+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structures of a Complete Human V-ATPase Reveal Mechanisms of Its Assembly. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Mol Cell, Vol. 80, Issue 3, Page 501-511.e3, Year 2020 |
| Publish date | Nov 5, 2020 |
 Authors Authors | Longfei Wang / Di Wu / Carol V Robinson / Hao Wu / Tian-Min Fu /   |
| PubMed Abstract | Vesicular- or vacuolar-type adenosine triphosphatases (V-ATPases) are ATP-driven proton pumps comprised of a cytoplasmic V complex for ATP hydrolysis and a membrane-embedded V complex for proton ...Vesicular- or vacuolar-type adenosine triphosphatases (V-ATPases) are ATP-driven proton pumps comprised of a cytoplasmic V complex for ATP hydrolysis and a membrane-embedded V complex for proton transfer. They play important roles in acidification of intracellular vesicles, organelles, and the extracellular milieu in eukaryotes. Here, we report cryoelectron microscopy structures of human V-ATPase in three rotational states at up to 2.9-Å resolution. Aided by mass spectrometry, we build all known protein subunits with associated N-linked glycans and identify glycolipids and phospholipids in the V complex. We define ATP6AP1 as a structural hub for V complex assembly because it connects to multiple V subunits and phospholipids in the c-ring. The glycolipids and the glycosylated V subunits form a luminal glycan coat critical for V-ATPase folding, localization, and stability. This study identifies mechanisms of V-ATPase assembly and biogenesis that rely on the integrated roles of ATP6AP1, glycans, and lipids. |
 External links External links |  Mol Cell / Mol Cell /  PubMed:33065002 / PubMed:33065002 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.9 - 3.6 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-21844, PDB-6wlw: EMDB-21845, PDB-6wlz: EMDB-21847, PDB-6wm2: EMDB-21848, PDB-6wm3: EMDB-21849, PDB-6wm4: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-WSS:  ChemComp-PTY:  ChemComp-WJS:  ChemComp-CLR:  ChemComp-PSF:  ChemComp-WJP:  ChemComp-NAG:  ChemComp-ADP: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / V-ATPase / proton pump / pump |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers



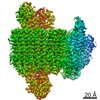
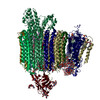
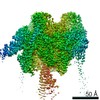

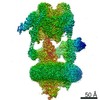
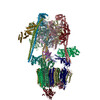
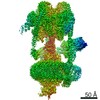

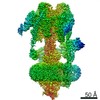

 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human) Legionella pneumophila subsp. pneumophila (bacteria)
Legionella pneumophila subsp. pneumophila (bacteria)