[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-5ms0: pseudo-atomic model of the RNA polymerase lambda-based antitermin... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5ms0 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
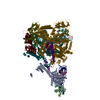
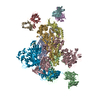
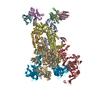
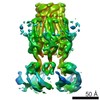
| Title | pseudo-atomic model of the RNA polymerase lambda-based antitermination complex solved by cryo-EM | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION/DNA/RNA / DNA-DEPENDENT RNA POLYMERASE / BACTERIAL TRANSCRIPTION / TERNARY ELONGATION COMPLEX / ANTITERMINATION / TRANSCRIPTION-DNA-RNA complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationRNA polymerase binding / transcription elongation-coupled chromatin remodeling / RNA polymerase complex / submerged biofilm formation / cellular response to cell envelope stress / regulation of DNA-templated transcription initiation / protein complex oligomerization / bacterial-type flagellum assembly / transcription antitermination factor activity, RNA binding / bacterial-type RNA polymerase core enzyme binding ...RNA polymerase binding / transcription elongation-coupled chromatin remodeling / RNA polymerase complex / submerged biofilm formation / cellular response to cell envelope stress / regulation of DNA-templated transcription initiation / protein complex oligomerization / bacterial-type flagellum assembly / transcription antitermination factor activity, RNA binding / bacterial-type RNA polymerase core enzyme binding / cytosolic DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility / nitrate assimilation / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation / transcription elongation factor complex / transcription antitermination / DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / cell motility / DNA-templated transcription initiation / DNA-templated transcription termination / RNA stem-loop binding / ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / ribosome biogenesis / response to heat / protein-containing complex assembly / small ribosomal subunit / cytosolic small ribosomal subunit / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / cytoplasmic translation / tRNA binding / protein dimerization activity / single-stranded RNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / DNA-binding transcription factor activity / protein domain specific binding / response to antibiotic / nucleotide binding / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / DNA-templated transcription / magnesium ion binding / DNA binding / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Escherichia phage lambda (virus) Escherichia phage lambda (virus)  | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 9.8 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Said, N. / Krupp, F. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 1items Germany, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Microbiol / Year: 2017 Journal: Nat Microbiol / Year: 2017Title: Structural basis for λN-dependent processive transcription antitermination. Authors: Nelly Said / Ferdinand Krupp / Ekaterina Anedchenko / Karine F Santos / Olexandr Dybkov / Yong-Heng Huang / Chung-Tien Lee / Bernhard Loll / Elmar Behrmann / Jörg Bürger / Thorsten Mielke ...Authors: Nelly Said / Ferdinand Krupp / Ekaterina Anedchenko / Karine F Santos / Olexandr Dybkov / Yong-Heng Huang / Chung-Tien Lee / Bernhard Loll / Elmar Behrmann / Jörg Bürger / Thorsten Mielke / Justus Loerke / Henning Urlaub / Christian M T Spahn / Gert Weber / Markus C Wahl /  Abstract: λN-mediated processive antitermination constitutes a paradigmatic transcription regulatory event, during which phage protein λN, host factors NusA, NusB, NusE and NusG, and an RNA nut site render ...λN-mediated processive antitermination constitutes a paradigmatic transcription regulatory event, during which phage protein λN, host factors NusA, NusB, NusE and NusG, and an RNA nut site render elongating RNA polymerase termination-resistant. The structural basis of the process has so far remained elusive. Here we describe a crystal structure of a λN-NusA-NusB-NusE-nut site complex and an electron cryo-microscopic structure of a complete transcription antitermination complex, comprising RNA polymerase, DNA, nut site RNA, all Nus factors and λN, validated by crosslinking/mass spectrometry. Due to intrinsic disorder, λN can act as a multiprotein/RNA interaction hub, which, together with nut site RNA, arranges NusA, NusB and NusE into a triangular complex. This complex docks via the NusA N-terminal domain and the λN C-terminus next to the RNA exit channel on RNA polymerase. Based on the structures, comparative crosslinking analyses and structure-guided mutagenesis, we hypothesize that λN mounts a multipronged strategy to reprogram the transcriptional machinery, which may include (1) the λN C terminus clamping the RNA exit channel, thus stabilizing the DNA:RNA hybrid; (2) repositioning of NusA and RNAP elements, thus redirecting nascent RNA and sequestering the upstream branch of a terminator hairpin; and (3) hindering RNA engagement of termination factor ρ and/or obstructing ρ translocation on the transcript. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5ms0.cif.gz 5ms0.cif.gz | 651.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5ms0.ent.gz pdb5ms0.ent.gz | 429.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5ms0.json.gz 5ms0.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ms/5ms0 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ms/5ms0 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ms/5ms0 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ms/5ms0 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 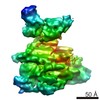 3561MC  5lm7C  5lm9C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 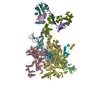
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 3 types, 3 molecules NEL
| #1: Protein | Mass: 9877.343 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: lambda N factor / Source: (gene. exp.)  Escherichia phage lambda (virus) / Gene: N, lambdap49 / Production host: Escherichia phage lambda (virus) / Gene: N, lambdap49 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #6: Protein | Mass: 11340.067 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #11: Protein | Mass: 15709.967 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
-RNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules RH
| #2: RNA chain | Mass: 9339.650 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|---|
| #8: RNA chain | Mass: 4492.788 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
-DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit ... , 4 types, 5 molecules ABCDO
| #3: Protein | Mass: 36558.680 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #4: Protein | | Mass: 150804.922 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: rpoB, groN, nitB, rif, ron, stl, stv, tabD, b3987, JW3950 Production host:  #5: Protein | | Mass: 156537.031 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #13: Protein | | Mass: 10249.547 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|
-Transcription termination/antitermination protein ... , 2 types, 2 molecules FM
| #7: Protein | Mass: 20688.654 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|---|
| #12: Protein | Mass: 55059.828 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules IJ
| #9: DNA chain | Mass: 8355.408 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|---|
| #10: DNA chain | Mass: 11942.696 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 3 molecules 


| #14: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
|---|---|
| #15: Chemical |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: lambdaN-dependent antitermination complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#13 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: 10 mM HEPES-NaOH, pH 7.5, 50 mM NaCl, 1 mM DTT |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI POLARA 300 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 1 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 9.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 23983 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj


































































