[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
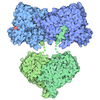
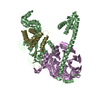
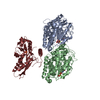
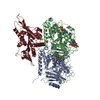
Yorodumi- PDB-4aqv: Model of human kinesin-5 motor domain (3HQD) and mammalian tubuli... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 4aqv | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
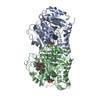
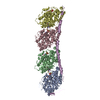
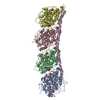
| Title | Model of human kinesin-5 motor domain (3HQD) and mammalian tubulin heterodimer (1JFF) docked into the 9.7-angstrom cryo-EM map of microtubule-bound kinesin-5 motor domain in the AMPPPNP state. | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MOTOR PROTEIN / MICROTUBULE / MITOSIS / CANCER | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationspindle elongation / regulation of mitotic centrosome separation / plus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / Kinesins / mitotic centrosome separation / positive regulation of axon guidance / kinesin complex / microtubule motor activity / spindle organization / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic ...spindle elongation / regulation of mitotic centrosome separation / plus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / Kinesins / mitotic centrosome separation / positive regulation of axon guidance / kinesin complex / microtubule motor activity / spindle organization / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / microtubule-based movement / mitotic spindle assembly / microtubule-based process / MHC class II antigen presentation / mitotic spindle organization / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / spindle / neuron migration / spindle pole / mitotic spindle / mitotic cell cycle / microtubule cytoskeleton / microtubule binding / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / microtubule / ciliary basal body / hydrolase activity / protein heterodimerization activity / cell division / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / GTPase activity / protein kinase binding / GTP binding / protein-containing complex / ATP binding / metal ion binding / nucleus / membrane / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  HOMO SAPIENS (human) HOMO SAPIENS (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 9.7 Å | ||||||
| Model type details | CA ATOMS ONLY, CHAIN A, B, C | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Goulet, A. / Behnke-Parks, W.M. / Sindelar, C.V. / Rosenfeld, S.S. / Moores, C.A. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2012 Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2012Title: The structural basis of force generation by the mitotic motor kinesin-5. Authors: Adeline Goulet / William M Behnke-Parks / Charles V Sindelar / Jennifer Major / Steven S Rosenfeld / Carolyn A Moores /  Abstract: Kinesin-5 is required for forming the bipolar spindle during mitosis. Its motor domain, which contains nucleotide and microtubule binding sites and mechanical elements to generate force, has evolved ...Kinesin-5 is required for forming the bipolar spindle during mitosis. Its motor domain, which contains nucleotide and microtubule binding sites and mechanical elements to generate force, has evolved distinct properties for its spindle-based functions. In this study, we report subnanometer resolution cryoelectron microscopy reconstructions of microtubule-bound human kinesin-5 before and after nucleotide binding and combine this information with studies of the kinetics of nucleotide-induced neck linker and cover strand movement. These studies reveal coupled, nucleotide-dependent conformational changes that explain many of this motor's properties. We find that ATP binding induces a ratchet-like docking of the neck linker and simultaneous, parallel docking of the N-terminal cover strand. Loop L5, the binding site for allosteric inhibitors of kinesin-5, also undergoes a dramatic reorientation when ATP binds, suggesting that it is directly involved in controlling nucleotide binding. Our structures indicate that allosteric inhibitors of human kinesin-5, which are being developed as anti-cancer therapeutics, bind to a motor conformation that occurs in the course of normal function. However, due to evolutionarily defined sequence variations in L5, this conformation is not adopted by invertebrate kinesin-5s, explaining their resistance to drug inhibition. Together, our data reveal the precision with which the molecular mechanism of kinesin-5 motors has evolved for force generation. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  4aqv.cif.gz 4aqv.cif.gz | 67.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb4aqv.ent.gz pdb4aqv.ent.gz | 36.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  4aqv.json.gz 4aqv.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/aq/4aqv https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/aq/4aqv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/aq/4aqv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/aq/4aqv | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  2077MC  2078C  2079C  2080C  2081C  2152C  4aqwC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 3 types, 3 molecules ABC
| #1: Protein | Mass: 50236.352 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 49907.770 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 41673.105 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: MOTOR DOMAIN, RESIDUES 1-367 / Mutation: YES Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host:  |
-Non-polymers , 5 types, 6 molecules 








| #4: Chemical | | #5: Chemical | ChemComp-GTP / | #6: Chemical | ChemComp-GDP / | #7: Chemical | ChemComp-TA1 / | #8: Chemical | ChemComp-ANP / | |
|---|
-Details
| Sequence details | CYS-LIGHT CONSTRUCT (C25V,C43S,C87A,C99A). THE MUTATION T126C WAS INTRODUCED |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: 13-PROTOFILAMENT MICROTUBULE-BOUND HUMAN KINESIN-5 MOTOR DOMAIN WITH AMPPNP Type: COMPLEX |
|---|---|
| Buffer solution | Name: 80 MM PIPES, 5 MM MGCL2, 1 MM EGTA, 5MM AMPPNP / pH: 6.8 / Details: 80 MM PIPES, 5 MM MGCL2, 1 MM EGTA, 5MM AMPPNP |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Details: HOLEY CARBON |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK I / Cryogen name: ETHANE Details: CRYOGEN- ETHANE, HUMIDITY- 100, INSTRUMENT- FEI VITROBOT MARK I, METHOD- CHAMBER AT 24 DEGREES C, BLOT 2.5 SEC, |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI F20 / Date: Jan 10, 2011 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 50000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2200 nm / Nominal defocus min: 700 nm / Cs: 2 mm |
| Specimen holder | Temperature: 90 K |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 18 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM |
| Image scans | Num. digital images: 46 |
| Radiation wavelength | Relative weight: 1 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: FREALIGN | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 9.7 Å / Num. of particles: 3587 / Nominal pixel size: 2.8 Å Details: THE N-TERMINAL RESIDUES 6 TO 16 WERE BUILT MANUALLY IN THE EM DENSITY. SUBMISSION BASED ON EXPERIMENTAL DATA FROM EMDB EMD-2077. (DEPOSITION ID: 10751). Symmetry type: HELICAL | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Cross-correlation coefficient Details: METHOD--RIGID BODY (1JFF). RIGID BODY AND FLEXIBLE FITTING (3HQD) REFINEMENT PROTOCOL--X-RAY | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 9.7 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Highest resolution: 9.7 Å
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



















 PDBj
PDBj