[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
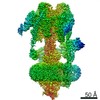
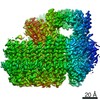
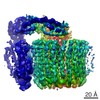
Yorodumi- EMDB-21844: The Vo region of human V-ATPase in state 1 (focused refinement) -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-21844 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | The Vo region of human V-ATPase in state 1 (focused refinement) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | The Vo region of human V-ATPase in state 1 (focused refinement) | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | V-ATPase / proton pump / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationproton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex / Ion channel transport / plasma membrane proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in lysosome biogenesis and autophagy / intracellular pH reduction / eye pigmentation / central nervous system maturation / ATPase-coupled ion transmembrane transporter activity / rostrocaudal neural tube patterning / positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta1 production ...proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex / Ion channel transport / plasma membrane proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in lysosome biogenesis and autophagy / intracellular pH reduction / eye pigmentation / central nervous system maturation / ATPase-coupled ion transmembrane transporter activity / rostrocaudal neural tube patterning / positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta1 production / Golgi lumen acidification / synaptic vesicle lumen acidification / vacuolar transport / proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / cellular response to increased oxygen levels / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / endosome to plasma membrane protein transport / clathrin-coated vesicle membrane / lysosomal lumen acidification / endosomal lumen acidification / XBP1(S) activates chaperone genes / proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / head morphogenesis / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / osteoclast development / vacuolar acidification / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / regulation of cellular pH / dendritic spine membrane / azurophil granule membrane / ATPase activator activity / regulation of MAPK cascade / tertiary granule membrane / autophagosome membrane / ficolin-1-rich granule membrane / cilium assembly / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / RHOA GTPase cycle / regulation of macroautophagy / positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / transporter activator activity / Metabolism of Angiotensinogen to Angiotensins / Insulin receptor recycling / angiotensin maturation / receptor-mediated endocytosis of virus by host cell / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / axon terminus / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / RNA endonuclease activity / proton transmembrane transport / receptor-mediated endocytosis / secretory granule membrane / transmembrane transport / small GTPase binding / phagocytic vesicle membrane / synaptic vesicle membrane / melanosome / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / signaling receptor activity / ATPase binding / Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / postsynaptic membrane / early endosome / lysosome / endosome membrane / nuclear speck / apical plasma membrane / Golgi membrane / axon / external side of plasma membrane / lysosomal membrane / focal adhesion / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / Neutrophil degranulation / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / protein-containing complex binding / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / Golgi apparatus / extracellular exosome / membrane / plasma membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang L / Wu H | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2020 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2020Title: Structures of a Complete Human V-ATPase Reveal Mechanisms of Its Assembly. Authors: Longfei Wang / Di Wu / Carol V Robinson / Hao Wu / Tian-Min Fu /   Abstract: Vesicular- or vacuolar-type adenosine triphosphatases (V-ATPases) are ATP-driven proton pumps comprised of a cytoplasmic V complex for ATP hydrolysis and a membrane-embedded V complex for proton ...Vesicular- or vacuolar-type adenosine triphosphatases (V-ATPases) are ATP-driven proton pumps comprised of a cytoplasmic V complex for ATP hydrolysis and a membrane-embedded V complex for proton transfer. They play important roles in acidification of intracellular vesicles, organelles, and the extracellular milieu in eukaryotes. Here, we report cryoelectron microscopy structures of human V-ATPase in three rotational states at up to 2.9-Å resolution. Aided by mass spectrometry, we build all known protein subunits with associated N-linked glycans and identify glycolipids and phospholipids in the V complex. We define ATP6AP1 as a structural hub for V complex assembly because it connects to multiple V subunits and phospholipids in the c-ring. The glycolipids and the glycosylated V subunits form a luminal glycan coat critical for V-ATPase folding, localization, and stability. This study identifies mechanisms of V-ATPase assembly and biogenesis that rely on the integrated roles of ATP6AP1, glycans, and lipids. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_21844.map.gz emd_21844.map.gz | 169.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-21844-v30.xml emd-21844-v30.xml emd-21844.xml emd-21844.xml | 19.3 KB 19.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_21844.png emd_21844.png | 69.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-21844.cif.gz emd-21844.cif.gz | 7.6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21844 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21844 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21844 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21844 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 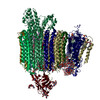 6wlwMC  6wlzC  6wm2C  6wm3C  6wm4C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-11132 (Title: Cryo-EM structures of human V-ATPase / Data size: 8.4 TB EMPIAR-11132 (Title: Cryo-EM structures of human V-ATPase / Data size: 8.4 TBData #1: Unaligned multi frame micrographs of human V-ATPase in complex with SidK [micrographs - multiframe]) |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_21844.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_21844.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | The Vo region of human V-ATPase in state 1 (focused refinement) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.08 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Human V-ATPase with SidK
+Supramolecule #1: Human V-ATPase with SidK
+Macromolecule #1: V-type proton ATPase 21 kDa proteolipid subunit
+Macromolecule #2: V-type proton ATPase 16 kDa proteolipid subunit
+Macromolecule #3: V-type proton ATPase subunit d 1
+Macromolecule #4: V-type proton ATPase 116 kDa subunit a isoform 1
+Macromolecule #5: V-type proton ATPase subunit e 1
+Macromolecule #6: Ribonuclease kappa
+Macromolecule #7: V-type proton ATPase subunit S1
+Macromolecule #8: Renin receptor
+Macromolecule #13: tri(methyl)-[2-[[(2~{R})-2-[(~{Z})-octadec-9-enoyl]oxy-3-[(~{E})-...
+Macromolecule #14: PHOSPHATIDYLETHANOLAMINE
+Macromolecule #15: (2~{S})-2-$l^{4}-azanyl-3-[[(2~{R})-3-octadecanoyloxy-2-oxidanyl-...
+Macromolecule #16: CHOLESTEROL
+Macromolecule #17: 1,2-DICAPROYL-SN-PHOSPHATIDYL-L-SERINE
+Macromolecule #18: methyl (3R,6Z,10E,14E)-3,7,11,15,19-pentamethylicosa-6,10,14,18-t...
+Macromolecule #19: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.1 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 1000000 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
| Final angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)