+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-0644 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
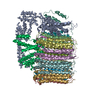
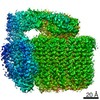
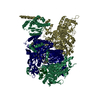
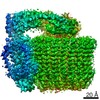
| Title | Saccharomyces cerevisiae V-ATPase Vph1-VO | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Proton pump / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcell wall mannoprotein biosynthetic process / ATPase-coupled ion transmembrane transporter activity / cellular response to alkaline pH / protein localization to vacuolar membrane / Insulin receptor recycling / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / polyphosphate metabolic process / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / Golgi lumen acidification ...cell wall mannoprotein biosynthetic process / ATPase-coupled ion transmembrane transporter activity / cellular response to alkaline pH / protein localization to vacuolar membrane / Insulin receptor recycling / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / polyphosphate metabolic process / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / Golgi lumen acidification / P-type proton-exporting transporter activity / vacuolar transport / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / endosomal lumen acidification / vacuole organization / protein targeting to vacuole / proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / fungal-type vacuole / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / cellular hyperosmotic response / vacuolar acidification / fungal-type vacuole membrane / phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate binding / proton transmembrane transporter activity / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / intracellular copper ion homeostasis / Neutrophil degranulation / RNA endonuclease activity / proton transmembrane transport / cell periphery / transmembrane transport / endocytosis / ATPase binding / protein-containing complex assembly / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / membrane raft / Golgi membrane / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Vasanthakumar T / Bueler SA / Wu D / Beilsten-Edmands V / Robinson CV / Rubinstein JL | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Canada, 1 items Canada, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2019 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2019Title: Structural comparison of the vacuolar and Golgi V-ATPases from . Authors: Thamiya Vasanthakumar / Stephanie A Bueler / Di Wu / Victoria Beilsten-Edmands / Carol V Robinson / John L Rubinstein /   Abstract: Proton-translocating vacuolar-type ATPases (V-ATPases) are necessary for numerous processes in eukaryotic cells, including receptor-mediated endocytosis, protein maturation, and lysosomal ...Proton-translocating vacuolar-type ATPases (V-ATPases) are necessary for numerous processes in eukaryotic cells, including receptor-mediated endocytosis, protein maturation, and lysosomal acidification. In mammals, V-ATPase subunit isoforms are differentially targeted to various intracellular compartments or tissues, but how these subunit isoforms influence enzyme activity is not clear. In the yeast , isoform diversity is limited to two different versions of the proton-translocating subunit a: Vph1p, which is targeted to the vacuole, and Stv1p, which is targeted to the Golgi apparatus and endosomes. We show that purified V-ATPase complexes containing Vph1p have higher ATPase activity than complexes containing Stv1p and that the relative difference in activity depends on the presence of lipids. We also show that V complexes containing Stv1p could be readily purified without attached V regions. We used this effect to determine structures of the membrane-embedded V region with Stv1p at 3.1-Å resolution, which we compare with a structure of the V region with Vph1p that we determine to 3.2-Å resolution. These maps reveal differences in the surface charge near the cytoplasmic proton half-channel. Both maps also show the presence of bound lipids, as well as regularly spaced densities that may correspond to ergosterol or bound detergent, around the c-ring. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_0644.map.gz emd_0644.map.gz | 5.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-0644-v30.xml emd-0644-v30.xml emd-0644.xml emd-0644.xml | 18.5 KB 18.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_0644.png emd_0644.png | 42.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-0644.cif.gz emd-0644.cif.gz | 6.7 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0644 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0644 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0644 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0644 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6o7tMC 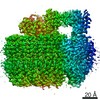 0645C  0646C 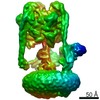 0647C  0648C  6o7uC  6o7vC  6o7wC  6o7xC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_0644.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_0644.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Saccharomyces cerevisiae V-ATPase Vph1-VO
| Entire | Name: Saccharomyces cerevisiae V-ATPase Vph1-VO |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Saccharomyces cerevisiae V-ATPase Vph1-VO
| Supramolecule | Name: Saccharomyces cerevisiae V-ATPase Vph1-VO / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: V-type proton ATPase subunit a, vacuolar isoform
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type proton ATPase subunit a, vacuolar isoform / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 98.34418 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MAEKEEAIFR SAEMALVQFY IPQEISRDSA YTLGQLGLVQ FRDLNSKVRA FQRTFVNEIR RLDNVERQYR YFYSLLKKHD IKLYEGDTD KYLDGSGELY VPPSGSVIDD YVRNASYLEE RLIQMEDATD QIEVQKNDLE QYRFILQSGD EFFLKGDNTD S TSYMDEDM ...String: MAEKEEAIFR SAEMALVQFY IPQEISRDSA YTLGQLGLVQ FRDLNSKVRA FQRTFVNEIR RLDNVERQYR YFYSLLKKHD IKLYEGDTD KYLDGSGELY VPPSGSVIDD YVRNASYLEE RLIQMEDATD QIEVQKNDLE QYRFILQSGD EFFLKGDNTD S TSYMDEDM IDANGENIAA AIGASVNYVT GVIARDKVAT LEQILWRVLR GNLFFKTVEI EQPVYDVKTR EYKHKNAFIV FS HGDLIIK RIRKIAESLD ANLYDVDSSN EGRSQQLAKV NKNLSDLYTV LKTTSTTLES ELYAIAKELD SWFQDVTREK AIF EILNKS NYDTNRKILI AEGWIPRDEL ATLQARLGEM IARLGIDVPS IIQVLDTNHT PPTFHRTNKF TAGFQSICDC YGIA QYREI NAGLPTIVTF PFMFAIMFGD MGHGFLMTLA ALSLVLNEKK INKMKRGEIF DMAFTGRYII LLMGVFSMYT GFLYN DIFS KTMTIFKSGW KWPDHWKKGE SITATSVGTY PIGLDWAWHG TENALLFSNS YKMKLSILMG FIHMTYSYFF SLANHL YFN SMIDIIGNFI PGLLFMQGIF GYLSVCIVYK WAVDWVKDGK PAPGLLNMLI NMFLSPGTID DELYPHQAKV QVFLLLM AL VCIPWLLLVK PLHFKFTHKK KSHEPLPSTE ADASSEDLEA QQLISAMDAD DAEEEEVGSG SHGEDFGDIM IHQVIHTI E FCLNCVSHTA SYLRLWALSL AHAQLSSVLW TMTIQIAFGF RGFVGVFMTV ALFAMWFALT CAVLVLMEGT SAMLHSLRL HWVESMSKFF VGEGLPYEPF AFEYKDMEVA VASASSSASS DYKDHDGDYK DHDIDYKDDD DK UniProtKB: V-type proton ATPase subunit a, vacuolar isoform |
-Macromolecule #2: V0 assembly protein 1
| Macromolecule | Name: V0 assembly protein 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 29.694885 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MVFGQLYALF IFTLSCCISK TVQADSSKES SSFISFDKES NWDTISTISS TADVISSVDS AIAVFEFDNF SLLDNLMIDE EYPFFNRFF ANDVSLTVHD DSPLNISQSL SPIMEQFTVD ELPESASDLL YEYSLDDKSI VLFKFTSDAY DLKKLDEFID S CLSFLEDK ...String: MVFGQLYALF IFTLSCCISK TVQADSSKES SSFISFDKES NWDTISTISS TADVISSVDS AIAVFEFDNF SLLDNLMIDE EYPFFNRFF ANDVSLTVHD DSPLNISQSL SPIMEQFTVD ELPESASDLL YEYSLDDKSI VLFKFTSDAY DLKKLDEFID S CLSFLEDK SGDNLTVVIN SLGWAFEDED GDDEYATEET LSHHDNNKGK EGDDDILSSI WTEGLLMCLI VSALLLFILI VA LSWISNL DITYGALEKS TNPIKKNN UniProtKB: V0 assembly protein 1 |
-Macromolecule #3: V-type proton ATPase subunit c''
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type proton ATPase subunit c'' / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 22.610641 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MNKESKDDDM SLGKFSFSHF LYYLVLIVVI VYGLYKLFTG HGSDINFGKF LLRTSPYMWA NLGIALCVGL SVVGAAWGIF ITGSSMIGA GVRAPRITTK NLISIIFCEV VAIYGLIIAI VFSSKLTVAT AENMYSKSNL YTGYSLFWAG ITVGASNLIC G IAVGITGA ...String: MNKESKDDDM SLGKFSFSHF LYYLVLIVVI VYGLYKLFTG HGSDINFGKF LLRTSPYMWA NLGIALCVGL SVVGAAWGIF ITGSSMIGA GVRAPRITTK NLISIIFCEV VAIYGLIIAI VFSSKLTVAT AENMYSKSNL YTGYSLFWAG ITVGASNLIC G IAVGITGA TAAISDAADS ALFVKILVIE IFGSILGLLG LIVGLLMAGK ASEFQ UniProtKB: V-type proton ATPase subunit c'' |
-Macromolecule #4: V-type proton ATPase subunit d
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type proton ATPase subunit d / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 39.822484 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MEGVYFNIDN GFIEGVVRGY RNGLLSNNQY INLTQCDTLE DLKLQLSSTD YGNFLSSVSS ESLTTSLIQE YASSKLYHEF NYIRDQSSG STRKFMDYIT YGYMIDNVAL MITGTIHDRD KGEILQRCHP LGWFDTLPTL SVATDLESLY ETVLVDTPLA P YFKNCFDT ...String: MEGVYFNIDN GFIEGVVRGY RNGLLSNNQY INLTQCDTLE DLKLQLSSTD YGNFLSSVSS ESLTTSLIQE YASSKLYHEF NYIRDQSSG STRKFMDYIT YGYMIDNVAL MITGTIHDRD KGEILQRCHP LGWFDTLPTL SVATDLESLY ETVLVDTPLA P YFKNCFDT AEELDDMNIE IIRNKLYKAY LEDFYNFVTE EIPEPAKECM QTLLGFEADR RSINIALNSL QSSDIDPDLK SD LLPNIGK LYPLATFHLA QAQDFEGVRA ALANVYEYRG FLETGNLEDH FYQLEMELCR DAFTQQFAIS TVWAWMKSKE QEV RNITWI AECIAQNQRE RINNYISVY UniProtKB: V-type proton ATPase subunit d |
-Macromolecule #5: Putative protein YPR170W-B
| Macromolecule | Name: Putative protein YPR170W-B / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 9.369934 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MRPVVSTGKA WCCTVLSAFG VVILSVIAHL FNTNHESFVG SINDPEDGPA VAHTVYLAAL VYLVFFVFCG FQVYLARRKP SIELR UniProtKB: V-type proton ATPase subunit f |
-Macromolecule #6: V-type proton ATPase subunit c
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type proton ATPase subunit c / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 8 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 16.357501 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MTELCPVYAP FFGAIGCASA IIFTSLGAAY GTAKSGVGIC ATCVLRPDLL FKNIVPVIMA GIIAIYGLVV SVLVCYSLGQ KQALYTGFI QLGAGLSVGL SGLAAGFAIG IVGDAGVRGS SQQPRLFVGM ILILIFAEVL GLYGLIVALL LNSRATQDVV C UniProtKB: V-type proton ATPase subunit c |
-Macromolecule #7: V-type proton ATPase subunit c'
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type proton ATPase subunit c' / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 17.046361 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MSTQLASNIY APLYAPFFGF AGCAAAMVLS CLGAAIGTAK SGIGIAGIGT FKPELIMKSL IPVVMSGILA IYGLVVAVLI AGNLSPTED YTLFNGFMHL SCGLCVGFAC LSSGYAIGMV GDVGVRKYMH QPRLFVGIVL ILIFSEVLGL YGMIVALILN T RGSE UniProtKB: V-type proton ATPase subunit c' |
-Macromolecule #8: V-type proton ATPase subunit e
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type proton ATPase subunit e / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 8.387065 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MSSFYTVVGV FIVVSAMSVL FWIMAPKNNQ AVWRSTVILT LAMMFLMWAI TFLCQLHPLV APRRSDLRPE FAE UniProtKB: V-type proton ATPase subunit e |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 4096 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 4096 pixel / Average electron dose: 42.7 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER / Details: Ab initio |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 296105 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















