+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7ubj | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Transcription antitermination factor Qlambda, type-I crystal | ||||||
 Components Components | Antitermination protein Q | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GENE REGULATION / RNA polymerase / DNA Binding / transcription / Q-dependent antitermination / Q antitermination factor | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationtranscription antitermination / DNA-templated transcription termination / DNA binding / zinc ion binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Escherichia phage Lambda (virus) Escherichia phage Lambda (virus) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT /  molecular replacement / Resolution: 1.46 Å molecular replacement / Resolution: 1.46 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Yin, Z. / Ebright, R.H. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2022 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2022Title: In transcription antitermination by Qλ, NusA induces refolding of Qλ to form a nozzle that extends the RNA polymerase RNA-exit channel. Authors: Zhou Yin / Jeremy G Bird / Jason T Kaelber / Bryce E Nickels / Richard H Ebright /  Abstract: Lambdoid bacteriophage Q proteins are transcription antipausing and antitermination factors that enable RNA polymerase (RNAP) to read through pause and termination sites. Q proteins load onto RNAP ...Lambdoid bacteriophage Q proteins are transcription antipausing and antitermination factors that enable RNA polymerase (RNAP) to read through pause and termination sites. Q proteins load onto RNAP engaged in promoter-proximal pausing at a Q binding element (QBE) and adjacent sigma-dependent pause element to yield a Q-loading complex, and they translocate with RNAP as a pausing-deficient, termination-deficient Q-loaded complex. In previous work, we showed that the Q protein of bacteriophage 21 (Q21) functions by forming a nozzle that narrows and extends the RNAP RNA-exit channel, preventing formation of pause and termination RNA hairpins. Here, we report atomic structures of four states on the pathway of antitermination by the Q protein of bacteriophage λ (Qλ), a Q protein that shows no sequence similarity to Q21 and that, unlike Q21, requires the transcription elongation factor NusA for efficient antipausing and antitermination. We report structures of Qλ, the Qλ-QBE complex, the NusA-free pre-engaged Qλ-loading complex, and the NusA-containing engaged Qλ-loading complex. The results show that Qλ, like Q21, forms a nozzle that narrows and extends the RNAP RNA-exit channel, preventing formation of RNA hairpins. However, the results show that Qλ has no three-dimensional structural similarity to Q21, employs a different mechanism of QBE recognition than Q21, and employs a more complex process for loading onto RNAP than Q21, involving recruitment of Qλ to form a pre-engaged loading complex, followed by NusA-facilitated refolding of Qλ to form an engaged loading complex. The results establish that Qλ and Q21 are not structural homologs and are solely functional analogs. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7ubj.cif.gz 7ubj.cif.gz | 137.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7ubj.ent.gz pdb7ubj.ent.gz | 106.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7ubj.json.gz 7ubj.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ub/7ubj https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ub/7ubj ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ub/7ubj ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ub/7ubj | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7ubkC  7ublC  7ubmC  7ubnC  4mo1S S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 1 types, 2 molecules AB
| #1: Protein | Mass: 16222.834 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Fragment: UNP residues 62-207 / Mutation: E134K Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Escherichia phage Lambda (virus) / Production host: Escherichia phage Lambda (virus) / Production host:  |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 7 types, 461 molecules 



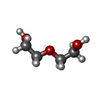








| #2: Chemical | | #3: Chemical | #4: Chemical | #5: Chemical | ChemComp-EDO / #6: Chemical | #7: Chemical | ChemComp-PO4 / | #8: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.89 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 57.47 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 292 K / Method: vapor diffusion, sitting drop / pH: 7 Details: 20% v/v glycerol, 0.4 M potassium phosphate dibasic, 16% PEG8000 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  APS APS  / Beamline: 19-ID / Wavelength: 0.987 Å / Beamline: 19-ID / Wavelength: 0.987 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS PILATUS3 6M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Dec 5, 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.987 Å / Relative weight: 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection | Resolution: 1.46→50 Å / Num. obs: 63011 / % possible obs: 99.7 % / Redundancy: 5.1 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.049 / Rpim(I) all: 0.024 / Rrim(I) all: 0.055 / Χ2: 0.85 / Net I/σ(I): 11.9 / Num. measured all: 319426 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection shell | Diffraction-ID: 1
|
-Phasing
| Phasing | Method:  molecular replacement molecular replacement |
|---|
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: PDB entry 4MO1 Resolution: 1.46→43.273 Å / SU ML: 0.14 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 1.98 / Phase error: 22.63 / Stereochemistry target values: ML
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 88.93 Å2 / Biso mean: 23.5208 Å2 / Biso min: 4.42 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: final / Resolution: 1.46→43.273 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Rfactor Rfree error: 0
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj






