[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
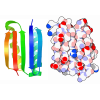
Yorodumi- PDB-3bat: Crystal structure of the N-terminal region of the scallop myosin ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 3bat | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Crystal structure of the N-terminal region of the scallop myosin rod, monoclinic (P21) form | ||||||
 Components Components | Myosin heavy chain, striated muscle/General control protein GCN4 | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CONTRACTILE PROTEIN / Alpha-helical coiled coil / disorder / salt links / Actin-binding / ATP-binding / Calmodulin-binding / Cytoplasm / Motor protein / Muscle protein / Myosin / Nucleotide-binding / Thick filament | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationFCERI mediated MAPK activation / protein localization to nuclear periphery / Activation of the AP-1 family of transcription factors / response to amino acid starvation / negative regulation of ribosomal protein gene transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of cellular response to amino acid starvation / mediator complex binding / myosin filament / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / myosin II complex ...FCERI mediated MAPK activation / protein localization to nuclear periphery / Activation of the AP-1 family of transcription factors / response to amino acid starvation / negative regulation of ribosomal protein gene transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of cellular response to amino acid starvation / mediator complex binding / myosin filament / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / myosin II complex / microfilament motor activity / myofibril / TFIID-class transcription factor complex binding / amino acid biosynthetic process / positive regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex assembly / positive regulation of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II / cellular response to nutrient levels / cellular response to amino acid starvation / RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex / actin filament binding / DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / transcription regulator complex / sequence-specific DNA binding / RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding / DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / calmodulin binding / intracellular signal transduction / RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / DNA-binding transcription factor activity / chromatin binding / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / ATP binding / identical protein binding / nucleus Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Argopecten irradians (bay scallop) Argopecten irradians (bay scallop) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.3 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.3 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Brown, J.H. / Cohen, C. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J.Mol.Biol. / Year: 2008 Journal: J.Mol.Biol. / Year: 2008Title: An unstable head-rod junction may promote folding into the compact off-state conformation of regulated myosins. Authors: Brown, J.H. / Yang, Y. / Reshetnikova, L. / Gourinath, S. / Suveges, D. / Kardos, J. / Hobor, F. / Reutzel, R. / Nyitray, L. / Cohen, C. #1:  Journal: Nature / Year: 2003 Journal: Nature / Year: 2003Title: Visualization of an unstable coiled coil from the scallop myosin rod. Authors: Li, Y. / Brown, J.H. / Reshetnikova, L. / Blazsek, A. / Farkas, L. / Nyitray, L. / Cohen, C. #2:  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2006 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2006Title: Crystal structures of human cardiac beta-myosin II S2-Delta provide insight into the functional role of the S2 subfragment. Authors: Wulf Blankenfeldt / Nicolas H Thomä / John S Wray / Mathias Gautel / Ilme Schlichting /  Abstract: Myosin II is the major component of the muscle thick filament. It consists of two N-terminal S1 subfragments ("heads") connected to a long dimeric coiled-coil rod. The rod is in itself twofold ...Myosin II is the major component of the muscle thick filament. It consists of two N-terminal S1 subfragments ("heads") connected to a long dimeric coiled-coil rod. The rod is in itself twofold symmetric, but in the filament, the two heads point away from the filament surface and are therefore not equivalent. This breaking of symmetry requires the initial section of the rod, subfragment 2 (S2), to be relatively flexible. S2 is an important functional element, involved in various mechanisms by which the activity of smooth and striated muscle is regulated. We have determined crystal structures of the 126 N-terminal residues of S2 from human cardiac beta-myosin II (S2-Delta), of both WT and the disease-associated E924K mutant. S2-Delta is a straight parallel dimeric coiled coil, but the N terminus of one chain is disordered in WT-S2-Delta due to crystal contacts, indicative of unstable local structure. Bulky noncanonical side chains pack into a/d positions of S2-Delta's N terminus, leading to defined local asymmetry and axial stagger, which could induce nonequivalence of the S1 subfragments. Additionally, S2 possesses a conserved charge distribution with three prominent rings of negative potential within S2-Delta, the first of which may provide a binding interface for the "blocked head" of smooth muscle myosin in the OFF state. The observation that many disease-associated mutations affect the second negatively charged ring further suggests that charge interactions play an important role in regulation of cardiac muscle activity through myosin-binding protein C. | ||||||
| History |
| ||||||
| Remark 999 | SEQUENCE THE PEPTIDE CONTAINS A GSHM TETRAPEPTIDE, FOLLOWED BY THE N-TERMINAL 51 RESIDUES OF THE ... SEQUENCE THE PEPTIDE CONTAINS A GSHM TETRAPEPTIDE, FOLLOWED BY THE N-TERMINAL 51 RESIDUES OF THE BAY SCALLOP MYOSIN ROD (RESIDUES 835-885 OF THE BAY SCALLOP MYOSIN HEAVY CHAIN, GI:5612), FOLLOWED BY A GS LINKER, FOLLOWED BY THE LEUCINE ZIPPER OF THE YEAST GCN4 TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR (RESIDUES 250-281 OF GI:171584 DENOTED AS RESIDUES 888-919 IN THE SUBMITTED COORDINATES). |
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  3bat.cif.gz 3bat.cif.gz | 80.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb3bat.ent.gz pdb3bat.ent.gz | 61.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  3bat.json.gz 3bat.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ba/3bat https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ba/3bat ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ba/3bat ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ba/3bat | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  3basC  1nknS C: citing same article ( S: Starting model for refinement |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 
| ||||||||
| 2 | 
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 10559.174 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Fragment: Bay Scallop Myosin (Residues 835-885)/Yeast GCN4 Transcription Factor (Residues 250-281) Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Argopecten irradians (bay scallop), (gene. exp.) Argopecten irradians (bay scallop), (gene. exp.)  Genus: Argopecten, Saccharomyces / Species: , / Strain: , / Tissue: Adductor muscle/- / Gene: -/GCN4, AAS3, ARG9, YEL009C / Plasmid: pET15b / Production host:  #2: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.25 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 45.45 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 277 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / pH: 6.2 Details: 2 microliters of protein solution (4 mg/ml protein in 30 mM MOPS buffer pH 7.2, 40 mM NaCl, 2 mM NaN3) mixed with 2 microliters of (25% PEG 3350, 50 mM NH4I) and equilibrated against 1 ml of ...Details: 2 microliters of protein solution (4 mg/ml protein in 30 mM MOPS buffer pH 7.2, 40 mM NaCl, 2 mM NaN3) mixed with 2 microliters of (25% PEG 3350, 50 mM NH4I) and equilibrated against 1 ml of (17.5% PEG 3350, 35 mM NH4I, 28 mM NaCl, 2 mM NaN3, 20 mM MOPS pH 6.2). Harvested crystals were cryoprotected in 25.5% PEG 3350 and 15% glycerol, VAPOR DIFFUSION, HANGING DROP, temperature 277K |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  NSLS NSLS  / Beamline: X26C / Wavelength: 0.9791 Å / Beamline: X26C / Wavelength: 0.9791 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Detector | Type: ADSC QUANTUM 4 / Detector: CCD Details: channel-cut Si(111) crystal monochromator followed by a doubly focusing toroidal mirror | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation | Monochromator: Si(111) crystal / Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.9791 Å / Relative weight: 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection | Resolution: 1.95→30 Å / Num. obs: 27340 / % possible obs: 98.5 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.052 / Χ2: 1.085 / Net I/σ(I): 13.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection shell |
|
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: PDB entry 1NKN Resolution: 2.3→30 Å / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 0
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Bsol: 38.499 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 53.827 Å2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine analyze |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 2.3→30 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Resolution: 2.3→2.44 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Xplor file |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





















 PDBj
PDBj