+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6wlz | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
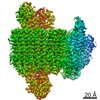
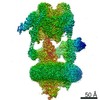
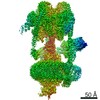
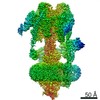
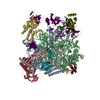
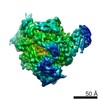
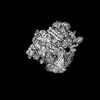
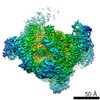
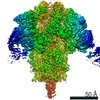
| Title | The V1 region of human V-ATPase in state 1 (focused refinement) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / V-ATPase / proton pump | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationproton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex / Ion channel transport / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in lysosome biogenesis and autophagy / intracellular pH reduction / symbiont-mediated suppression of host phagosome acidification / ATPase-coupled ion transmembrane transporter activity / Golgi lumen acidification / synaptic vesicle lumen acidification / extrinsic component of synaptic vesicle membrane / cellular response to increased oxygen levels ...proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex / Ion channel transport / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in lysosome biogenesis and autophagy / intracellular pH reduction / symbiont-mediated suppression of host phagosome acidification / ATPase-coupled ion transmembrane transporter activity / Golgi lumen acidification / synaptic vesicle lumen acidification / extrinsic component of synaptic vesicle membrane / cellular response to increased oxygen levels / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain / clathrin-coated vesicle membrane / lysosomal lumen acidification / endosomal lumen acidification / proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / protein localization to cilium / vacuolar acidification / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / proton transmembrane transporter activity / microvillus / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / cilium assembly / regulation of macroautophagy / ATP metabolic process / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / specific granule membrane / Insulin receptor recycling / ruffle / proton transmembrane transport / secretory granule / melanosome / synaptic vesicle membrane / ATPase binding / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / apical plasma membrane / endosome / endosome membrane / cilium / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / Golgi membrane / lysosomal membrane / Neutrophil degranulation / centrosome / ATP hydrolysis activity / extracellular exosome / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / membrane / plasma membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) Legionella pneumophila subsp. pneumophila (bacteria) Legionella pneumophila subsp. pneumophila (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.9 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang, L. / Wu, H. / Fu, T.M. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2020 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2020Title: Structures of a Complete Human V-ATPase Reveal Mechanisms of Its Assembly. Authors: Longfei Wang / Di Wu / Carol V Robinson / Hao Wu / Tian-Min Fu /   Abstract: Vesicular- or vacuolar-type adenosine triphosphatases (V-ATPases) are ATP-driven proton pumps comprised of a cytoplasmic V complex for ATP hydrolysis and a membrane-embedded V complex for proton ...Vesicular- or vacuolar-type adenosine triphosphatases (V-ATPases) are ATP-driven proton pumps comprised of a cytoplasmic V complex for ATP hydrolysis and a membrane-embedded V complex for proton transfer. They play important roles in acidification of intracellular vesicles, organelles, and the extracellular milieu in eukaryotes. Here, we report cryoelectron microscopy structures of human V-ATPase in three rotational states at up to 2.9-Å resolution. Aided by mass spectrometry, we build all known protein subunits with associated N-linked glycans and identify glycolipids and phospholipids in the V complex. We define ATP6AP1 as a structural hub for V complex assembly because it connects to multiple V subunits and phospholipids in the c-ring. The glycolipids and the glycosylated V subunits form a luminal glycan coat critical for V-ATPase folding, localization, and stability. This study identifies mechanisms of V-ATPase assembly and biogenesis that rely on the integrated roles of ATP6AP1, glycans, and lipids. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6wlz.cif.gz 6wlz.cif.gz | 887.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6wlz.ent.gz pdb6wlz.ent.gz | 729.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6wlz.json.gz 6wlz.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wl/6wlz https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wl/6wlz ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wl/6wlz ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wl/6wlz | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 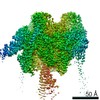 21845MC 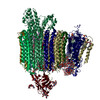 6wlwC  6wm2C  6wm3C  6wm4C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-11132 (Title: Cryo-EM structures of human V-ATPase / Data size: 8.4 TB EMPIAR-11132 (Title: Cryo-EM structures of human V-ATPase / Data size: 8.4 TBData #1: Unaligned multi frame micrographs of human V-ATPase in complex with SidK [micrographs - multiframe]) |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 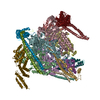
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 2 types, 6 molecules ABCXYZ
| #1: Protein | Mass: 68379.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)References: UniProt: P38606, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase #3: Protein | Mass: 65505.297 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Legionella pneumophila subsp. pneumophila (strain Philadelphia 1 / ATCC 33152 / DSM 7513) (bacteria) Legionella pneumophila subsp. pneumophila (strain Philadelphia 1 / ATCC 33152 / DSM 7513) (bacteria)Strain: Philadelphia 1 / ATCC 33152 / DSM 7513 / References: UniProt: Q5ZWW6 |
|---|
-V-type proton ATPase subunit ... , 5 types, 11 molecules DEFJIHMLKGN
| #2: Protein | Mass: 56561.500 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P21281 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P21281#4: Protein | Mass: 26183.346 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P36543 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P36543#5: Protein | Mass: 13781.547 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O75348 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O75348#6: Protein | | Mass: 28311.918 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9Y5K8 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9Y5K8#7: Protein | | Mass: 13388.210 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q16864 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q16864 |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 1 types, 1 molecules 
| #8: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50.1 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.17.1_3660: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 1000000 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj









