+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6o7v | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
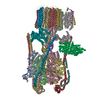
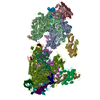
| Title | Saccharomyces cerevisiae V-ATPase Stv1-V1VO State 1 | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Proton pump | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationvacuole-mitochondrion membrane contact site / cell wall mannoprotein biosynthetic process / ATPase-coupled ion transmembrane transporter activity / proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain / Insulin receptor recycling / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / Golgi lumen acidification / proteasome storage granule assembly ...vacuole-mitochondrion membrane contact site / cell wall mannoprotein biosynthetic process / ATPase-coupled ion transmembrane transporter activity / proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain / Insulin receptor recycling / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / Golgi lumen acidification / proteasome storage granule assembly / P-type proton-exporting transporter activity / vacuolar transport / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / endosomal lumen acidification / vacuole organization / protein targeting to vacuole / proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / pexophagy / fungal-type vacuole / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / vacuolar acidification / fungal-type vacuole membrane / phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate binding / proton transmembrane transporter activity / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / intracellular copper ion homeostasis / ATP metabolic process / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / Neutrophil degranulation / RNA endonuclease activity / proton transmembrane transport / cell periphery / transmembrane transport / endocytosis / cytoplasmic stress granule / intracellular calcium ion homeostasis / late endosome / ATPase binding / protein-containing complex assembly / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / endosome membrane / membrane raft / Golgi membrane / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / Golgi apparatus / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
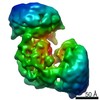
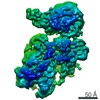
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.6 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Vasanthakumar, T. / Bueler, S.A. / Wu, D. / Beilsten-Edmands, V. / Robinson, C.V. / Rubinstein, J.L. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Canada, 1items Canada, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2019 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2019Title: Structural comparison of the vacuolar and Golgi V-ATPases from . Authors: Thamiya Vasanthakumar / Stephanie A Bueler / Di Wu / Victoria Beilsten-Edmands / Carol V Robinson / John L Rubinstein /   Abstract: Proton-translocating vacuolar-type ATPases (V-ATPases) are necessary for numerous processes in eukaryotic cells, including receptor-mediated endocytosis, protein maturation, and lysosomal ...Proton-translocating vacuolar-type ATPases (V-ATPases) are necessary for numerous processes in eukaryotic cells, including receptor-mediated endocytosis, protein maturation, and lysosomal acidification. In mammals, V-ATPase subunit isoforms are differentially targeted to various intracellular compartments or tissues, but how these subunit isoforms influence enzyme activity is not clear. In the yeast , isoform diversity is limited to two different versions of the proton-translocating subunit a: Vph1p, which is targeted to the vacuole, and Stv1p, which is targeted to the Golgi apparatus and endosomes. We show that purified V-ATPase complexes containing Vph1p have higher ATPase activity than complexes containing Stv1p and that the relative difference in activity depends on the presence of lipids. We also show that V complexes containing Stv1p could be readily purified without attached V regions. We used this effect to determine structures of the membrane-embedded V region with Stv1p at 3.1-Å resolution, which we compare with a structure of the V region with Vph1p that we determine to 3.2-Å resolution. These maps reveal differences in the surface charge near the cytoplasmic proton half-channel. Both maps also show the presence of bound lipids, as well as regularly spaced densities that may correspond to ergosterol or bound detergent, around the c-ring. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6o7v.cif.gz 6o7v.cif.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6o7v.ent.gz pdb6o7v.ent.gz | 732.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6o7v.json.gz 6o7v.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o7/6o7v https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o7/6o7v ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o7/6o7v ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o7/6o7v | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  0646MC  0644C  0645C  0647C  0648C  6o7tC  6o7uC  6o7wC  6o7xC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 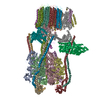
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-V-type proton ATPase subunit ... , 13 types, 26 molecules MNBDFLHJKGIPOacdghijklmnoe
| #1: Protein | Mass: 29235.023 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P32610 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 13479.170 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P39111 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| #4: Protein | Mass: 57815.023 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P16140 #5: Protein | Mass: 12738.706 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P48836 #6: Protein | Mass: 26508.393 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P22203 #7: Protein | | Mass: 54482.609 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P41807 #8: Protein | | Mass: 44241.352 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P31412 #9: Protein | | Mass: 101762.438 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P37296 #11: Protein | | Mass: 22610.641 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #12: Protein | | Mass: 39822.484 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P32366 #13: Protein | Mass: 16357.501 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P25515 #14: Protein | | Mass: 17046.361 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P32842 #15: Protein | | Mass: 8387.065 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: Q3E7B6 |
-Protein , 3 types, 5 molecules ACEbf
| #3: Protein | Mass: 70515.203 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: RM11-1a / References: UniProt: B3LH69 #10: Protein | | Mass: 29694.885 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #16: Protein | | Mass: 9369.934 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P0C5R9 |
|---|
-Details
| Sequence details | Authors state that the C-terminal 3XFLAG tag of V-type proton ATPase catalytic subunit A was ...Authors state that the C-terminal 3XFLAG tag of V-type proton ATPase catalytic subunit A was incorporated into the chromosome of S. cerevisiae by homologous recombination. |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Saccharomyces cerevisiae V-ATPase Stv1-V1VO State 1 / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI F20 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 35 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 6.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 25045 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj











