[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
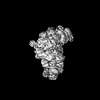
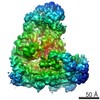
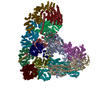
Yorodumi- EMDB-3433: Anaphase-promoting complex/Cyclosome (APC/C)-CDH1-UBE2S-Ubiquitin... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-3433 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
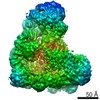
| Title | Anaphase-promoting complex/Cyclosome (APC/C)-CDH1-UBE2S-Ubiquitin (variant)-substrate | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Anaphase-promoting complex/Cyclosome (APC/C)-CDH1-UBE2S-Ubiquitin (variant)-substrate | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Anaphase Promoting Complex / ubiquitin ligation | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of diacylglycerol biosynthetic process / protein localization to septin ring / mitotic morphogenesis checkpoint signaling / cellular bud neck septin ring / positive regulation of anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / protein K29-linked ubiquitination / free ubiquitin chain polymerization / positive regulation of synapse maturation / regulation of meiotic nuclear division / Conversion from APC/C:Cdc20 to APC/C:Cdh1 in late anaphase ...negative regulation of diacylglycerol biosynthetic process / protein localization to septin ring / mitotic morphogenesis checkpoint signaling / cellular bud neck septin ring / positive regulation of anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / protein K29-linked ubiquitination / free ubiquitin chain polymerization / positive regulation of synapse maturation / regulation of meiotic nuclear division / Conversion from APC/C:Cdc20 to APC/C:Cdh1 in late anaphase / regulation of mitotic cell cycle spindle assembly checkpoint / Inactivation of APC/C via direct inhibition of the APC/C complex / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of mitotic proteins / positive regulation of synaptic plasticity / anaphase-promoting complex / Phosphorylation of Emi1 / Aberrant regulation of mitotic exit in cancer due to RB1 defects / regulation of meiotic cell cycle / anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / metaphase/anaphase transition of mitotic cell cycle / protein branched polyubiquitination / lens fiber cell differentiation / Phosphorylation of the APC/C / anaphase-promoting complex binding / regulation of exit from mitosis / cellular bud neck / protein K6-linked ubiquitination / positive regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / positive regulation of ubiquitin protein ligase activity / exit from mitosis / ubiquitin ligase activator activity / protein K27-linked ubiquitination / positive regulation of dendrite morphogenesis / protein K11-linked ubiquitination / hypothalamus gonadotrophin-releasing hormone neuron development / female meiosis I / positive regulation of protein monoubiquitination / fat pad development / regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / mitochondrion transport along microtubule / ubiquitin-ubiquitin ligase activity / E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme / mitotic metaphase chromosome alignment / female gonad development / seminiferous tubule development / mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / Regulation of APC/C activators between G1/S and early anaphase / ubiquitin conjugating enzyme activity / male meiosis I / Transcriptional Regulation by VENTX / negative regulation of cellular senescence / cullin family protein binding / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator / protein K63-linked ubiquitination / enzyme-substrate adaptor activity / positive regulation of axon extension / ubiquitin-like ligase-substrate adaptor activity / Cyclin A:Cdk2-associated events at S phase entry / protein K48-linked ubiquitination / energy homeostasis / intercellular bridge / heterochromatin / neuron projection morphogenesis / regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / Maturation of protein E / Maturation of protein E / ER Quality Control Compartment (ERQC) / Myoclonic epilepsy of Lafora / FLT3 signaling by CBL mutants / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD Domain Mutants / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex / Prevention of phagosomal-lysosomal fusion / Alpha-protein kinase 1 signaling pathway / Glycogen synthesis / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / Endosomal Sorting Complex Required For Transport (ESCRT) / Membrane binding and targetting of GAG proteins / Negative regulation of FLT3 / Regulation of TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE)-mediated activation of IRF3, IRF7 / PTK6 Regulates RTKs and Their Effectors AKT1 and DOK1 / Regulation of TBK1, IKKε-mediated activation of IRF3, IRF7 upon TLR3 ligation / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / NOTCH2 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / TICAM1,TRAF6-dependent induction of TAK1 complex / TICAM1-dependent activation of IRF3/IRF7 / nuclear periphery / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / regulation of mitotic cell cycle / Regulation of FZD by ubiquitination / Downregulation of ERBB4 signaling / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / InlA-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cells / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation in TLR7/8 or 9 signaling / Regulation of pyruvate metabolism / TRAF6-mediated induction of TAK1 complex within TLR4 complex / regulation of neuron apoptotic process / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / Regulation of innate immune responses to cytosolic DNA Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Brown N / VanderLinden R / Watson E / Weissmann F / Ordureau A / Wu K-P / Yu S / Mercedi P / Harrison J / Davidson I ...Brown N / VanderLinden R / Watson E / Weissmann F / Ordureau A / Wu K-P / Yu S / Mercedi P / Harrison J / Davidson I / Coudevylle R / Lu Y / Dube P / Brunner M / Grace CRR / Miller D / Haselbach D / Jarvis M / Yamaguchi M / Yanishevski D / Petzold G / Sidhu S / Kuhlman B / Kirschner M / Harper JW / Peters J-M / Stark H / Schulman BA | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2016 Journal: Cell / Year: 2016Title: Dual RING E3 Architectures Regulate Multiubiquitination and Ubiquitin Chain Elongation by APC/C. Authors: Nicholas G Brown / Ryan VanderLinden / Edmond R Watson / Florian Weissmann / Alban Ordureau / Kuen-Phon Wu / Wei Zhang / Shanshan Yu / Peter Y Mercredi / Joseph S Harrison / Iain F Davidson ...Authors: Nicholas G Brown / Ryan VanderLinden / Edmond R Watson / Florian Weissmann / Alban Ordureau / Kuen-Phon Wu / Wei Zhang / Shanshan Yu / Peter Y Mercredi / Joseph S Harrison / Iain F Davidson / Renping Qiao / Ying Lu / Prakash Dube / Michael R Brunner / Christy R R Grace / Darcie J Miller / David Haselbach / Marc A Jarvis / Masaya Yamaguchi / David Yanishevski / Georg Petzold / Sachdev S Sidhu / Brian Kuhlman / Marc W Kirschner / J Wade Harper / Jan-Michael Peters / Holger Stark / Brenda A Schulman /     Abstract: Protein ubiquitination involves E1, E2, and E3 trienzyme cascades. E2 and RING E3 enzymes often collaborate to first prime a substrate with a single ubiquitin (UB) and then achieve different forms of ...Protein ubiquitination involves E1, E2, and E3 trienzyme cascades. E2 and RING E3 enzymes often collaborate to first prime a substrate with a single ubiquitin (UB) and then achieve different forms of polyubiquitination: multiubiquitination of several sites and elongation of linkage-specific UB chains. Here, cryo-EM and biochemistry show that the human E3 anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) and its two partner E2s, UBE2C (aka UBCH10) and UBE2S, adopt specialized catalytic architectures for these two distinct forms of polyubiquitination. The APC/C RING constrains UBE2C proximal to a substrate and simultaneously binds a substrate-linked UB to drive processive multiubiquitination. Alternatively, during UB chain elongation, the RING does not bind UBE2S but rather lures an evolving substrate-linked UB to UBE2S positioned through a cullin interaction to generate a Lys11-linked chain. Our findings define mechanisms of APC/C regulation, and establish principles by which specialized E3-E2-substrate-UB architectures control different forms of polyubiquitination. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_3433.map.gz emd_3433.map.gz | 57.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-3433-v30.xml emd-3433-v30.xml emd-3433.xml emd-3433.xml | 9.9 KB 9.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_3433.png emd_3433.png | 436 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3433 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3433 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3433 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3433 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5l9tMC  3432C  5jg6C  5l9uC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_3433.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 62.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_3433.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 62.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Anaphase-promoting complex/Cyclosome (APC/C)-CDH1-UBE2S-Ubiquitin (variant)-substrate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.57 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Anaphase-promoting complex/Cyclosome (APC/C)-CDH1-UBE2S-Ubiquitin...
| Entire | Name: Anaphase-promoting complex/Cyclosome (APC/C)-CDH1-UBE2S-Ubiquitin (variant)-substrate |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Anaphase-promoting complex/Cyclosome (APC/C)-CDH1-UBE2S-Ubiquitin...
| Supramolecule | Name: Anaphase-promoting complex/Cyclosome (APC/C)-CDH1-UBE2S-Ubiquitin (variant)-substrate type: sample / ID: 1000 / Number unique components: 1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 1.5 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Anaphase Promoting Complex
| Macromolecule | Name: Anaphase Promoting Complex / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 / Details: 50 mM Hepes, 150 mM NaCl, 2 mM MgCl2 |
| Grid | Details: 200 mesh copper grids, quantifoil with thin carbon support |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Date | Jul 31, 2015 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Number real images: 2070 / Average electron dose: 40 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 89000 / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 0.0001 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.7 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| CTF correction | Details: each particle |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 6.0 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Number images used: 125390 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


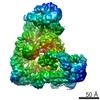
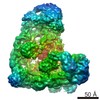
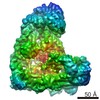
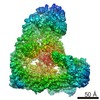






























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)