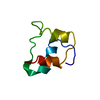
登録情報 データベース : PDB / ID : 6oizタイトル Amyloid-Beta (20-34) wild type Amyloid beta A4 protein キーワード / / 機能・相同性 分子機能 ドメイン・相同性 構成要素
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / 生物種 Homo sapiens (ヒト)手法 / / / 解像度 : 1.1 Å Model details Protofilament structure of Amyloid-beta 20-34 with the age-associated post-translational ... Protofilament structure of Amyloid-beta 20-34 with the age-associated post-translational modification of aspartate isomerization at position 23 データ登録者 Sawaya, M.R. / Warmack, R.A. / Zee, C.T. / Gonen, T. / Clarke, S.G. / Eisenberg, D.S. 資金援助 組織 認可番号 国 National Institutes of Health/National Center for Research Resources (NIH/NCRR) 5T32GM008496 National Science Foundation (NSF, United States) MCB-1714569 National Institutes of Health/National Center for Research Resources (NIH/NCRR) GM-007185 Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI)
ジャーナル : Nat Commun / 年 : 2019タイトル : Structure of amyloid-β (20-34) with Alzheimer's-associated isomerization at Asp23 reveals a distinct protofilament interface.著者 : Rebeccah A Warmack / David R Boyer / Chih-Te Zee / Logan S Richards / Michael R Sawaya / Duilio Cascio / Tamir Gonen / David S Eisenberg / Steven G Clarke / 要旨 : Amyloid-β (Aβ) harbors numerous posttranslational modifications (PTMs) that may affect Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathogenesis. Here we present the 1.1 Å resolution MicroED structure of an Aβ 20- ... Amyloid-β (Aβ) harbors numerous posttranslational modifications (PTMs) that may affect Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathogenesis. Here we present the 1.1 Å resolution MicroED structure of an Aβ 20-34 fibril with and without the disease-associated PTM, L-isoaspartate, at position 23 (L-isoAsp23). Both wild-type and L-isoAsp23 protofilaments adopt β-helix-like folds with tightly packed cores, resembling the cores of full-length fibrillar Aβ structures, and both self-associate through two distinct interfaces. One of these is a unique Aβ interface strengthened by the isoaspartyl modification. Powder diffraction patterns suggest a similar structure may be adopted by protofilaments of an analogous segment containing the heritable Iowa mutation, Asp23Asn. Consistent with its early onset phenotype in patients, Asp23Asn accelerates aggregation of Aβ 20-34, as does the L-isoAsp23 modification. These structures suggest that the enhanced amyloidogenicity of the modified Aβ segments may also reduce the concentration required to achieve nucleation and therefore help spur the pathogenesis of AD. 履歴 登録 2019年4月10日 登録サイト / 処理サイト 改定 1.0 2019年8月7日 Provider / タイプ 改定 1.1 2019年11月20日 Group / カテゴリ / Item 改定 1.2 2022年9月7日 Group / Database references / カテゴリ / em_diffraction_shellItem _database_2.pdbx_DOI / _database_2.pdbx_database_accession ... _database_2.pdbx_DOI / _database_2.pdbx_database_accession / _em_diffraction_shell.em_diffraction_stats_id / _em_diffraction_shell.id 改定 1.3 2024年5月15日 Group / カテゴリ / chem_comp_bond
すべて表示 表示を減らす
 データを開く
データを開く 基本情報
基本情報 要素
要素 キーワード
キーワード 機能・相同性情報
機能・相同性情報 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) データ登録者
データ登録者 米国, 4件
米国, 4件  引用
引用 ジャーナル: Nat Commun / 年: 2019
ジャーナル: Nat Commun / 年: 2019
 構造の表示
構造の表示 ムービービューア
ムービービューア Molmil
Molmil Jmol/JSmol
Jmol/JSmol ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク ダウンロード
ダウンロード 6oiz.cif.gz
6oiz.cif.gz PDBx/mmCIF形式
PDBx/mmCIF形式 pdb6oiz.ent.gz
pdb6oiz.ent.gz PDB形式
PDB形式 6oiz.json.gz
6oiz.json.gz PDBx/mmJSON形式
PDBx/mmJSON形式 その他のダウンロード
その他のダウンロード 6oiz_validation.pdf.gz
6oiz_validation.pdf.gz wwPDB検証レポート
wwPDB検証レポート 6oiz_full_validation.pdf.gz
6oiz_full_validation.pdf.gz 6oiz_validation.xml.gz
6oiz_validation.xml.gz 6oiz_validation.cif.gz
6oiz_validation.cif.gz https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oi/6oiz
https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oi/6oiz ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oi/6oiz
ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oi/6oiz リンク
リンク 集合体
集合体

 要素
要素 Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: L7XCZ9, UniProt: P05067*PLUS
Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: L7XCZ9, UniProt: P05067*PLUS 試料調製
試料調製 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト)
 FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 200 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM
FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 200 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM 解析
解析 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー













 PDBj
PDBj