[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7ubn: Transcription antitermination complex: NusA-containing "engaged" ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7ubn | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
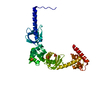
| Title | Transcription antitermination complex: NusA-containing "engaged" Qlambda-loading complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GENE REGULATION / TRANSFERASE/DNA/RNA / RNA polymerase / DNA Binding / transcription / Q-dependent antitermination / Q antitermination factor / TRANSFERASE-DNA-RNA complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsubmerged biofilm formation / cellular response to cell envelope stress / regulation of DNA-templated transcription initiation / sigma factor activity / bacterial-type flagellum assembly / cytosolic DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility / nitrate assimilation / translation elongation factor activity / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation ...submerged biofilm formation / cellular response to cell envelope stress / regulation of DNA-templated transcription initiation / sigma factor activity / bacterial-type flagellum assembly / cytosolic DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility / nitrate assimilation / translation elongation factor activity / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation / transcription elongation factor complex / transcription antitermination / DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / cell motility / DNA-templated transcription initiation / DNA-templated transcription termination / ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / response to heat / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / protein dimerization activity / DNA-binding transcription factor activity / response to antibiotic / nucleotide binding / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / DNA-templated transcription / magnesium ion binding / DNA binding / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / metal ion binding / membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Escherichia phage Lambda (virus) Escherichia phage Lambda (virus) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.36 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Yin, Z. / Ebright, R.H. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2022 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2022Title: In transcription antitermination by Qλ, NusA induces refolding of Qλ to form a nozzle that extends the RNA polymerase RNA-exit channel. Authors: Zhou Yin / Jeremy G Bird / Jason T Kaelber / Bryce E Nickels / Richard H Ebright /  Abstract: Lambdoid bacteriophage Q proteins are transcription antipausing and antitermination factors that enable RNA polymerase (RNAP) to read through pause and termination sites. Q proteins load onto RNAP ...Lambdoid bacteriophage Q proteins are transcription antipausing and antitermination factors that enable RNA polymerase (RNAP) to read through pause and termination sites. Q proteins load onto RNAP engaged in promoter-proximal pausing at a Q binding element (QBE) and adjacent sigma-dependent pause element to yield a Q-loading complex, and they translocate with RNAP as a pausing-deficient, termination-deficient Q-loaded complex. In previous work, we showed that the Q protein of bacteriophage 21 (Q21) functions by forming a nozzle that narrows and extends the RNAP RNA-exit channel, preventing formation of pause and termination RNA hairpins. Here, we report atomic structures of four states on the pathway of antitermination by the Q protein of bacteriophage λ (Qλ), a Q protein that shows no sequence similarity to Q21 and that, unlike Q21, requires the transcription elongation factor NusA for efficient antipausing and antitermination. We report structures of Qλ, the Qλ-QBE complex, the NusA-free pre-engaged Qλ-loading complex, and the NusA-containing engaged Qλ-loading complex. The results show that Qλ, like Q21, forms a nozzle that narrows and extends the RNAP RNA-exit channel, preventing formation of RNA hairpins. However, the results show that Qλ has no three-dimensional structural similarity to Q21, employs a different mechanism of QBE recognition than Q21, and employs a more complex process for loading onto RNAP than Q21, involving recruitment of Qλ to form a pre-engaged loading complex, followed by NusA-facilitated refolding of Qλ to form an engaged loading complex. The results establish that Qλ and Q21 are not structural homologs and are solely functional analogs. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7ubn.cif.gz 7ubn.cif.gz | 816.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7ubn.ent.gz pdb7ubn.ent.gz | 643.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7ubn.json.gz 7ubn.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ub/7ubn https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ub/7ubn ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ub/7ubn ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ub/7ubn | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  26439MC 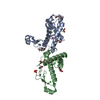 7ubjC  7ubkC 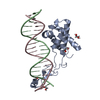 7ublC  7ubmC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 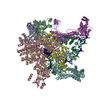
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules 12
| #1: DNA chain | Mass: 18933.164 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Escherichia phage Lambda (virus) Escherichia phage Lambda (virus) |
|---|---|
| #2: DNA chain | Mass: 18600.982 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Escherichia phage Lambda (virus) Escherichia phage Lambda (virus) |
-DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit ... , 4 types, 5 molecules ABCDE
| #3: Protein | Mass: 36558.680 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #4: Protein | | Mass: 150820.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #5: Protein | | Mass: 158314.891 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #6: Protein | | Mass: 10249.547 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|
-Protein , 3 types, 3 molecules FNQ
| #7: Protein | Mass: 71912.906 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|---|
| #8: Protein | Mass: 57104.047 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #9: Protein | Mass: 22505.967 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: Q, AAS29_003868, ELT39_15625, ELV12_09750, G4A38_03705, SAMEA3472067_02047 Production host:  |
-RNA chain , 1 types, 1 molecules R
| #10: RNA chain | Mass: 3626.226 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 4 molecules 


| #11: Chemical | | #12: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Transcription antitermination complex: NusA-containing "engaged" Qlambda-loading complex Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#10 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.55 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 9 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 292 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 5 sec. / Electron dose: 1.1 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 1643 |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 40 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: dev_3699: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 511891 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.36 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 12391 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 100 / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Correlation coefficient | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj