+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6eny | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
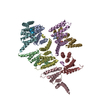
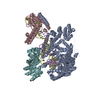
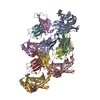
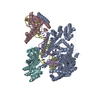
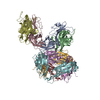
| Title | Structure of the human PLC editing module | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | IMMUNE SYSTEM / adaptive immunity / antigen processing / chaperone / MHC class I | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationMHC class Ib protein complex assembly / peptide antigen stabilization / Tapasin-ERp57 complex / response to biphenyl / Calnexin/calreticulin cycle / MHC class I protein complex binding / cytolytic granule / TAP2 binding / TAP1 binding / protein disulfide-isomerase ...MHC class Ib protein complex assembly / peptide antigen stabilization / Tapasin-ERp57 complex / response to biphenyl / Calnexin/calreticulin cycle / MHC class I protein complex binding / cytolytic granule / TAP2 binding / TAP1 binding / protein disulfide-isomerase / nuclear receptor-mediated glucocorticoid signaling pathway / positive regulation of dendritic cell chemotaxis / Assembly of Viral Components at the Budding Site / ATF6 (ATF6-alpha) activates chaperone genes / cortical granule / negative regulation of trophoblast cell migration / cellular response to electrical stimulus / regulation of meiotic nuclear division / response to peptide / negative regulation of retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway / : / complement component C1q complex binding / endoplasmic reticulum quality control compartment / protein folding in endoplasmic reticulum / sarcoplasmic reticulum lumen / disulfide oxidoreductase activity / negative regulation of intracellular steroid hormone receptor signaling pathway / regulation of protein complex stability / nuclear export signal receptor activity / C-type glycerophospholipase activity / cardiac muscle cell differentiation / retrograde vesicle-mediated transport, Golgi to endoplasmic reticulum / cellular response to interleukin-7 / cortical actin cytoskeleton organization / positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / response to glycoside / positive regulation of memory T cell activation / T cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target / TAP complex binding / Scavenging by Class A Receptors / positive regulation of CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell activation / CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell activation / Golgi medial cisterna / positive regulation of CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell proliferation / nuclear androgen receptor binding / cellular response to lithium ion / Scavenging by Class F Receptors / CD8 receptor binding / protein disulfide isomerase activity / negative regulation of neuron differentiation / response to testosterone / antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I / antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I via ER pathway, TAP-dependent / lncRNA binding / beta-2-microglobulin binding / endoplasmic reticulum exit site / smooth endoplasmic reticulum / MHC class I protein binding / TAP binding / hormone binding / protection from natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity / protein-disulfide reductase activity / molecular sequestering activity / antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class Ib / antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I via ER pathway, TAP-independent / detection of bacterium / protein localization to nucleus / T cell receptor binding / phagocytic vesicle / extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / ERAD pathway / positive regulation of cell cycle / endocytic vesicle lumen / positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of endothelial cell migration / peptide binding / protein folding chaperone / acrosomal vesicle / protein export from nucleus / positive regulation of phagocytosis / response to endoplasmic reticulum stress / early endosome lumen / Nef mediated downregulation of MHC class I complex cell surface expression / DAP12 interactions / Endosomal/Vacuolar pathway / protein maturation / Antigen Presentation: Folding, assembly and peptide loading of class I MHC / negative regulation of iron ion transport / lumenal side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane / T cell mediated cytotoxicity / cellular response to iron(III) ion / negative regulation of forebrain neuron differentiation / antigen processing and presentation of exogenous protein antigen via MHC class Ib, TAP-dependent / ER to Golgi transport vesicle membrane / peptide antigen assembly with MHC class I protein complex / transferrin transport / regulation of iron ion transport / regulation of erythrocyte differentiation / negative regulation of receptor-mediated endocytosis Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
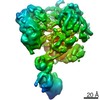
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 5.8 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Trowitzsch, S. / Januliene, D. / Blees, A. / Moeller, A. / Tampe, R. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 2items Germany, 2items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2017 Journal: Nature / Year: 2017Title: Structure of the human MHC-I peptide-loading complex. Authors: Andreas Blees / Dovile Januliene / Tommy Hofmann / Nicole Koller / Carla Schmidt / Simon Trowitzsch / Arne Moeller / Robert Tampé /  Abstract: The peptide-loading complex (PLC) is a transient, multisubunit membrane complex in the endoplasmic reticulum that is essential for establishing a hierarchical immune response. The PLC coordinates ...The peptide-loading complex (PLC) is a transient, multisubunit membrane complex in the endoplasmic reticulum that is essential for establishing a hierarchical immune response. The PLC coordinates peptide translocation into the endoplasmic reticulum with loading and editing of major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) molecules. After final proofreading in the PLC, stable peptide-MHC-I complexes are released to the cell surface to evoke a T-cell response against infected or malignant cells. Sampling of different MHC-I allomorphs requires the precise coordination of seven different subunits in a single macromolecular assembly, including the transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP1 and TAP2, jointly referred to as TAP), the oxidoreductase ERp57, the MHC-I heterodimer, and the chaperones tapasin and calreticulin. The molecular organization of and mechanistic events that take place in the PLC are unknown owing to the heterogeneous composition and intrinsically dynamic nature of the complex. Here, we isolate human PLC from Burkitt's lymphoma cells using an engineered viral inhibitor as bait and determine the structure of native PLC by electron cryo-microscopy. Two endoplasmic reticulum-resident editing modules composed of tapasin, calreticulin, ERp57, and MHC-I are centred around TAP in a pseudo-symmetric orientation. A multivalent chaperone network within and across the editing modules establishes the proofreading function at two lateral binding platforms for MHC-I molecules. The lectin-like domain of calreticulin senses the MHC-I glycan, whereas the P domain reaches over the MHC-I peptide-binding pocket towards ERp57. This arrangement allows tapasin to facilitate peptide editing by clamping MHC-I. The translocation pathway of TAP opens out into a large endoplasmic reticulum lumenal cavity, confined by the membrane entry points of tapasin and MHC-I. Two lateral windows channel the antigenic peptides to MHC-I. Structures of PLC captured at distinct assembly states provide mechanistic insight into the recruitment and release of MHC-I. Our work defines the molecular symbiosis of an ABC transporter and an endoplasmic reticulum chaperone network in MHC-I assembly and provides insight into the onset of the adaptive immune response. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6eny.cif.gz 6eny.cif.gz | 257.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6eny.ent.gz pdb6eny.ent.gz | 168 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6eny.json.gz 6eny.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/en/6eny https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/en/6eny ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/en/6eny ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/en/6eny | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  3906MC  3904C  3905C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 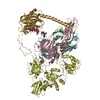
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 5 types, 5 molecules BCDFG
| #1: Protein | Mass: 11748.160 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P61769 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P61769 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 45761.184 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O15533 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O15533 |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 54341.102 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P30101, protein disulfide-isomerase Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P30101, protein disulfide-isomerase |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 38363.535 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P04439 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P04439 |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 46507.145 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P27797 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P27797 |
-Sugars , 2 types, 2 molecules
| #6: Polysaccharide | 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source |
|---|---|
| #7: Polysaccharide | beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-3)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-mannopyranose Type: oligosaccharide / Mass: 666.578 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Protein Complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#5 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 2 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid type: C-flat-2/2 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 55 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: CTF correction was performed internally in Relion and Frealign Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 5.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 141078 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 5.8 Å |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj









