+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 4ui9 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
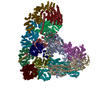
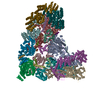
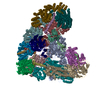
| Title | Atomic structure of the human Anaphase-Promoting Complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CELL CYCLE / UBIQUITINATION / APC/C / APC SUBUNITS / ANAPHASE PROMOTING COMPLEX | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of DNA endoreduplication / positive regulation of biomineral tissue development / negative regulation of meiotic nuclear division / positive regulation of mesenchymal stem cell migration / positive regulation of anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / negative regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / Mitotic Metaphase/Anaphase Transition / negative regulation of ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / positive regulation of synapse maturation / regulation of meiotic nuclear division ...negative regulation of DNA endoreduplication / positive regulation of biomineral tissue development / negative regulation of meiotic nuclear division / positive regulation of mesenchymal stem cell migration / positive regulation of anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / negative regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / Mitotic Metaphase/Anaphase Transition / negative regulation of ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / positive regulation of synapse maturation / regulation of meiotic nuclear division / Conversion from APC/C:Cdc20 to APC/C:Cdh1 in late anaphase / regulation of mitotic cell cycle spindle assembly checkpoint / Inactivation of APC/C via direct inhibition of the APC/C complex / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of mitotic proteins / positive regulation of synaptic plasticity / anaphase-promoting complex / Phosphorylation of Emi1 / regulation of meiotic cell cycle / Aberrant regulation of mitotic exit in cancer due to RB1 defects / anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / vesicle organization / protein branched polyubiquitination / metaphase/anaphase transition of mitotic cell cycle / lens fiber cell differentiation / Phosphorylation of the APC/C / anaphase-promoting complex binding / regulation of exit from mitosis / spindle assembly involved in female meiosis I / positive regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / positive regulation of ubiquitin protein ligase activity / ubiquitin ligase activator activity / positive regulation of dendrite morphogenesis / protein K11-linked ubiquitination / meiotic spindle / oocyte maturation / regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / molecular function inhibitor activity / ubiquitin-ubiquitin ligase activity / mitotic metaphase chromosome alignment / regulation of mitotic nuclear division / negative regulation of ubiquitin protein ligase activity / G1/S-Specific Transcription / mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / microtubule polymerization / Regulation of APC/C activators between G1/S and early anaphase / regulation of DNA replication / Transcriptional Regulation by VENTX / negative regulation of cellular senescence / cullin family protein binding / positive regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / enzyme-substrate adaptor activity / ubiquitin ligase inhibitor activity / positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation / positive regulation of axon extension / ubiquitin-like ligase-substrate adaptor activity / Cyclin A:Cdk2-associated events at S phase entry / protein K48-linked ubiquitination / intercellular bridge / heterochromatin / nuclear periphery / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / regulation of mitotic cell cycle / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Securin / SCF-beta-TrCP mediated degradation of Emi1 / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / Cdc20:Phospho-APC/C mediated degradation of Cyclin A / APC/C:Cdh1 mediated degradation of Cdc20 and other APC/C:Cdh1 targeted proteins in late mitosis/early G1 / G protein-coupled receptor binding / brain development / kinetochore / CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 / spindle / neuron projection development / ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / mitotic spindle / Separation of Sister Chromatids / ubiquitin protein ligase activity / nervous system development / mitotic cell cycle / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / microtubule cytoskeleton / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / protein phosphatase binding / nuclear membrane / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / molecular adaptor activity / cell differentiation / protein ubiquitination / negative regulation of gene expression / cell division / DNA repair / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / DNA damage response / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / centrosome / protein kinase binding / nucleolus / zinc ion binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  HOMO SAPIENS (human) HOMO SAPIENS (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Chang, L. / Zhang, Z. / Yang, J. / McLaughlin, S.H. / Barford, D. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2015 Journal: Nature / Year: 2015Title: Atomic structure of the APC/C and its mechanism of protein ubiquitination. Authors: Leifu Chang / Ziguo Zhang / Jing Yang / Stephen H McLaughlin / David Barford /  Abstract: The anaphase-promoting complex (APC/C) is a multimeric RING E3 ubiquitin ligase that controls chromosome segregation and mitotic exit. Its regulation by coactivator subunits, phosphorylation, the ...The anaphase-promoting complex (APC/C) is a multimeric RING E3 ubiquitin ligase that controls chromosome segregation and mitotic exit. Its regulation by coactivator subunits, phosphorylation, the mitotic checkpoint complex and interphase early mitotic inhibitor 1 (Emi1) ensures the correct order and timing of distinct cell-cycle transitions. Here we use cryo-electron microscopy to determine atomic structures of APC/C-coactivator complexes with either Emi1 or a UbcH10-ubiquitin conjugate. These structures define the architecture of all APC/C subunits, the position of the catalytic module and explain how Emi1 mediates inhibition of the two E2s UbcH10 and Ube2S. Definition of Cdh1 interactions with the APC/C indicates how they are antagonized by Cdh1 phosphorylation. The structure of the APC/C with UbcH10-ubiquitin reveals insights into the initiating ubiquitination reaction. Our results provide a quantitative framework for the design of future experiments to investigate APC/C functions in vivo. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  4ui9.cif.gz 4ui9.cif.gz | 1.7 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb4ui9.ent.gz pdb4ui9.ent.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  4ui9.json.gz 4ui9.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ui/4ui9 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ui/4ui9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ui/4ui9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ui/4ui9 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  2924MC  2925C  2926C  5a31C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-ANAPHASE-PROMOTING COMPLEX SUBUNIT ... , 12 types, 13 molecules ABDEGILMNOWXY
| #1: Protein | Mass: 216777.656 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q9H1A4 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q9H1A4 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 9866.702 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q9NYG5 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q9NYG5 |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 14302.727 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: P60006 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: P60006 |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 11677.995 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q96DE5 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q96DE5 |
| #7: Protein | Mass: 9808.025 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q8NHZ8 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q8NHZ8 |
| #8: Protein | Mass: 92205.195 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX5 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX5 |
| #11: Protein | Mass: 21021.834 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q9UM13 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q9UM13 |
| #12: Protein | Mass: 8528.309 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q9BS18 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q9BS18 |
| #13: Protein | Mass: 93938.977 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX6 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX6 |
| #14: Protein | Mass: 85216.719 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX4 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX4 |
| #19: Protein | Mass: 9793.999 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q8NHZ8 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q8NHZ8 |
| #20: Protein | Mass: 63106.809 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX3 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX3 |
-CELL DIVISION CYCLE PROTEIN ... , 4 types, 6 molecules CPFHJK
| #3: Protein | Mass: 68356.406 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX2 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX2#6: Protein | Mass: 92005.062 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: P30260 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: P30260#9: Protein | | Mass: 71747.578 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q13042 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q13042#10: Protein | | Mass: 71806.672 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q13042 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q13042 |
|---|
-Protein , 2 types, 2 molecules RS
| #15: Protein | Mass: 54838.688 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q9UM11 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q9UM11 |
|---|---|
| #16: Protein | Mass: 50297.645 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q9UKT4 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q9UKT4 |
-Protein/peptide , 2 types, 2 molecules TU
| #17: Protein/peptide | Mass: 1609.780 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) HOMO SAPIENS (human) |
|---|---|
| #18: Protein/peptide | Mass: 2258.669 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q9UKT4*PLUS HOMO SAPIENS (human) / References: UniProt: Q9UKT4*PLUS |
-Non-polymers , 1 types, 5 molecules 
| #21: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: HUMAN ANAPHASE-PROMOTING COMPLEX / Type: COMPLEX |
|---|---|
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.2 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Details: HOLEY CARBON |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F30 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI F30 / Date: Feb 9, 2014 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 78000 X / Nominal defocus max: 4000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 2000 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 27 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) |
| Radiation wavelength | Relative weight: 1 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.6 Å / Num. of particles: 202084 / Nominal pixel size: 1.36 Å / Actual pixel size: 1.36 Å / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 3.6 Å | ||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Highest resolution: 3.6 Å
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj




















