+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 | データベース: PDB / ID: 6q6h | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
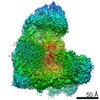
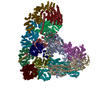
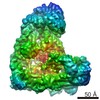
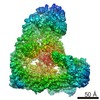
| タイトル | Cryo-EM structure of the APC/C-Cdc20-Cdk2-cyclinA2-Cks2 complex, the D2 box class | |||||||||
 要素 要素 |
| |||||||||
 キーワード キーワード | CELL CYCLE / spindle assembly checkpoint / anaphase-promoting complex / cyclin / ubiquitination | |||||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報metaphase/anaphase transition of cell cycle / metaphase/anaphase transition of meiosis I / Inhibition of the proteolytic activity of APC/C required for the onset of anaphase by mitotic spindle checkpoint components / mitotic checkpoint complex / positive regulation of anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / positive regulation of synapse maturation / regulation of meiotic nuclear division / Conversion from APC/C:Cdc20 to APC/C:Cdh1 in late anaphase / regulation of mitotic cell cycle spindle assembly checkpoint / regulation of dendrite development ...metaphase/anaphase transition of cell cycle / metaphase/anaphase transition of meiosis I / Inhibition of the proteolytic activity of APC/C required for the onset of anaphase by mitotic spindle checkpoint components / mitotic checkpoint complex / positive regulation of anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / positive regulation of synapse maturation / regulation of meiotic nuclear division / Conversion from APC/C:Cdc20 to APC/C:Cdh1 in late anaphase / regulation of mitotic cell cycle spindle assembly checkpoint / regulation of dendrite development / Inactivation of APC/C via direct inhibition of the APC/C complex / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of mitotic proteins / positive regulation of synaptic plasticity / : / anaphase-promoting complex / cyclin A2-CDK1 complex / Phosphorylation of Emi1 / Aberrant regulation of mitotic exit in cancer due to RB1 defects / regulation of meiotic cell cycle / anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / metaphase/anaphase transition of mitotic cell cycle / protein branched polyubiquitination / cell cycle G1/S phase transition / cellular response to luteinizing hormone stimulus / Phosphorylation of the APC/C / anaphase-promoting complex binding / regulation of exit from mitosis / positive regulation of dendrite morphogenesis / positive regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / positive regulation of ubiquitin protein ligase activity / Transcription of E2F targets under negative control by p107 (RBL1) and p130 (RBL2) in complex with HDAC1 / cellular response to leptin stimulus / ubiquitin ligase activator activity / male pronucleus / female pronucleus / protein K11-linked ubiquitination / cellular response to cocaine / response to glucagon / regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity / positive regulation of DNA biosynthetic process / mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / ubiquitin-ubiquitin ligase activity / mitotic metaphase chromosome alignment / cellular response to insulin-like growth factor stimulus / mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint signaling / cyclin A2-CDK2 complex / G2 Phase / p53-Dependent G1 DNA Damage Response / Regulation of APC/C activators between G1/S and early anaphase / regulation of DNA replication / microtubule organizing center / Transcriptional Regulation by VENTX / G0 and Early G1 / cochlea development / cullin family protein binding / animal organ regeneration / Telomere Extension By Telomerase / mitotic spindle assembly / enzyme-substrate adaptor activity / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Genes Involved in G1 Cell Cycle Arrest / positive regulation of axon extension / ubiquitin-like ligase-substrate adaptor activity / Cyclin A:Cdk2-associated events at S phase entry / protein K48-linked ubiquitination / heterochromatin / Cyclin A/B1/B2 associated events during G2/M transition / cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex / intercellular bridge / cellular response to platelet-derived growth factor stimulus / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / cellular response to nitric oxide / Mitotic Prometaphase / nuclear periphery / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / post-translational protein modification / regulation of mitotic cell cycle / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Securin / SCF-beta-TrCP mediated degradation of Emi1 / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / cellular response to estradiol stimulus / Cdc20:Phospho-APC/C mediated degradation of Cyclin A / G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / APC/C:Cdh1 mediated degradation of Cdc20 and other APC/C:Cdh1 targeted proteins in late mitosis/early G1 / G protein-coupled receptor binding / brain development / kinetochore / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / histone deacetylase binding / SCF(Skp2)-mediated degradation of p27/p21 / spindle / positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation / neuron projection development 類似検索 - 分子機能 | |||||||||
| 生物種 |  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) | |||||||||
| 手法 | 電子顕微鏡法 / 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 3.2 Å | |||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Zhang, S. / Barford, D. | |||||||||
| 資金援助 |  英国, 2件 英国, 2件
| |||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Nat Commun / 年: 2019 ジャーナル: Nat Commun / 年: 2019タイトル: Cyclin A2 degradation during the spindle assembly checkpoint requires multiple binding modes to the APC/C. 著者: Suyang Zhang / Thomas Tischer / David Barford /   要旨: The anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) orchestrates cell cycle progression by controlling the temporal degradation of specific cell cycle regulators. Although cyclin A2 and cyclin B1 are ...The anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) orchestrates cell cycle progression by controlling the temporal degradation of specific cell cycle regulators. Although cyclin A2 and cyclin B1 are both targeted for degradation by the APC/C, during the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), the mitotic checkpoint complex (MCC) represses APC/C's activity towards cyclin B1, but not cyclin A2. Through structural, biochemical and in vivo analysis, we identify a non-canonical D box (D2) that is critical for cyclin A2 ubiquitination in vitro and degradation in vivo. During the SAC, cyclin A2 is ubiquitinated by the repressed APC/C-MCC, mediated by the cooperative engagement of its KEN and D2 boxes, ABBA motif, and the cofactor Cks. Once the SAC is satisfied, cyclin A2 binds APC/C-Cdc20 through two mutually exclusive binding modes, resulting in differential ubiquitination efficiency. Our findings reveal that a single substrate can engage an E3 ligase through multiple binding modes, affecting its degradation timing and efficiency. | |||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| ムービー |
 ムービービューア ムービービューア |
|---|---|
| 構造ビューア | 分子:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
- ダウンロード
ダウンロード
| PDBx/mmCIF形式 |  6q6h.cif.gz 6q6h.cif.gz | 1.5 MB | 表示 |  PDBx/mmCIF形式 PDBx/mmCIF形式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB形式 |  pdb6q6h.ent.gz pdb6q6h.ent.gz | 1.2 MB | 表示 |  PDB形式 PDB形式 |
| PDBx/mmJSON形式 |  6q6h.json.gz 6q6h.json.gz | ツリー表示 |  PDBx/mmJSON形式 PDBx/mmJSON形式 | |
| その他 |  その他のダウンロード その他のダウンロード |
-検証レポート
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q6/6q6h https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q6/6q6h ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q6/6q6h ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q6/6q6h | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-関連構造データ
- リンク
リンク
- 集合体
集合体
| 登録構造単位 | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- 要素
要素
-Anaphase-promoting complex subunit ... , 10種, 12分子 LDNIOCGWMHYZ
| #1: タンパク質 | 分子量: 21282.143 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: ANAPC10, APC10 / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: ANAPC10, APC10 / 発現宿主:  unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q9UM13 unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q9UM13 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: タンパク質 | 分子量: 14286.727 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: ANAPC15, C11orf51, HSPC020 / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: ANAPC15, C11orf51, HSPC020 / 発現宿主:  unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: P60006 unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: P60006 | ||||||
| #4: タンパク質 | 分子量: 93938.977 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: ANAPC2, APC2, KIAA1406 / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: ANAPC2, APC2, KIAA1406 / 発現宿主:  unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q9UJX6 unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q9UJX6 | ||||||
| #5: タンパク質 | 分子量: 92219.227 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: ANAPC4, APC4 / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: ANAPC4, APC4 / 発現宿主:  unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q9UJX5 unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q9UJX5 | ||||||
| #6: タンパク質 | 分子量: 85179.766 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: ANAPC5, APC5 / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: ANAPC5, APC5 / 発現宿主:  unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q9UJX4 unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q9UJX4 | ||||||
| #8: タンパク質 | 分子量: 9854.647 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: ANAPC11, HSPC214 / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: ANAPC11, HSPC214 / 発現宿主:  unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q9NYG5 unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q9NYG5 | ||||||
| #9: タンパク質 | 分子量: 9793.999 Da / 分子数: 2 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: CDC26, ANAPC12, C9orf17 / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: CDC26, ANAPC12, C9orf17 / 発現宿主:  unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q8NHZ8 unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q8NHZ8#10: タンパク質 | | 分子量: 8528.309 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: ANAPC13 / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: ANAPC13 / 発現宿主:  unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q9BS18 unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q9BS18#11: タンパク質 | | 分子量: 11677.995 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: ANAPC16, C10orf104, CENP-27 / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: ANAPC16, C10orf104, CENP-27 / 発現宿主:  unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q96DE5 unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q96DE5#13: タンパク質 | 分子量: 66929.367 Da / 分子数: 2 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: ANAPC7, APC7 / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: ANAPC7, APC7 / 発現宿主:  unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q9UJX3 unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q9UJX3 |
-タンパク質 , 2種, 2分子 AS
| #3: タンパク質 | 分子量: 207240.234 Da / 分子数: 1 / Mutation: deletion of residues 307-395 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 発現宿主:  unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q9H1A4*PLUS unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q9H1A4*PLUS |
|---|---|
| #16: タンパク質 | 分子量: 44427.766 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: CCNA2, CCN1, CCNA / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: CCNA2, CCN1, CCNA / 発現宿主:  |
-Cell division cycle protein ... , 4種, 7分子 KQJPUVR
| #7: タンパク質 | 分子量: 71747.516 Da / 分子数: 2 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: CDC16, ANAPC6 / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: CDC16, ANAPC6 / 発現宿主:  unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q13042 unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q13042#12: タンパク質 | 分子量: 91973.125 Da / 分子数: 2 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: CDC27, ANAPC3, D0S1430E, D17S978E / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: CDC27, ANAPC3, D0S1430E, D17S978E / 発現宿主:  unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: P30260 unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: P30260#14: タンパク質 | 分子量: 68921.031 Da / 分子数: 2 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: CDC23, ANAPC8 / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: CDC23, ANAPC8 / 発現宿主:  unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q9UJX2 unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q9UJX2#15: タンパク質 | | 分子量: 54796.508 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: CDC20 / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: CDC20 / 発現宿主:  unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q12834 unidentified baculovirus (ウイルス) / 参照: UniProt: Q12834 |
|---|
-実験情報
-実験
| 実験 | 手法: 電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
| EM実験 | 試料の集合状態: PARTICLE / 3次元再構成法: 単粒子再構成法 |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 構成要素 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分子量 | 値: 1.3 MDa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 由来(天然) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 由来(組換発現) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 緩衝液 | pH: 8 / 詳細: 20mM Hepes, 150mM NaCl, 0.5mM TCEP | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 試料 | 濃度: 0.15 mg/ml / 包埋: NO / シャドウイング: NO / 染色: NO / 凍結: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 急速凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE |
- 電子顕微鏡撮影
電子顕微鏡撮影
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| 顕微鏡 | モデル: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| 電子銃 | 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM |
| 電子レンズ | モード: BRIGHT FIELD |
| 撮影 | 電子線照射量: 28 e/Å2 フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- 解析
解析
| EMソフトウェア | 名称: RELION / バージョン: 3 / カテゴリ: 3次元再構成 |
|---|---|
| CTF補正 | タイプ: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
| 対称性 | 点対称性: C1 (非対称) |
| 3次元再構成 | 解像度: 3.2 Å / 解像度の算出法: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / 粒子像の数: 117044 / 対称性のタイプ: POINT |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー











 PDBj
PDBj


















