[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8uqa: Crystal structure of RNF168 (RING)-UbcH5c fused to H2A-H2B via a ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8uqa | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Crystal structure of RNF168 (RING)-UbcH5c fused to H2A-H2B via a 12-residue linker | |||||||||
 Components Components | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF168,Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 D3,Histone H2B type 2-E,Histone H2A type 1-B/E | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSFERASE / RNF168 / UbcH5c / Histone H2A / Histone H2B / Chromatin / Ubiquitin ligase / Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme / DNA damage response / DNA double-strand break repair / PROTEIN BINDING / PROTEIN BINDING-Transferase complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationhistone H2AK15 ubiquitin ligase activity / histone ubiquitin ligase activity / Signaling by BMP / protein K6-linked ubiquitination / (E3-independent) E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme / double-strand break repair via classical nonhomologous end joining / isotype switching / protein K11-linked ubiquitination / : / K63-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding ...histone H2AK15 ubiquitin ligase activity / histone ubiquitin ligase activity / Signaling by BMP / protein K6-linked ubiquitination / (E3-independent) E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme / double-strand break repair via classical nonhomologous end joining / isotype switching / protein K11-linked ubiquitination / : / K63-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme / DNA repair-dependent chromatin remodeling / response to ionizing radiation / ubiquitin conjugating enzyme activity / negative regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / negative regulation of BMP signaling pathway / protein K63-linked ubiquitination / protein monoubiquitination / ubiquitin ligase complex / interstrand cross-link repair / SUMOylation of DNA damage response and repair proteins / nucleosome binding / protein autoubiquitination / protein K48-linked ubiquitination / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Meiotic synapsis / ubiquitin binding / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / TICAM1, RIP1-mediated IKK complex recruitment / positive regulation of DNA repair / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / IKK complex recruitment mediated by RIP1 / PINK1-PRKN Mediated Mitophagy / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / innate immune response in mucosa / Defective pyroptosis / Negative Regulation of CDH1 Gene Transcription / HDACs deacetylate histones / Negative regulators of DDX58/IFIH1 signaling / Peroxisomal protein import / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / protein modification process / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Downregulation of SMAD2/3:SMAD4 transcriptional activity / Regulation of TNFR1 signaling / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / Inactivation of CSF3 (G-CSF) signaling / RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / Oxygen-dependent proline hydroxylation of Hypoxia-inducible Factor Alpha / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Meiotic recombination / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / Metalloprotease DUBs / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / protein polyubiquitination / RMTs methylate histone arginines / HCMV Early Events / ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / structural constituent of chromatin / ubiquitin protein ligase activity / UCH proteinases / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / double-strand break repair / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / nucleosome assembly / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / antibacterial humoral response / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / site of double-strand break / HATs acetylate histones / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.049 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.049 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hu, Q. / Botuyan, M.V. / Mer, G. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2024 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2024Title: Mechanisms of RNF168 nucleosome recognition and ubiquitylation. Authors: Qi Hu / Debiao Zhao / Gaofeng Cui / Janarjan Bhandari / James R Thompson / Maria Victoria Botuyan / Georges Mer /  Abstract: RNF168 plays a central role in the DNA damage response (DDR) by ubiquitylating histone H2A at K13 and K15. These modifications direct BRCA1-BARD1 and 53BP1 foci formation in chromatin, essential for ...RNF168 plays a central role in the DNA damage response (DDR) by ubiquitylating histone H2A at K13 and K15. These modifications direct BRCA1-BARD1 and 53BP1 foci formation in chromatin, essential for cell-cycle-dependent DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair pathway selection. The mechanism by which RNF168 catalyzes the targeted accumulation of H2A ubiquitin conjugates to form repair foci around DSBs remains unclear. Here, using cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, and functional assays, we provide a molecular description of the reaction cycle and dynamics of RNF168 as it modifies the nucleosome and recognizes its ubiquitylation products. We demonstrate an interaction of a canonical ubiquitin-binding domain within full-length RNF168, which not only engages ubiquitin but also the nucleosome surface, clarifying how such site-specific ubiquitin recognition propels a signal amplification loop. Beyond offering mechanistic insights into a key DDR protein, our study aids in understanding site specificity in both generating and interpreting chromatin ubiquitylation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8uqa.cif.gz 8uqa.cif.gz | 109.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8uqa.ent.gz pdb8uqa.ent.gz | 80.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8uqa.json.gz 8uqa.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/uq/8uqa https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/uq/8uqa ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/uq/8uqa ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/uq/8uqa | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8smwC  8smxC  8smyC  8smzC  8sn0C  8sn1C  8sn2C  8sn3C  8sn4C  8sn5C  8sn6C  8sn7C  8sn8C  8sn9C  8snaC  8txvC  8txwC  8txxC  8u13C  8u14C  8upfC  8uq8C  8uq9C  8uqbC  8uqcC  8uqdC  8uqeC  4gb0S  5eggS S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 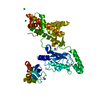
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
| ||||||||
| Components on special symmetry positions |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 49523.863 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: C85K in UbcH5c Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: residues 1-94 of RNF168, followed by residues 2-147 of UbcH5c, followed by residues 33-123 of H2B, followed by residues 12-105 of H2A Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: RNF168, UBE2D3, UBC5C, UBCH5C, H2BC21, H2BFQ, HIST2H2BE, H2AC4, H2AFM, HIST1H2AB, H2AC8, H2AFA, HIST1H2AE Production host:  References: UniProt: Q8IYW5, UniProt: P61077, UniProt: Q16778, UniProt: P04908, RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase, E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, (E3-independent) E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Chemical | | #3: Chemical | #4: Chemical | ChemComp-CL / #5: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | Has ligand of interest | Y | |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.69 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 54.31 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 288 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / pH: 7.5 Details: Crystals were obtained by mixing 2 microliters of the protein fusion (8.0 mg/mL) in 10 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 600 mM NaCl, 1 mM TCEP and 2 microliters of the reservoir solution containing 0.1 M ...Details: Crystals were obtained by mixing 2 microliters of the protein fusion (8.0 mg/mL) in 10 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 600 mM NaCl, 1 mM TCEP and 2 microliters of the reservoir solution containing 0.1 M HEPES, pH 7.5, 2.4 M NaCl |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  APS APS  / Beamline: 19-BM / Wavelength: 0.9792 Å / Beamline: 19-BM / Wavelength: 0.9792 Å |
| Detector | Type: ADSC QUANTUM 315r / Detector: CCD / Date: Jun 17, 2017 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.9792 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.049→50 Å / Num. obs: 33909 / % possible obs: 99.78 % / Redundancy: 14.2 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 32.99 Å2 / CC1/2: 0.999 / CC star: 1 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.09873 / Rpim(I) all: 0.02712 / Rrim(I) all: 0.1024 / Net I/σ(I): 31.56 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 2.049→2.122 Å / Redundancy: 12.6 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.8334 / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 4.73 / Num. unique obs: 3326 / CC1/2: 0.853 / CC star: 0.96 / Rpim(I) all: 0.2426 / Rrim(I) all: 0.8685 / % possible all: 99.52 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 4GB0, 5EGG Resolution: 2.049→39.179 Å / SU ML: 0.19 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.34 / Phase error: 23.32 / Stereochemistry target values: ML
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 2.049→39.179 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



















 PDBj
PDBj




















