[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-5295: 3D reconstruction of negatively stained PCSK9 in complex with a Fab -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-5295 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | 3D reconstruction of negatively stained PCSK9 in complex with a Fab | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | 3D reconstruction of negatively stained PCSK9-Fab complex | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PCSK9-Fab complex | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / negative staining / Resolution: 25.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wu S / Avila-Sakar A / Kim J / Booth DS / Greenberg CH / Rossi A / Liao M / Alian A / Griner SL / Juge N ...Wu S / Avila-Sakar A / Kim J / Booth DS / Greenberg CH / Rossi A / Liao M / Alian A / Griner SL / Juge N / Mergel CM / Chaparro-Riggers J / Strop P / Tampe R / Edwards RH / Stroud RM / Craik CS / Cheng Y | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Structure / Year: 2012 Journal: Structure / Year: 2012Title: Fabs enable single particle cryoEM studies of small proteins. Authors: Shenping Wu / Agustin Avila-Sakar / JungMin Kim / David S Booth / Charles H Greenberg / Andrea Rossi / Maofu Liao / Xueming Li / Akram Alian / Sarah L Griner / Narinobu Juge / Yadong Yu / ...Authors: Shenping Wu / Agustin Avila-Sakar / JungMin Kim / David S Booth / Charles H Greenberg / Andrea Rossi / Maofu Liao / Xueming Li / Akram Alian / Sarah L Griner / Narinobu Juge / Yadong Yu / Claudia M Mergel / Javier Chaparro-Riggers / Pavel Strop / Robert Tampé / Robert H Edwards / Robert M Stroud / Charles S Craik / Yifan Cheng /  Abstract: In spite of its recent achievements, the technique of single particle electron cryomicroscopy (cryoEM) has not been widely used to study proteins smaller than 100 kDa, although it is a highly ...In spite of its recent achievements, the technique of single particle electron cryomicroscopy (cryoEM) has not been widely used to study proteins smaller than 100 kDa, although it is a highly desirable application of this technique. One fundamental limitation is that images of small proteins embedded in vitreous ice do not contain adequate features for accurate image alignment. We describe a general strategy to overcome this limitation by selecting a fragment antigen binding (Fab) to form a stable and rigid complex with a target protein, thus providing a defined feature for accurate image alignment. Using this approach, we determined a three-dimensional structure of an ∼65 kDa protein by single particle cryoEM. Because Fabs can be readily generated against a wide range of proteins by phage display, this approach is generally applicable to study many small proteins by single particle cryoEM. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_5295.map.gz emd_5295.map.gz | 799.7 KB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-5295-v30.xml emd-5295-v30.xml emd-5295.xml emd-5295.xml | 10.4 KB 10.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_5295_1.jpg emd_5295_1.jpg | 16.6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-5295 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-5295 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-5295 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-5295 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_5295.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 825.2 KB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_5295.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 825.2 KB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | 3D reconstruction of negatively stained PCSK9-Fab complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 4.26 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : human PCSK9 in complex with a Fab
| Entire | Name: human PCSK9 in complex with a Fab |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: human PCSK9 in complex with a Fab
| Supramolecule | Name: human PCSK9 in complex with a Fab / type: sample / ID: 1000 / Oligomeric state: monomer / Number unique components: 2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 120 KDa / Theoretical: 120 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: PCSK9
| Macromolecule | Name: PCSK9 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Oligomeric state: monomer / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: human Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: human |
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 120 KDa / Theoretical: 120 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE / Details: uranyl formate |
|---|---|
| Grid | Details: 200 mesh copper grid |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: NONE / Instrument: OTHER |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI 20 |
|---|---|
| Alignment procedure | Legacy - Astigmatism: each particle |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: GATAN ULTRASCAN 4000 (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 30 e/Å2 |
| Tilt angle min | 0 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 120 kV / Electron source: LAB6 |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 50000 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 0.0015 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.0015 µm / Nominal magnification: 50000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder: single tilt / Specimen holder model: SIDE ENTRY, EUCENTRIC / Tilt angle max: 60 |
- Image processing
Image processing
| CTF correction | Details: each particle |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 25.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: Frealign / Number images used: 3876 |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: REAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


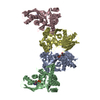
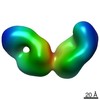
 UCSF Chimera
UCSF Chimera







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)