+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5lm7 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
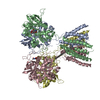
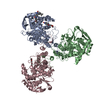
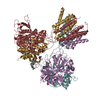
| Title | Crystal structure of the lambda N-Nus factor complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION / Transcription regulation antitermination Nus proteins Phage lambda N protein | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationRNA polymerase binding / transcription antitermination factor activity, RNA binding / bacterial-type RNA polymerase core enzyme binding / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation / transcription antitermination / DNA-templated transcription termination / RNA stem-loop binding / tRNA binding / single-stranded RNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome ...RNA polymerase binding / transcription antitermination factor activity, RNA binding / bacterial-type RNA polymerase core enzyme binding / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation / transcription antitermination / DNA-templated transcription termination / RNA stem-loop binding / tRNA binding / single-stranded RNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / translation / DNA-binding transcription factor activity / ribonucleoprotein complex / nucleotide binding / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / DNA binding / RNA binding / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |    Enterobacteria phage lambda (virus) Enterobacteria phage lambda (virus) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 3.35 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 3.35 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Said, N. / Santos, K. / Weber, G. / Wahl, M.C. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Microbiol / Year: 2017 Journal: Nat Microbiol / Year: 2017Title: Structural basis for λN-dependent processive transcription antitermination. Authors: Nelly Said / Ferdinand Krupp / Ekaterina Anedchenko / Karine F Santos / Olexandr Dybkov / Yong-Heng Huang / Chung-Tien Lee / Bernhard Loll / Elmar Behrmann / Jörg Bürger / Thorsten Mielke ...Authors: Nelly Said / Ferdinand Krupp / Ekaterina Anedchenko / Karine F Santos / Olexandr Dybkov / Yong-Heng Huang / Chung-Tien Lee / Bernhard Loll / Elmar Behrmann / Jörg Bürger / Thorsten Mielke / Justus Loerke / Henning Urlaub / Christian M T Spahn / Gert Weber / Markus C Wahl /  Abstract: λN-mediated processive antitermination constitutes a paradigmatic transcription regulatory event, during which phage protein λN, host factors NusA, NusB, NusE and NusG, and an RNA nut site render ...λN-mediated processive antitermination constitutes a paradigmatic transcription regulatory event, during which phage protein λN, host factors NusA, NusB, NusE and NusG, and an RNA nut site render elongating RNA polymerase termination-resistant. The structural basis of the process has so far remained elusive. Here we describe a crystal structure of a λN-NusA-NusB-NusE-nut site complex and an electron cryo-microscopic structure of a complete transcription antitermination complex, comprising RNA polymerase, DNA, nut site RNA, all Nus factors and λN, validated by crosslinking/mass spectrometry. Due to intrinsic disorder, λN can act as a multiprotein/RNA interaction hub, which, together with nut site RNA, arranges NusA, NusB and NusE into a triangular complex. This complex docks via the NusA N-terminal domain and the λN C-terminus next to the RNA exit channel on RNA polymerase. Based on the structures, comparative crosslinking analyses and structure-guided mutagenesis, we hypothesize that λN mounts a multipronged strategy to reprogram the transcriptional machinery, which may include (1) the λN C terminus clamping the RNA exit channel, thus stabilizing the DNA:RNA hybrid; (2) repositioning of NusA and RNAP elements, thus redirecting nascent RNA and sequestering the upstream branch of a terminator hairpin; and (3) hindering RNA engagement of termination factor ρ and/or obstructing ρ translocation on the transcript. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5lm7.cif.gz 5lm7.cif.gz | 330.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5lm7.ent.gz pdb5lm7.ent.gz | 265.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5lm7.json.gz 5lm7.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lm/5lm7 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lm/5lm7 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lm/5lm7 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lm/5lm7 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  3561C  5lm9C  5ms0C  1l2fS  1qfqS  1u9lS  2kwpS  3b3dS S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 
| ||||||||
| 2 | 
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 47666.641 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #2: Protein | Mass: 15838.161 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: S88 / ExPEC / Gene: nusB, ECS88_0411 / Production host:  #3: Protein | Mass: 12167.051 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: S88 / ExPEC / Gene: rpsJ, ECS88_3708 / Production host:  #4: Protein | Mass: 10279.788 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Enterobacteria phage lambda (virus) / Gene: N, lambdap49 / Production host: Enterobacteria phage lambda (virus) / Gene: N, lambdap49 / Production host:  #5: RNA chain | Mass: 9573.745 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Enterobacteria phage lambda (virus) Enterobacteria phage lambda (virus) |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 3.57 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 65.56 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 295 K / Method: vapor diffusion, sitting drop Details: 0.1M HEPES pH 7.5, 40%(v/v) ethylene glycol, 5% (w/v) PEG 3000 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  BESSY BESSY  / Beamline: 14.1 / Wavelength: 0.918 Å / Beamline: 14.1 / Wavelength: 0.918 Å |
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS PILATUS3 S 6M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Jan 29, 2016 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.918 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 3.35→50 Å / Num. obs: 40077 / % possible obs: 99.3 % / Redundancy: 7.3 % / Rsym value: 0.15 / Net I/σ(I): 11.56 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 3.35→3.55 Å / Redundancy: 7.5 % / Rsym value: 2.02 / % possible all: 98.3 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 1L2F, 2KWP, 1U9L, 3B3D, 1QFQ Resolution: 3.35→39.52 Å / SU ML: 0.62 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.35 / Phase error: 42.66 / Stereochemistry target values: ML
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 3.35→39.52 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj

































