquitin ligase activity / double-strand break repair via classical nonhomologous end joining / isotype switching / hypothalamus gonadotrophin-releasing hormone neuron development / female meiosis I / positive regulation of protein monoubiquitination / fat pad development / mitochondrion transport along microtubule / K63-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / female gonad development / DNA repair-dependent chromatin remodeling / seminiferous tubule development / response to ionizing radiation / male meiosis I / negative regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator / protein K63-linked ubiquitination / ubiquitin ligase complex / interstrand cross-link repair / SUMOylation of DNA damage response and repair proteins / nucleosome binding / energy homeostasis / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / neuron projection morphogenesis / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Maturation of protein E / Maturation of protein E / ER Quality Control Compartment (ERQC) / Myoclonic epilepsy of Lafora / FLT3 signaling by CBL mutants / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD Domain Mutants / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex / Prevention of phagosomal-lysosomal fusion / Alpha-protein kinase 1 signaling pathway / Glycogen synthesis / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / Endosomal Sorting Complex Required For Transport (ESCRT) / Membrane binding and targetting of GAG proteins / Negative regulation of FLT3 / Regulation of TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE)-mediated activation of IRF3, IRF7 / PTK6 Regulates RTKs and Their Effectors AKT1 and DOK1 / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / Regulation of TBK1, IKKε-mediated activation of IRF3, IRF7 upon TLR3 ligation / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / NOTCH2 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / TICAM1,TRAF6-dependent induction of TAK1 complex / TICAM1-dependent activation of IRF3/IRF7 / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / telomere organization / Regulation of FZD by ubiquitination / Downregulation of ERBB4 signaling / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Interleukin-7 signaling / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / InlA-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cells / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation in TLR7/8 or 9 signaling / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Regulation of pyruvate metabolism / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / TRAF6-mediated induction of TAK1 complex within TLR4 complex / regulation of neuron apoptotic process / Downregulation of ERBB2:ERBB3 signaling / Pexophagy / Regulation of innate immune responses to cytosolic DNA / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Regulation of PTEN localization / Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Meiotic synapsis / VLDLR internalisation and degradation / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / ubiquitin binding / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / positive regulation of protein ubiquitination / Synthesis of active ubiquitin: roles of E1 and E2 enzymes / TICAM1, RIP1-mediated IKK complex recruitment / Regulation of BACH1 activity / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / positive regulation of DNA repair / MAP3K8 (TPL2)-dependent MAPK1/3 activation / Degradation of CDH1 / Translesion synthesis by POLK / DNA methylation / InlB-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cell / JNK (c-Jun kinases) phosphorylation and activation mediated by activated human TAK1 / Activation of IRF3, IRF7 mediated by TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE) / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hu, Q. / Botuyan, M.V. / Zhao, D. / Cui, G. / Mer, G. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2024 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2024Title: Mechanisms of RNF168 nucleosome recognition and ubiquitylation. Authors: Qi Hu / Debiao Zhao / Gaofeng Cui / Janarjan Bhandari / James R Thompson / Maria Victoria Botuyan / Georges Mer /  Abstract: RNF168 plays a central role in the DNA damage response (DDR) by ubiquitylating histone H2A at K13 and K15. These modifications direct BRCA1-BARD1 and 53BP1 foci formation in chromatin, essential for ...RNF168 plays a central role in the DNA damage response (DDR) by ubiquitylating histone H2A at K13 and K15. These modifications direct BRCA1-BARD1 and 53BP1 foci formation in chromatin, essential for cell-cycle-dependent DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair pathway selection. The mechanism by which RNF168 catalyzes the targeted accumulation of H2A ubiquitin conjugates to form repair foci around DSBs remains unclear. Here, using cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, and functional assays, we provide a molecular description of the reaction cycle and dynamics of RNF168 as it modifies the nucleosome and recognizes its ubiquitylation products. We demonstrate an interaction of a canonical ubiquitin-binding domain within full-length RNF168, which not only engages ubiquitin but also the nucleosome surface, clarifying how such site-specific ubiquitin recognition propels a signal amplification loop. Beyond offering mechanistic insights into a key DDR protein, our study aids in understanding site specificity in both generating and interpreting chromatin ubiquitylation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8txx.cif.gz 8txx.cif.gz | 319.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8txx.ent.gz pdb8txx.ent.gz | 234.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8txx.json.gz 8txx.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tx/8txx https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tx/8txx ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tx/8txx ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tx/8txx | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  41708MC  8smwC  8smxC  8smyC  8smzC  8sn0C  8sn1C  8sn2C  8sn3C  8sn4C  8sn5C  8sn6C  8sn7C  8sn8C  8sn9C  8snaC  8txvC  8txwC 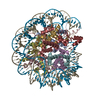 8u13C  8u14C  8upfC  8uq8C  8uq9C  8uqaC  8uqbC  8uqcC 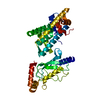 8uqdC 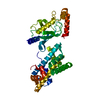 8uqeC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 6 types, 10 molecules AEBFDHKMCG
| #1: Protein | Mass: 15786.534 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: H3C1, H3FA, HIST1H3A, H3C2, H3FL, HIST1H3B, H3C3, H3FC HIST1H3C, H3C4, H3FB, HIST1H3D, H3C6, H3FD, HIST1H3E, H3C7, H3FI, HIST1H3F, H3C8, H3FH, HIST1H3G, H3C10, H3FK, HIST1H3H, H3C11, H3FF, ...Gene: H3C1, H3FA, HIST1H3A, H3C2, H3FL, HIST1H3B, H3C3, H3FC HIST1H3C, H3C4, H3FB, HIST1H3D, H3C6, H3FD, HIST1H3E, H3C7, H3FI, HIST1H3F, H3C8, H3FH, HIST1H3G, H3C10, H3FK, HIST1H3H, H3C11, H3FF, HIST1H3I, H3C12, H3FJ, HIST1H3J Plasmid: pHISPP / Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 11743.792 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: H4C1, H4/A, H4FA, HIST1H4A, H4C2, H4/I, H4FI, HIST1H4B, H4C3, H4/G, H4FG, HIST1H4C, H4C4, H4/B, H4FB, HIST1H4D, H4C5, H4/J, H4FJ, HIST1H4E, H4C6, H4/C, H4FC, HIST1H4F, H4C8, H4/H, H4FH, ...Gene: H4C1, H4/A, H4FA, HIST1H4A, H4C2, H4/I, H4FI, HIST1H4B, H4C3, H4/G, H4FG, HIST1H4C, H4C4, H4/B, H4FB, HIST1H4D, H4C5, H4/J, H4FJ, HIST1H4E, H4C6, H4/C, H4FC, HIST1H4F, H4C8, H4/H, H4FH, HIST1H4H, H4C9, H4/M, H4FM, HIST1H4I, H4C11, H4/E, H4FE, HIST1H4J, H4C12, H4/D, H4FD, HIST1H4K, H4C13, H4/K, H4FK, HIST1H4L, H4C14, H4/N, H4F2, H4FN, HIST2H4, HIST2H4A, H4C15, H4/O, H4FO, HIST2H4B, H4-16, HIST4H4 Plasmid: pHISPP / Production host:  #3: Protein | Mass: 14084.348 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: H2BC4, H2BFL, HIST1H2BC, H2BC6, H2BFH, HIST1H2BE, H2BC7, H2BFG, HIST1H2BF, H2BC8, H2BFA, HIST1H2BG, H2BC10, H2BFK, HIST1H2BI Plasmid: pHISPP / Production host:  #6: Protein | | Mass: 66168.180 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RNF168 / Plasmid: pHISPP / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RNF168 / Plasmid: pHISPP / Production host:  #7: Protein | | Mass: 9057.391 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: UBB / Plasmid: pHISPP / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: UBB / Plasmid: pHISPP / Production host:  #8: Protein | Mass: 12992.091 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: K13S Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H2AC4, H2AFM, HIST1H2AB, H2AC8, H2AFA, HIST1H2AE / Plasmid: pHISPP / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H2AC4, H2AFM, HIST1H2AB, H2AC8, H2AFA, HIST1H2AE / Plasmid: pHISPP / Production host:  |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules IJ
| #4: DNA chain | Mass: 45138.770 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
|---|---|
| #5: DNA chain | Mass: 45610.043 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Details
| Has protein modification | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Human nucleosome core particle ubiquitylated at histone H2A K15 in complex with RNF168 (Class 3) Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.28 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.25 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: 10 mM HEPES, 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM DTT, pH 7.5 |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 130000 X / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 11712 Details: 11712 images were recorded in movie-mode of which 10993 were retained for particle picking. |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 9619981 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 35548 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


















 PDBj
PDBj