+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 1ld4 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
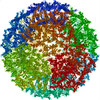
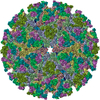
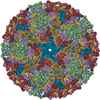
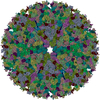
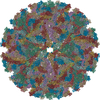
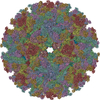
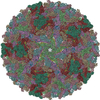
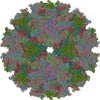
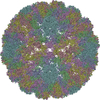
| Title | Placement of the Structural Proteins in Sindbis Virus | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRUS / sindbis virus / alphavirus structure / glycoprotein organization / nucleocapsid structure / transmembrane coiled coils / Icosahedral virus | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationicosahedral viral capsid, spike / FCERI mediated MAPK activation / protein localization to nuclear periphery / Activation of the AP-1 family of transcription factors / response to amino acid starvation / negative regulation of ribosomal protein gene transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of cellular response to amino acid starvation / mediator complex binding / togavirin / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence ...icosahedral viral capsid, spike / FCERI mediated MAPK activation / protein localization to nuclear periphery / Activation of the AP-1 family of transcription factors / response to amino acid starvation / negative regulation of ribosomal protein gene transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of cellular response to amino acid starvation / mediator complex binding / togavirin / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / T=4 icosahedral viral capsid / TFIID-class transcription factor complex binding / ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding / amino acid biosynthetic process / positive regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex assembly / positive regulation of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II / cellular response to nutrient levels / cellular response to amino acid starvation / RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex / DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / transcription regulator complex / clathrin-dependent endocytosis of virus by host cell / symbiont-mediated suppression of host toll-like receptor signaling pathway / sequence-specific DNA binding / RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding / membrane fusion / host cell cytoplasm / DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / intracellular signal transduction / RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / DNA-binding transcription factor activity / viral translational frameshifting / serine-type endopeptidase activity / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / chromatin binding / virion attachment to host cell / host cell nucleus / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane / structural molecule activity / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / proteolysis / RNA binding / identical protein binding / membrane / nucleus Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Sindbis virus Sindbis virus | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 11.4 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhang, W. / Mukhopadhyay, S. / Pletnev, S.V. / Baker, T.S. / Kuhn, R.J. / Rossmann, M.G. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Virol / Year: 2002 Journal: J Virol / Year: 2002Title: Placement of the structural proteins in Sindbis virus. Authors: Wei Zhang / Suchetana Mukhopadhyay / Sergei V Pletnev / Timothy S Baker / Richard J Kuhn / Michael G Rossmann /  Abstract: The structure of the lipid-enveloped Sindbis virus has been determined by fitting atomic resolution crystallographic structures of component proteins into an 11-A resolution cryoelectron microscopy ...The structure of the lipid-enveloped Sindbis virus has been determined by fitting atomic resolution crystallographic structures of component proteins into an 11-A resolution cryoelectron microscopy map. The virus has T=4 quasisymmetry elements that are accurately maintained between the external glycoproteins, the transmembrane helical region, and the internal nucleocapsid core. The crystal structure of the E1 glycoprotein was fitted into the cryoelectron microscopy density, in part by using the known carbohydrate positions as restraints. A difference map showed that the E2 glycoprotein was shaped similarly to E1, suggesting a possible common evolutionary origin for these two glycoproteins. The structure shows that the E2 glycoprotein would have to move away from the center of the trimeric spike in order to expose enough viral membrane surface to permit fusion with the cellular membrane during the initial stages of host infection. The well-resolved E1-E2 transmembrane regions form alpha-helical coiled coils that were consistent with T=4 symmetry. The known structure of the capsid protein was fitted into the density corresponding to the nucleocapsid, revising the structure published earlier. | ||||||
| History |
| ||||||
| Remark 99 | Chains E-L contain alpha-carbons only. The C-terminal residues of chains M-P contain alpha-carbons only. | ||||||
| Remark 600 | HETEROGEN THE COORDINATES OF UNX 1139, 1141, 1245, 1196, 1200, 1262, 1318, 4139, 4141, 4245, 4196, ...HETEROGEN THE COORDINATES OF UNX 1139, 1141, 1245, 1196, 1200, 1262, 1318, 4139, 4141, 4245, 4196, 4200, 4262, 4318, 5139, 5141, 5245, 5196, 5200, 5262, 5318, 6139, 6141, 6245, 6196, 6200, 6262, 6318 ARE THE CENTERS OF DIFFERENCE DENSITY PEAKS THAT CORRESPOND TO THE CARBOHYDRATE MOLECULES OF THE VIRION. THE COORDINATES OF UNX 1000, 4000, 5000, AND 6000 ARE THE POINTS WHERE THE GLYCOPROTEINS E1 AND E2 ENTERS INTO MEMBRANE. |
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  1ld4.cif.gz 1ld4.cif.gz | 420.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb1ld4.ent.gz pdb1ld4.ent.gz | 322.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  1ld4.json.gz 1ld4.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ld/1ld4 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ld/1ld4 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ld/1ld4 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ld/1ld4 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | x 60
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 | x 5
|
| 4 | x 6
|
| 5 | 
|
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: (Hermann–Mauguin notation: 532 / Schoenflies symbol: I (icosahedral)) |
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 29410.010 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Sindbis virus / Genus: Alphavirus Sindbis virus / Genus: AlphavirusReferences: UniProt: P03316, Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Serine endopeptidases #2: Protein | Mass: 6718.774 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 / Fragment: LEUCINE-ZIPPER (residues 225-281) / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #3: Protein | Mass: 47416.836 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Sindbis virus / Genus: Alphavirus / References: UniProt: P03316 Sindbis virus / Genus: Alphavirus / References: UniProt: P03316#4: Chemical | ChemComp-UNX / Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Sindbis Virus / Type: VIRUS |
|---|---|
| Details of virus | Host category: VERTEBRATES / Type: VIRION |
| Natural host | Organism: Homo sapiens |
| Buffer solution | Name: 50mM Tris-HCl, 200mM NaCl, 0.1mM EDTA / pH: 7.5 / Details: 50mM Tris-HCl, 200mM NaCl, 0.1mM EDTA |
| Specimen | Conc.: 6 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Crystal grow | *PLUS Method: cryo-electron microscopy / Details: cryo-electron microscopy |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: FEI/PHILIPS CM200T / Date: Jun 15, 2000 |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 38000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2580 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1100 nm / Cs: 2 mm |
| Specimen holder | Temperature: 87 K / Tilt angle max: 0 ° / Tilt angle min: 0 ° |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 18.4 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM Details: films were developed in full-strength of Kodak D19 developer for 12 minutes at 20 C |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: each viral image was CTF corrected before reconstruction, based on the following equation: F(corr)=F(obs)/[|CTF|+wiener] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: I (icosahedral) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Method: FOURIER-BESSEL method Reference: Baker, T. S., N. H. Olson, and S. D. Fuller (1999). Adding the third dimension to virus life cycles: Three-dimensional reconstruction of icosahedral viruses ...Method: FOURIER-BESSEL method Reference: Baker, T. S., N. H. Olson, and S. D. Fuller (1999). Adding the third dimension to virus life cycles: Three-dimensional reconstruction of icosahedral viruses from cryo-electron micrographs. Micro. & Mol. Bio. Rev. 63:862-922. Resolution: 11.4 Å / Nominal pixel size: 3.68 Å / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 1000 / Space: REAL Details: DETAILS--The structure of the lipid-enveloped Sindbis virus has been determined by fitting atomic resolution crystallographic structures of component proteins into an 11 resolution cryo- ...Details: DETAILS--The structure of the lipid-enveloped Sindbis virus has been determined by fitting atomic resolution crystallographic structures of component proteins into an 11 resolution cryo- electron microscopy (cryoEM) map (with significant terms to 10 resolution). The E1 glycoprotein, whose structure had been determined independently for the homologous Semliki Forest virus by X-ray crystallography (Lescar, J., Roussel,A., Wein, M.W., Navaza, J., Fuller, S.D., Wengler, G., and Rey, F.A. (2001). The fusion glycoprotein shell of Semliki Forest virus- an icosahedral assembly primed for fusogenic activation at endosomal pH. Cell 105, 137-148), was fitted into the cryoEM density, in part by using the known positions of glycoprotein sites as restraints. The well-resolved transmembrane regions form coiled coils that could be fitted with the dimeric GCN4 coiled-coil structure. The helices could be seen to extend to E1 and E2 on the outside of the membrane and to the nucleocapsid on the inside. The known structure of the capsid protein (Choi, H.K., Tong, L., Minor, W., Dumas, P., Boege, U., Rossmann, M.G., and Wengler, G. (1991). Structure of Sindbis virus core protein reveals a chymotrypsin-like serine proteinase and the organization of the virion. Nature 354, 37-43.) was fitted into the density corresponding to the nucleocapsid, revising an earlier published structure. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 11.4 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Highest resolution: 11.4 Å
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj