[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6thd: Multiple Genomic RNA-Coat Protein Contacts Play Vital Roles in th... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6thd | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
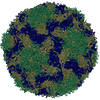
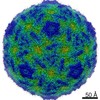
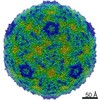
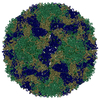
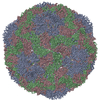
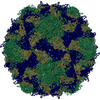
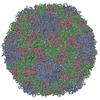
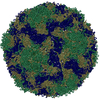
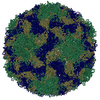
| Title | Multiple Genomic RNA-Coat Protein Contacts Play Vital Roles in the Assembly of Infectious Enterovirus-E | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | (Genome polyprotein) x 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRUS / BEV1 / enterovirus / picornavirus / RNA | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsymbiont-mediated suppression of host cytoplasmic pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway via inhibition of RIG-I activity / picornain 2A / symbiont-mediated suppression of host mRNA export from nucleus / symbiont genome entry into host cell via pore formation in plasma membrane / picornain 3C / T=pseudo3 icosahedral viral capsid / host cell cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / ribonucleoside triphosphate phosphatase activity / nucleoside-triphosphate phosphatase / channel activity ...symbiont-mediated suppression of host cytoplasmic pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway via inhibition of RIG-I activity / picornain 2A / symbiont-mediated suppression of host mRNA export from nucleus / symbiont genome entry into host cell via pore formation in plasma membrane / picornain 3C / T=pseudo3 icosahedral viral capsid / host cell cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / ribonucleoside triphosphate phosphatase activity / nucleoside-triphosphate phosphatase / channel activity / monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / DNA replication / RNA helicase activity / endocytosis involved in viral entry into host cell / symbiont-mediated activation of host autophagy / RNA-directed RNA polymerase / cysteine-type endopeptidase activity / viral RNA genome replication / RNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / DNA-templated transcription / virion attachment to host cell / host cell nucleus / structural molecule activity / proteolysis / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / ATP binding / membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species | Bovine enterovirus | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.23 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Chandler-Bostock, R. / Mata, C.P. / Bingham, R. / Dykeman, E.J. / Meng, B. / Tuthill, T.J. / Rowlands, D.J. / Ranson, N.A. / Twarock, R. / Stockley, P.G. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 7items United Kingdom, 7items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: PLoS Pathog / Year: 2020 Journal: PLoS Pathog / Year: 2020Title: Assembly of infectious enteroviruses depends on multiple, conserved genomic RNA-coat protein contacts. Authors: Rebecca Chandler-Bostock / Carlos P Mata / Richard J Bingham / Eric C Dykeman / Bo Meng / Tobias J Tuthill / David J Rowlands / Neil A Ranson / Reidun Twarock / Peter G Stockley /  Abstract: Picornaviruses are important viral pathogens, but despite extensive study, the assembly process of their infectious virions is still incompletely understood, preventing the development of anti-viral ...Picornaviruses are important viral pathogens, but despite extensive study, the assembly process of their infectious virions is still incompletely understood, preventing the development of anti-viral strategies targeting this essential part of the life cycle. We report the identification, via RNA SELEX and bioinformatics, of multiple RNA sites across the genome of a typical enterovirus, enterovirus-E (EV-E), that each have affinity for the cognate viral capsid protein (CP) capsomer. Many of these sites are evolutionarily conserved across known EV-E variants, suggesting they play essential functional roles. Cryo-electron microscopy was used to reconstruct the EV-E particle at ~2.2 Å resolution, revealing extensive density for the genomic RNA. Relaxing the imposed symmetry within the reconstructed particles reveals multiple RNA-CP contacts, a first for any picornavirus. Conservative mutagenesis of the individual RNA-contacting amino acid side chains in EV-E, many of which are conserved across the enterovirus family including poliovirus, is lethal but does not interfere with replication or translation. Anti-EV-E and anti-poliovirus aptamers share sequence similarities with sites distributed across the poliovirus genome. These data are consistent with the hypothesis that these RNA-CP contacts are RNA Packaging Signals (PSs) that play vital roles in assembly and suggest that the RNA PSs are evolutionarily conserved between pathogens within the family, augmenting the current protein-only assembly paradigm for this family of viruses. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6thd.cif.gz 6thd.cif.gz | 157 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6thd.ent.gz pdb6thd.ent.gz | 121.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6thd.json.gz 6thd.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/th/6thd https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/th/6thd ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/th/6thd ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/th/6thd | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 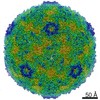 10504MC 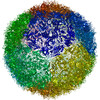 6thnC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10341 (Title: Multiple Genomic RNA-Coat Protein Contacts Play Vital Roles in the Assembly of Infectious Enterovirus-E EMPIAR-10341 (Title: Multiple Genomic RNA-Coat Protein Contacts Play Vital Roles in the Assembly of Infectious Enterovirus-EData size: 635.4 Data #1: Motion corrected micrographs of BEV1 [micrographs - single frame] Data #2: Polished particles of BEV1 [picked particles - single frame - processed]) |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | x 60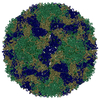
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 | x 5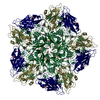
|
| 4 | x 6
|
| 5 | 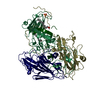
|
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: (Schoenflies symbol: I (icosahedral)) |
- Components
Components
-Protein , 4 types, 4 molecules 1234
| #1: Protein | Mass: 31280.955 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Bovine enterovirus (strain VG-5-27) Bovine enterovirus (strain VG-5-27)References: UniProt: P12915, picornain 2A, nucleoside-triphosphate phosphatase, picornain 3C, RNA-directed RNA polymerase |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 27325.604 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Bovine enterovirus (strain VG-5-27) Bovine enterovirus (strain VG-5-27)References: UniProt: P12915, picornain 2A, nucleoside-triphosphate phosphatase, picornain 3C, RNA-directed RNA polymerase |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 26627.221 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Bovine enterovirus (strain VG-5-27) Bovine enterovirus (strain VG-5-27)References: UniProt: P12915, picornain 2A, nucleoside-triphosphate phosphatase, picornain 3C, RNA-directed RNA polymerase |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 5619.105 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Bovine enterovirus (strain VG-5-27) Bovine enterovirus (strain VG-5-27)References: UniProt: P12915, picornain 2A, nucleoside-triphosphate phosphatase, picornain 3C, RNA-directed RNA polymerase |
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 101 molecules 




| #5: Chemical | | #6: Chemical | #7: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Bovine enterovirus (strain VG-5-27) / Type: VIRUS / Entity ID: #1-#4 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Bovine enterovirus (strain VG-5-27) Bovine enterovirus (strain VG-5-27) |
| Details of virus | Empty: NO / Enveloped: NO / Isolate: STRAIN / Type: VIRION |
| Virus shell | Triangulation number (T number): 3 |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 / Details: PBS |
| Buffer component | Formula: PBS |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Instrument: LEICA EM GP / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: OTHER / Nominal magnification: 75000 X / Nominal defocus max: 3500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 750 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 1 sec. / Electron dose: 49.5 e/Å2 / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 8785 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.15.2_3472: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 260348 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: I (icosahedral) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.23 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 105723 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 1BEV Accession code: 1BEV / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj