[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7sye: Cryo-EM structure of the extracellular module of the full-length ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7sye | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
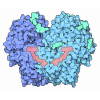
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the extracellular module of the full-length EGFR bound to EGF. "tips-separated" conformation | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN/RECEPTOR / receptor tyrosine kinases / epidermal growth factor receptor / SIGNALING PROTEIN / SIGNALING PROTEIN-RECEPTOR complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of hyaluronan biosynthetic process / negative regulation of secretion / negative regulation of cholesterol efflux / positive regulation of epithelial tube formation / positive regulation of cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation / regulation of protein localization to cell surface / positive regulation of protein localization to early endosome / cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation / regulation of calcium ion import / transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activator activity ...positive regulation of hyaluronan biosynthetic process / negative regulation of secretion / negative regulation of cholesterol efflux / positive regulation of epithelial tube formation / positive regulation of cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation / regulation of protein localization to cell surface / positive regulation of protein localization to early endosome / cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation / regulation of calcium ion import / transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activator activity / Developmental Lineage of Pancreatic Acinar Cells / positive regulation of ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / Differentiation of Keratinocytes in Interfollicular Epidermis in Mammalian Skin / positive regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / epidermal growth factor receptor binding / multivesicular body, internal vesicle lumen / negative regulation of cardiocyte differentiation / Shc-EGFR complex / positive regulation of protein kinase C signaling / regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT / Inhibition of Signaling by Overexpressed EGFR / epidermal growth factor receptor activity / EGFR interacts with phospholipase C-gamma / NFE2L2 regulating tumorigenic genes / regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation / positive regulation of DNA binding / epidermal growth factor binding / response to UV-A / PLCG1 events in ERBB2 signaling / ERBB2-EGFR signaling pathway / morphogenesis of an epithelial fold / PTK6 promotes HIF1A stabilization / Signaling by EGFR / ERBB2 Activates PTK6 Signaling / branching morphogenesis of an epithelial tube / digestive tract morphogenesis / intracellular vesicle / eyelid development in camera-type eye / negative regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway / cerebral cortex cell migration / protein insertion into membrane / ERBB2 Regulates Cell Motility / protein tyrosine kinase activator activity / Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) attachment and entry / Signaling by ERBB4 / positive regulation of receptor internalization / PI3K events in ERBB2 signaling / positive regulation of phosphorylation / mammary gland alveolus development / positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / Estrogen-dependent nuclear events downstream of ESR-membrane signaling / hair follicle development / MAP kinase kinase kinase activity / positive regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / GAB1 signalosome / embryonic placenta development / salivary gland morphogenesis / ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation / Signaling by ERBB2 / TFAP2 (AP-2) family regulates transcription of growth factors and their receptors / GRB2 events in EGFR signaling / transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity / SHC1 events in EGFR signaling / EGFR Transactivation by Gastrin / positive regulation of endothelial cell migration / positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division / GRB2 events in ERBB2 signaling / SHC1 events in ERBB2 signaling / ossification / basal plasma membrane / platelet alpha granule lumen / guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity / cellular response to epidermal growth factor stimulus / positive regulation of DNA repair / positive regulation of DNA replication / epithelial cell proliferation / positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation / Signal transduction by L1 / positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / growth factor activity / cellular response to amino acid stimulus / phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / NOTCH3 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / cellular response to estradiol stimulus / clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane / EGFR downregulation / Signaling by ERBB2 TMD/JMD mutants / cell-cell adhesion / Constitutive Signaling by EGFRvIII / receptor protein-tyrosine kinase / Signaling by ERBB2 ECD mutants / Signaling by ERBB2 KD Mutants / negative regulation of protein catabolic process / positive regulation of miRNA transcription / epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway / kinase binding / ruffle membrane / Downregulation of ERBB2 signaling / positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Huang, Y. / Ognjenovic, J. / Karandur, D. / Miller, K. / Merk, A. / Subramaniam, S. / Kuriyan, J. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2021 Journal: Elife / Year: 2021Title: A molecular mechanism for the generation of ligand-dependent differential outputs by the epidermal growth factor receptor. Authors: Yongjian Huang / Jana Ognjenovic / Deepti Karandur / Kate Miller / Alan Merk / Sriram Subramaniam / John Kuriyan /   Abstract: The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that couples the binding of extracellular ligands, such as EGF and transforming growth factor-α (TGF-α), to the initiation ...The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that couples the binding of extracellular ligands, such as EGF and transforming growth factor-α (TGF-α), to the initiation of intracellular signaling pathways. EGFR binds to EGF and TGF-α with similar affinity, but generates different signals from these ligands. To address the mechanistic basis of this phenomenon, we have carried out cryo-EM analyses of human EGFR bound to EGF and TGF-α. We show that the extracellular module adopts an ensemble of dimeric conformations when bound to either EGF or TGF-α. The two extreme states of this ensemble represent distinct ligand-bound quaternary structures in which the membrane-proximal tips of the extracellular module are either juxtaposed or separated. EGF and TGF-α differ in their ability to maintain the conformation with the membrane-proximal tips of the extracellular module separated, and this conformation is stabilized preferentially by an oncogenic EGFR mutation. Close proximity of the transmembrane helices at the junction with the extracellular module has been associated previously with increased EGFR activity. Our results show how EGFR can couple the binding of different ligands to differential modulation of this proximity, thereby suggesting a molecular mechanism for the generation of ligand-sensitive differential outputs in this receptor family. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7sye.cif.gz 7sye.cif.gz | 360.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7sye.ent.gz pdb7sye.ent.gz | 265 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7sye.json.gz 7sye.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sy/7sye https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sy/7sye ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sy/7sye ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sy/7sye | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  25523MC  7sydC  7sz0C  7sz1C  7sz5C  7sz7C C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 134433.328 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: EGFR, ERBB, ERBB1, HER1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: EGFR, ERBB, ERBB1, HER1 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)References: UniProt: P00533, receptor protein-tyrosine kinase #2: Protein | Mass: 6229.027 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: EGF / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: EGF / Production host:  Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: full-length human EGFR:EGF complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 750 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 89757 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 PDBj
PDBj