[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6w66: The structure of the F64A, S172A mutant Keap1-BTB domain in compl... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6w66 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
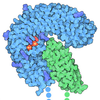
| Title | The structure of the F64A, S172A mutant Keap1-BTB domain in complex with SKP1-FBXL17 | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | LIGASE/SIGNALING PROTEIN / E3 Ligase / Complex / BTB domain / LIGASE / LIGASE-SIGNALING PROTEIN complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationF-box domain binding / PcG protein complex / regulation of epidermal cell differentiation / positive regulation of ubiquitin protein ligase activity / Cul7-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / maintenance of protein location in nucleus / regulation of smoothened signaling pathway / Loss of Function of FBXW7 in Cancer and NOTCH1 Signaling / Nuclear events mediated by NFE2L2 / negative regulation of response to oxidative stress ...F-box domain binding / PcG protein complex / regulation of epidermal cell differentiation / positive regulation of ubiquitin protein ligase activity / Cul7-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / maintenance of protein location in nucleus / regulation of smoothened signaling pathway / Loss of Function of FBXW7 in Cancer and NOTCH1 Signaling / Nuclear events mediated by NFE2L2 / negative regulation of response to oxidative stress / SCF ubiquitin ligase complex / neural crest cell differentiation / Cul3-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / SCF-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / Prolactin receptor signaling / ubiquitin ligase complex scaffold activity / protein quality control for misfolded or incompletely synthesized proteins / : / cullin family protein binding / protein monoubiquitination / transcription regulator inhibitor activity / protein K48-linked ubiquitination / ubiquitin-like ligase-substrate adaptor activity / Nuclear events stimulated by ALK signaling in cancer / inclusion body / cellular response to interleukin-4 / molecular function activator activity / Regulation of BACH1 activity / MAP3K8 (TPL2)-dependent MAPK1/3 activation / regulation of autophagy / actin filament / SCF-beta-TrCP mediated degradation of Emi1 / NIK-->noncanonical NF-kB signaling / Vpu mediated degradation of CD4 / Dectin-1 mediated noncanonical NF-kB signaling / Activation of NF-kappaB in B cells / Degradation of GLI1 by the proteasome / Iron uptake and transport / GSK3B and BTRC:CUL1-mediated-degradation of NFE2L2 / Negative regulation of NOTCH4 signaling / FBXL7 down-regulates AURKA during mitotic entry and in early mitosis / Degradation of GLI2 by the proteasome / GLI3 is processed to GLI3R by the proteasome / beta-catenin binding / Degradation of beta-catenin by the destruction complex / NOTCH1 Intracellular Domain Regulates Transcription / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) signaling / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 PEST Domain Mutants / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD+PEST Domain Mutants / SCF(Skp2)-mediated degradation of p27/p21 / FCERI mediated NF-kB activation / centriolar satellite / Interleukin-1 signaling / protein polyubiquitination / Orc1 removal from chromatin / disordered domain specific binding / Regulation of RUNX2 expression and activity / Cyclin D associated events in G1 / KEAP1-NFE2L2 pathway / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / Downstream TCR signaling / nervous system development / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / Neddylation / cellular response to oxidative stress / midbody / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / Potential therapeutics for SARS / in utero embryonic development / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding / Ub-specific processing proteases / protein ubiquitination / chromatin remodeling / protein domain specific binding / centrosome / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / endoplasmic reticulum / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT /  molecular replacement / Resolution: 3.21 Å molecular replacement / Resolution: 3.21 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Mena, E.L. / Gee, C.L. / Kuriyan, J. / Rape, M. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2020 Journal: Nature / Year: 2020Title: Structural basis for dimerization quality control. Authors: Elijah L Mena / Predrag Jevtić / Basil J Greber / Christine L Gee / Brandon G Lew / David Akopian / Eva Nogales / John Kuriyan / Michael Rape /  Abstract: Most quality control pathways target misfolded proteins to prevent toxic aggregation and neurodegeneration. Dimerization quality control further improves proteostasis by eliminating complexes of ...Most quality control pathways target misfolded proteins to prevent toxic aggregation and neurodegeneration. Dimerization quality control further improves proteostasis by eliminating complexes of aberrant composition, but how it detects incorrect subunits remains unknown. Here we provide structural insight into target selection by SCF-FBXL17, a dimerization-quality-control E3 ligase that ubiquitylates and helps to degrade inactive heterodimers of BTB proteins while sparing functional homodimers. We find that SCF-FBXL17 disrupts aberrant BTB dimers that fail to stabilize an intermolecular β-sheet around a highly divergent β-strand of the BTB domain. Complex dissociation allows SCF-FBXL17 to wrap around a single BTB domain, resulting in robust ubiquitylation. SCF-FBXL17 therefore probes both shape and complementarity of BTB domains, a mechanism that is well suited to establish quality control of complex composition for recurrent interaction modules. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6w66.cif.gz 6w66.cif.gz | 174.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6w66.ent.gz pdb6w66.ent.gz | 110.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6w66.json.gz 6w66.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/w6/6w66 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/w6/6w66 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/w6/6w66 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/w6/6w66 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6w67C  6w68C  6w69C  6wcqC  1fqvS  2assS  4cxiS S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 18679.965 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SKP1, EMC19, OCP2, SKP1A, TCEB1L / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SKP1, EMC19, OCP2, SKP1A, TCEB1L / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 44970.043 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: FBXL17, FBL17, FBX13, FBXO13 / Cell line (production host): High Five / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: FBXL17, FBL17, FBX13, FBXO13 / Cell line (production host): High Five / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UF56 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UF56 |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 14861.131 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: BTB domain / Mutation: F64A/S172A Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KEAP1, INRF2, KIAA0132, KLHL19 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KEAP1, INRF2, KIAA0132, KLHL19 / Production host:  |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 3.43 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 64.16 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 291 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop Details: well solution 37.5 ul of 50 mM MgCl2, 100 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 30% (v/v) PEG MME 550 (E7 Hampton Index) + 12.5ul H2O mixed 1:1 with complex at 15mg/ml in 150 mM NaCl, 25 mM Tris/HCl pH 8.0 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  ALS ALS  / Beamline: 8.3.1 / Wavelength: 1.11583 Å / Beamline: 8.3.1 / Wavelength: 1.11583 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS PILATUS 6M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Dec 3, 2018 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation | Monochromator: S111 / Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1.11583 Å / Relative weight: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection | Resolution: 3.21→159.06 Å / Num. obs: 17752 / % possible obs: 99.6 % / Redundancy: 10.6 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 101.91 Å2 / CC1/2: 0.998 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.289 / Rpim(I) all: 0.093 / Rrim(I) all: 0.304 / Net I/σ(I): 7.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection shell | Diffraction-ID: 1
|
-Phasing
| Phasing | Method:  molecular replacement molecular replacement | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phasing MR |
|
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 4CXI, 2ASS, 1FQV Resolution: 3.21→79.53 Å / SU ML: 0.4835 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 1.34 / Phase error: 37.2992
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 119.12 Å2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 3.21→79.53 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj