+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5g04 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the human APC-Cdc20-Hsl1 complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CELL CYCLE / PHOSPHORYLATION / MITOSIS / UBIQUITINATION | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of diacylglycerol biosynthetic process / protein localization to septin ring / mitotic morphogenesis checkpoint signaling / cellular bud neck septin ring / metaphase/anaphase transition of cell cycle / metaphase/anaphase transition of meiosis I / Inhibition of the proteolytic activity of APC/C required for the onset of anaphase by mitotic spindle checkpoint components / mitotic checkpoint complex / positive regulation of anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / positive regulation of synapse maturation ...negative regulation of diacylglycerol biosynthetic process / protein localization to septin ring / mitotic morphogenesis checkpoint signaling / cellular bud neck septin ring / metaphase/anaphase transition of cell cycle / metaphase/anaphase transition of meiosis I / Inhibition of the proteolytic activity of APC/C required for the onset of anaphase by mitotic spindle checkpoint components / mitotic checkpoint complex / positive regulation of anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / positive regulation of synapse maturation / regulation of meiotic nuclear division / Conversion from APC/C:Cdc20 to APC/C:Cdh1 in late anaphase / regulation of mitotic cell cycle spindle assembly checkpoint / regulation of dendrite development / Inactivation of APC/C via direct inhibition of the APC/C complex / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of mitotic proteins / positive regulation of synaptic plasticity / anaphase-promoting complex / Phosphorylation of Emi1 / Aberrant regulation of mitotic exit in cancer due to RB1 defects / regulation of meiotic cell cycle / anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / metaphase/anaphase transition of mitotic cell cycle / protein branched polyubiquitination / Phosphorylation of the APC/C / anaphase-promoting complex binding / regulation of exit from mitosis / positive regulation of dendrite morphogenesis / cellular bud neck / positive regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / positive regulation of ubiquitin protein ligase activity / ubiquitin ligase activator activity / protein K11-linked ubiquitination / regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / ubiquitin-ubiquitin ligase activity / mitotic metaphase chromosome alignment / mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint signaling / Regulation of APC/C activators between G1/S and early anaphase / Transcriptional Regulation by VENTX / cullin family protein binding / mitotic spindle assembly / enzyme-substrate adaptor activity / positive regulation of axon extension / ubiquitin-like ligase-substrate adaptor activity / protein K48-linked ubiquitination / heterochromatin / intercellular bridge / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / nuclear periphery / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / regulation of mitotic cell cycle / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Securin / SCF-beta-TrCP mediated degradation of Emi1 / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / Cdc20:Phospho-APC/C mediated degradation of Cyclin A / protein catabolic process / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / APC/C:Cdh1 mediated degradation of Cdc20 and other APC/C:Cdh1 targeted proteins in late mitosis/early G1 / G protein-coupled receptor binding / brain development / kinetochore / CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / histone deacetylase binding / spindle / neuron projection development / spindle pole / ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / mitotic spindle / ubiquitin protein ligase activity / Separation of Sister Chromatids / nervous system development / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / mitotic cell cycle / microtubule cytoskeleton / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / protein phosphatase binding / molecular adaptor activity / cell differentiation / protein kinase activity / non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase / regulation of cell cycle / Ub-specific processing proteases / protein ubiquitination / negative regulation of gene expression / cell division / protein serine kinase activity / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / protein serine/threonine kinase activity / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / centrosome / nucleolus Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  HOMO SAPIENS (human) HOMO SAPIENS (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhang, S. / Chang, L. / Alfieri, C. / Zhang, Z. / Yang, J. / Maslen, S. / Skehel, M. / Barford, D. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2016 Journal: Nature / Year: 2016Title: Molecular mechanism of APC/C activation by mitotic phosphorylation. Authors: Suyang Zhang / Leifu Chang / Claudio Alfieri / Ziguo Zhang / Jing Yang / Sarah Maslen / Mark Skehel / David Barford /  Abstract: In eukaryotes, the anaphase-promoting complex (APC/C, also known as the cyclosome) regulates the ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis of specific cell-cycle proteins to coordinate chromosome segregation ...In eukaryotes, the anaphase-promoting complex (APC/C, also known as the cyclosome) regulates the ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis of specific cell-cycle proteins to coordinate chromosome segregation in mitosis and entry into the G1 phase. The catalytic activity of the APC/C and its ability to specify the destruction of particular proteins at different phases of the cell cycle are controlled by its interaction with two structurally related coactivator subunits, Cdc20 and Cdh1. Coactivators recognize substrate degrons, and enhance the affinity of the APC/C for its cognate E2 (refs 4-6). During mitosis, cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) and polo-like kinase (Plk) control Cdc20- and Cdh1-mediated activation of the APC/C. Hyperphosphorylation of APC/C subunits, notably Apc1 and Apc3, is required for Cdc20 to activate the APC/C, whereas phosphorylation of Cdh1 prevents its association with the APC/C. Since both coactivators associate with the APC/C through their common C-box and Ile-Arg tail motifs, the mechanism underlying this differential regulation is unclear, as is the role of specific APC/C phosphorylation sites. Here, using cryo-electron microscopy and biochemical analysis, we define the molecular basis of how phosphorylation of human APC/C allows for its control by Cdc20. An auto-inhibitory segment of Apc1 acts as a molecular switch that in apo unphosphorylated APC/C interacts with the C-box binding site and obstructs engagement of Cdc20. Phosphorylation of the auto-inhibitory segment displaces it from the C-box-binding site. Efficient phosphorylation of the auto-inhibitory segment, and thus relief of auto-inhibition, requires the recruitment of Cdk-cyclin in complex with a Cdk regulatory subunit (Cks) to a hyperphosphorylated loop of Apc3. We also find that the small-molecule inhibitor, tosyl-l-arginine methyl ester, preferentially suppresses APC/C(Cdc20) rather than APC/C(Cdh1), and interacts with the binding sites of both the C-box and Ile-Arg tail motifs. Our results reveal the mechanism for the regulation of mitotic APC/C by phosphorylation and provide a rationale for the development of selective inhibitors of this state. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5g04.cif.gz 5g04.cif.gz | 1.6 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5g04.ent.gz pdb5g04.ent.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5g04.json.gz 5g04.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g0/5g04 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g0/5g04 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g0/5g04 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g0/5g04 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  3385MC  3386C  3387C  3388C  3389C 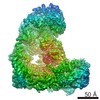 3390C  5g05C C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 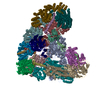
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-ANAPHASE-PROMOTING COMPLEX SUBUNIT ... , 11 types, 13 molecules ABDEGWILMNOXY
| #1: Protein | Mass: 216725.469 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host:  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 9854.647 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host:  | ||||||||||||
| #4: Protein | Mass: 14286.727 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host:  | ||||||||||||
| #5: Protein | Mass: 11677.995 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host:  | ||||||||||||
| #7: Protein | Mass: 9793.999 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host:  #8: Protein | | Mass: 92219.227 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host:  #10: Protein | | Mass: 21124.949 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host:  #11: Protein | | Mass: 8528.309 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host:  #12: Protein | | Mass: 93938.977 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host:  #13: Protein | | Mass: 85179.766 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host:  #16: Protein | Mass: 66929.367 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host:  |
-CELL DIVISION CYCLE PROTEIN ... , 4 types, 7 molecules CPFHJKR
| #3: Protein | Mass: 68921.031 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host:  #6: Protein | Mass: 91973.125 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host:  #9: Protein | Mass: 71747.516 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PF1, PU1 / Production host:  #14: Protein | | Mass: 54796.508 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: MODIFIED PFASTBAC HTA / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: MODIFIED PFASTBAC HTA / Production host:  |
|---|
-Protein / Non-polymers , 2 types, 4 molecules S

| #15: Protein | Mass: 23658.162 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: RESIDUES 667-872 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Plasmid: PET28A / Production host:  References: UniProt: P34244, non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase |
|---|---|
| #17: Chemical |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: RECOMBINANT APC-CDC20- HSL1 COMPLEX / Type: COMPLEX |
|---|---|
| Buffer solution | Name: 20MM HEPES, 150MM NACL, 0. 5MM TCEP / pH: 8 / Details: 20MM HEPES, 150MM NACL, 0. 5MM TCEP |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.15 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Details: CARBON |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Details: LIQUID ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI POLARA 300 / Date: Oct 30, 2015 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 78000 X / Calibrated magnification: 78000 X / Nominal defocus max: 4000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 2000 nm / Cs: 2 mm |
| Specimen holder | Temperature: 100 K |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 27 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 179660 / Refinement type: HALF-MAPS REFINED INDEPENDENTLY / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 3.9 Å | ||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Highest resolution: 4 Å
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





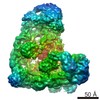
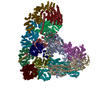

 PDBj
PDBj

















