[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-1jnx: Crystal structure of the BRCT repeat region from the breast cance... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 1jnx | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Crystal structure of the BRCT repeat region from the breast cancer associated protein, BRCA1 | ||||||
 Components Components | BREAST CANCER TYPE 1 SUSCEPTIBILITY PROTEIN | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GENE REGULATION / BRCT / CANCER / GENE EXPRESSION | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationhistone H2AK127 ubiquitin ligase activity / histone H2AK129 ubiquitin ligase activity / Defective DNA double strand break response due to BRCA1 loss of function / Defective DNA double strand break response due to BARD1 loss of function / BRCA1-BARD1 complex / BRCA1-B complex / BRCA1-A complex / BRCA1-C complex / negative regulation of centriole replication / sex-chromosome dosage compensation ...histone H2AK127 ubiquitin ligase activity / histone H2AK129 ubiquitin ligase activity / Defective DNA double strand break response due to BRCA1 loss of function / Defective DNA double strand break response due to BARD1 loss of function / BRCA1-BARD1 complex / BRCA1-B complex / BRCA1-A complex / BRCA1-C complex / negative regulation of centriole replication / sex-chromosome dosage compensation / random inactivation of X chromosome / ubiquitin-modified histone reader activity / chordate embryonic development / cellular response to indole-3-methanol / gamma-tubulin ring complex / negative regulation of intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway / nuclear ubiquitin ligase complex / DNA strand resection involved in replication fork processing / homologous recombination / negative regulation of fatty acid biosynthetic process / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in DNA replication, damage repair and senescence / protein K6-linked ubiquitination / lateral element / regulation of DNA damage checkpoint / Impaired BRCA2 binding to PALB2 / XY body / mitotic G2/M transition checkpoint / RNA polymerase binding / DNA repair complex / DNA damage tolerance / centrosome cycle / Homologous DNA Pairing and Strand Exchange / Defective homologous recombination repair (HRR) due to BRCA1 loss of function / Defective HDR through Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR) due to PALB2 loss of BRCA1 binding function / Defective HDR through Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR) due to PALB2 loss of BRCA2/RAD51/RAD51C binding function / Resolution of D-loop Structures through Synthesis-Dependent Strand Annealing (SDSA) / intracellular membraneless organelle / Resolution of D-loop Structures through Holliday Junction Intermediates / HDR through Single Strand Annealing (SSA) / negative regulation of gene expression via chromosomal CpG island methylation / response to ionizing radiation / Impaired BRCA2 binding to RAD51 / Transcriptional Regulation by E2F6 / mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / negative regulation of cell cycle / negative regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process / Presynaptic phase of homologous DNA pairing and strand exchange / positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production / ubiquitin ligase complex / SUMOylation of DNA damage response and repair proteins / regulation of DNA repair / negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors / protein autoubiquitination / tubulin binding / Meiotic synapsis / positive regulation of DNA repair / cellular response to ionizing radiation / male germ cell nucleus / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / chromosome segregation / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / negative regulation of cell growth / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase / HDR through Homologous Recombination (HRR) / Meiotic recombination / Metalloprotease DUBs / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage / positive regulation of angiogenesis / ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / fatty acid biosynthetic process / p53 binding / cellular response to tumor necrosis factor / KEAP1-NFE2L2 pathway / double-strand break repair / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / chromosome / Neddylation / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Phosphorylation / damaged DNA binding / transcription coactivator activity / transcription cis-regulatory region binding / regulation of cell cycle / nuclear body / protein ubiquitination / chromatin remodeling / ribonucleoprotein complex / DNA repair / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / DNA damage response / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / positive regulation of gene expression / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription / enzyme binding / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / protein-containing complex / DNA binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MAD / Resolution: 2.5 Å MAD / Resolution: 2.5 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Williams, R.S. / Green, R. / Glover, J.N.M. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Biol / Year: 2001 Journal: Nat Struct Biol / Year: 2001Title: Crystal structure of the BRCT repeat region from the breast cancer-associated protein BRCA1. Authors: R S Williams / R Green / J N Glover /  Abstract: The C-terminal BRCT region of BRCA1 is essential for its DNA repair, transcriptional regulation and tumor suppressor functions. Here we determine the crystal structure of the BRCT domain of human ...The C-terminal BRCT region of BRCA1 is essential for its DNA repair, transcriptional regulation and tumor suppressor functions. Here we determine the crystal structure of the BRCT domain of human BRCA1 at 2.5 A resolution. The domain contains two BRCT repeats that adopt similar structures and are packed together in a head-to-tail arrangement. Cancer-causing missense mutations occur at the interface between the two repeats and destabilize the structure. The manner by which the two BRCT repeats interact in BRCA1 may represent a general mode of interaction between homologous domains within proteins that interact to regulate the cellular response to DNA damage. The structure provides a basis to predict the structural consequences of uncharacterized BRCA1 mutations. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  1jnx.cif.gz 1jnx.cif.gz | 55.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb1jnx.ent.gz pdb1jnx.ent.gz | 39.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  1jnx.json.gz 1jnx.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jn/1jnx https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jn/1jnx ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jn/1jnx ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jn/1jnx | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 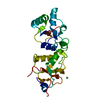
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 24531.234 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: residues 1646-1859 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: BRCA1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: BRCA1 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #2: Chemical | ChemComp-NI / |
| #3: Water | ChemComp-HOH / |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 4.74 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 74.03 % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 298 K / pH: 8.5 Details: Lithium sulphate, Nickel sulphate, calcium chloride, Tris, pH 8.5,VAPOR DIFFUSION, HANGING DROP at 298K | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal grow | *PLUS Temperature: 20-23 ℃ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Components of the solutions | *PLUS
|
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  APS APS  / Beamline: 14-BM-C / Wavelength: 1 / Beamline: 14-BM-C / Wavelength: 1 |
| Detector | Type: ADSC QUANTUM 4 / Detector: CCD / Date: Feb 4, 2001 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.5→40 Å / Num. obs: 16968 / % possible obs: 99.8 % / Observed criterion σ(I): 0 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 2.5→2.57 Å / % possible all: 100 |
| Reflection | *PLUS Lowest resolution: 40 Å / Num. measured all: 209566 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.048 |
| Reflection shell | *PLUS % possible obs: 100 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.292 / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 9.1 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MAD / Resolution: 2.5→25 Å / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 0 / Stereochemistry target values: Engh & Huber MAD / Resolution: 2.5→25 Å / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 0 / Stereochemistry target values: Engh & HuberDetails: TLS PARAMETERS FOR REFMAC: GROUP- CHAIN X,N,&W, ALL ATOMS: T TENSOR: T11: 0.3885 T22: 0.2528 T33: 0.0541 T12: 0.2422 T13: -0.0261 T23: 0.0567 L TENSOR: L11: 15.0684 L22: 14.6911 L33: 2.1404 ...Details: TLS PARAMETERS FOR REFMAC: GROUP- CHAIN X,N,&W, ALL ATOMS: T TENSOR: T11: 0.3885 T22: 0.2528 T33: 0.0541 T12: 0.2422 T13: -0.0261 T23: 0.0567 L TENSOR: L11: 15.0684 L22: 14.6911 L33: 2.1404 L12: -13.6906 L13: 4.0117 L23: -2.8964 S TENSOR: S11: 1.1964 S12: 1.4251 S13: 0.4307 S21: -1.4475 S22: -1.3203 S23: -0.2414 S31: 0.2422 S32: 0.5625 S33: 0.1239
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 2.5→25 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS params. | Method: refined / Origin x: 24.4147 Å / Origin y: 58.8128 Å / Origin z: 37.1148 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Software | *PLUS Name: REFMAC / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | *PLUS Highest resolution: 2.5 Å / Lowest resolution: 25 Å / σ(F): 0 / % reflection Rfree: 5.1 % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | *PLUS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | *PLUS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints | *PLUS
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj


















