[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-41800: Cryo-EM structure of the human nucleosome core particle ubiquityl... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
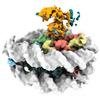
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the human nucleosome core particle ubiquitylated at histone H2A lysine 15 in complex with RNF168-UbcH5c (class 1) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Nucleosome core particle / chromatin / RNF168 / UbcH5c / DNA repair / DNA double-strand break / Homologous recombination / BRCA1-BARD1 / 53BP1 / ubiquitin / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN-DNA-TRANSFERASE complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationhistone H2AK15 ubiquitin ligase activity / histone ubiquitin ligase activity / isotype switching / double-strand break repair via classical nonhomologous end joining / K63-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / response to ionizing radiation / DNA repair-dependent chromatin remodeling / negative regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / protein K63-linked ubiquitination / ubiquitin ligase complex ...histone H2AK15 ubiquitin ligase activity / histone ubiquitin ligase activity / isotype switching / double-strand break repair via classical nonhomologous end joining / K63-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / response to ionizing radiation / DNA repair-dependent chromatin remodeling / negative regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / protein K63-linked ubiquitination / ubiquitin ligase complex / interstrand cross-link repair / SUMOylation of DNA damage response and repair proteins / nucleosome binding / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / telomere organization / Interleukin-7 signaling / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Meiotic synapsis / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / positive regulation of DNA repair / ubiquitin binding / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / innate immune response in mucosa / Defective pyroptosis / HDACs deacetylate histones / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / HDMs demethylate histones / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Meiotic recombination / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / Metalloprotease DUBs / RMTs methylate histone arginines / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / HCMV Early Events / ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / structural constituent of chromatin / UCH proteinases / antibacterial humoral response / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / double-strand break repair / nucleosome assembly / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / site of double-strand break / HATs acetylate histones / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / chromatin organization / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / histone binding / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / gene expression / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / chromosome, telomeric region / defense response to Gram-positive bacterium / Ub-specific processing proteases / protein ubiquitination / cadherin binding / protein heterodimerization activity / Amyloid fiber formation / negative regulation of cell population proliferation Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hu Q / Botuyan MV / Zhao D / Cui G / Mer G | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2024 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2024Title: Mechanisms of RNF168 nucleosome recognition and ubiquitylation. Authors: Qi Hu / Debiao Zhao / Gaofeng Cui / Janarjan Bhandari / James R Thompson / Maria Victoria Botuyan / Georges Mer /  Abstract: RNF168 plays a central role in the DNA damage response (DDR) by ubiquitylating histone H2A at K13 and K15. These modifications direct BRCA1-BARD1 and 53BP1 foci formation in chromatin, essential for ...RNF168 plays a central role in the DNA damage response (DDR) by ubiquitylating histone H2A at K13 and K15. These modifications direct BRCA1-BARD1 and 53BP1 foci formation in chromatin, essential for cell-cycle-dependent DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair pathway selection. The mechanism by which RNF168 catalyzes the targeted accumulation of H2A ubiquitin conjugates to form repair foci around DSBs remains unclear. Here, using cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, and functional assays, we provide a molecular description of the reaction cycle and dynamics of RNF168 as it modifies the nucleosome and recognizes its ubiquitylation products. We demonstrate an interaction of a canonical ubiquitin-binding domain within full-length RNF168, which not only engages ubiquitin but also the nucleosome surface, clarifying how such site-specific ubiquitin recognition propels a signal amplification loop. Beyond offering mechanistic insights into a key DDR protein, our study aids in understanding site specificity in both generating and interpreting chromatin ubiquitylation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_41800.map.gz emd_41800.map.gz | 6.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-41800-v30.xml emd-41800-v30.xml emd-41800.xml emd-41800.xml | 27.5 KB 27.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
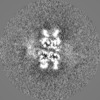
| Images |  emd_41800.png emd_41800.png | 140.8 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_41800_msk_1.map emd_41800_msk_1.map | 64 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-41800.cif.gz emd-41800.cif.gz | 7.4 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_41800_additional_1.map.gz emd_41800_additional_1.map.gz emd_41800_half_map_1.map.gz emd_41800_half_map_1.map.gz emd_41800_half_map_2.map.gz emd_41800_half_map_2.map.gz | 40.1 MB 50 MB 49.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41800 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41800 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41800 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41800 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8u13MC  8smwC  8smxC  8smyC  8smzC  8sn0C  8sn1C  8sn2C  8sn3C  8sn4C  8sn5C  8sn6C  8sn7C  8sn8C  8sn9C  8snaC  8txvC  8txwC  8txxC  8u14C  8upfC  8uq8C  8uq9C  8uqaC  8uqbC  8uqcC  8uqdC  8uqeC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_41800.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_41800.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
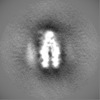
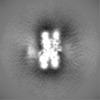
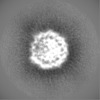
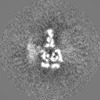
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.0276 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_41800_msk_1.map emd_41800_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: #1
| File | emd_41800_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_41800_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_41800_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human nucleosome core particle ubiquitylated at histone H2A lysin...
| Entire | Name: Human nucleosome core particle ubiquitylated at histone H2A lysine 15 in complex with RNF168-UbcH5c (class 1) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Human nucleosome core particle ubiquitylated at histone H2A lysin...
| Supramolecule | Name: Human nucleosome core particle ubiquitylated at histone H2A lysine 15 in complex with RNF168-UbcH5c (class 1) type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#7 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 255 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Histone H3.1
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H3.1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15.786534 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GPGHMARTKQ TARKSTGGKA PRKQLATKAA RKSAPATGGV KKPHRYRPGT VALREIRRYQ KSTELLIRKL PFQRLVREIA QDFKTDLRF QSSAVMALQE ACEAYLVGLF EDTNLCAIHA KRVTIMPKDI QLARRIRGER A UniProtKB: Histone H3.1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Histone H4
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.743792 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GPGHMSGRGK GGKGLGKGGA KRHRKVLRDN IQGITKPAIR RLARRGGVKR ISGLIYEETR GVLKVFLENV IRDAVTYTEH AKRKTVTAM DVVYALKRQG RTLYGFGG UniProtKB: Histone H4 |
-Macromolecule #3: Histone H2B type 1-C/E/F/G/I
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2B type 1-C/E/F/G/I / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.084348 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GPGHMPEPAK SAPAPKKGSK KAVTKAQKKD GKKRKRSRKE SYSIYVYKVL KQVHPDTGIS SKAMGIMNSF VNDIFERIAG EASRLAHYN KRSTITSREI QTAVRLLLPG ELAKHAVSEG TKAVTKYTS UniProtKB: Histone H2B type 1-C/E/F/G/I |
-Macromolecule #6: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF168
| Macromolecule | Name: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF168 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.1751 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MALPKDAIPS LSECQCGICM EILVEPVTLP CNHTLCKPCF QSTVEKASLC CPFCRRRVSS WTRYHTRRNS LVNVELWTII QKHYPRECK LRASGSGSGS UniProtKB: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF168 |
-Macromolecule #7: Histone H2A type 1-B/E
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2A type 1-B/E / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 12.992091 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SASAKTRSSR AGLQFPVGRV HRLLRKGNYS ERVGAGAPVY LAAVLEYLTA EILELAGNAA RDNKKTRIIP RHLQLAIRND EELNKLLGR VTIAQGGVLP NIQAVLLPKK TESHHKAKGK UniProtKB: Histone H2A type 1-B/E |
-Macromolecule #4: DNA (147-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (147-MER) / type: dna / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 45.13877 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC) (DC)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DA) (DG)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DA) (DA)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DA) (DG) (DA)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DT) ...String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC) (DC)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DA) (DG)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DA) (DA)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DA) (DG) (DA)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DT) (DA)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DT) (DA)(DA) (DA)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DG) (DT)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DT) (DC)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DT) (DT)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DC) (DA)(DA)(DG)(DG) (DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DT) (DA)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DT) (DC)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DA) (DG)(DG)(DC)(DA) (DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DT) (DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DC) (DA)(DT)(DC) (DC)(DG)(DA)(DT) |
-Macromolecule #5: DNA (146-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (146-MER) / type: dna / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 45.610043 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DA) (DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DC) (DA)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DG) (DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG) (DA) (DG)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC) ...String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DA) (DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DC) (DA)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DG) (DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG) (DA) (DG)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT) (DA)(DA) (DA)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG) (DG)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DC) (DG)(DT)(DA) (DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DG) (DT)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT) (DG)(DC)(DT)(DA) (DG)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DT) (DG)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DC) (DA)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DC)(DG) (DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC) (DC)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT) (DT)(DC)(DT) (DC)(DG)(DA)(DT) |
-Macromolecule #8: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.4 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 60 sec. |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
| Details | 10 mM HEPES, 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM DTT, pH 7.5 |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 5697 / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 Details: 5697 images were recorded in movie mode. 5503 were retained for particle picking. |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 22500 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model |
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT | |||||||||
| Output model |  PDB-8u13: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)