[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
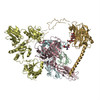
Yorodumi- PDB-7qpd: Structure of the human MHC I peptide-loading complex editing module -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7qpd | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the human MHC I peptide-loading complex editing module | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | IMMUNE SYSTEM / antigen processing / peptide proofreading / chaperones / MHC I | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationMHC class Ib protein complex assembly / peptide antigen stabilization / Tapasin-ERp57 complex / response to biphenyl / Calnexin/calreticulin cycle / MHC class I protein complex binding / cytolytic granule / TAP2 binding / TAP1 binding / protein disulfide-isomerase ...MHC class Ib protein complex assembly / peptide antigen stabilization / Tapasin-ERp57 complex / response to biphenyl / Calnexin/calreticulin cycle / MHC class I protein complex binding / cytolytic granule / TAP2 binding / TAP1 binding / protein disulfide-isomerase / nuclear receptor-mediated glucocorticoid signaling pathway / positive regulation of dendritic cell chemotaxis / Assembly of Viral Components at the Budding Site / ATF6 (ATF6-alpha) activates chaperone genes / cortical granule / negative regulation of trophoblast cell migration / cellular response to electrical stimulus / regulation of meiotic nuclear division / response to peptide / negative regulation of retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway / : / complement component C1q complex binding / endoplasmic reticulum quality control compartment / protein folding in endoplasmic reticulum / sarcoplasmic reticulum lumen / disulfide oxidoreductase activity / negative regulation of intracellular steroid hormone receptor signaling pathway / regulation of protein complex stability / nuclear export signal receptor activity / C-type glycerophospholipase activity / cardiac muscle cell differentiation / retrograde vesicle-mediated transport, Golgi to endoplasmic reticulum / cellular response to interleukin-7 / cortical actin cytoskeleton organization / positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / response to glycoside / positive regulation of memory T cell activation / T cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target / TAP complex binding / positive regulation of CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell activation / Scavenging by Class A Receptors / CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell activation / Golgi medial cisterna / positive regulation of CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell proliferation / Scavenging by Class F Receptors / nuclear androgen receptor binding / cellular response to lithium ion / CD8 receptor binding / protein disulfide isomerase activity / negative regulation of neuron differentiation / antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I via ER pathway, TAP-dependent / response to testosterone / antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I / lncRNA binding / beta-2-microglobulin binding / endoplasmic reticulum exit site / smooth endoplasmic reticulum / MHC class I protein binding / TAP binding / hormone binding / protection from natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity / protein-disulfide reductase activity / molecular sequestering activity / antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class Ib / antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I via ER pathway, TAP-independent / detection of bacterium / protein localization to nucleus / T cell receptor binding / phagocytic vesicle / extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / ERAD pathway / positive regulation of cell cycle / endocytic vesicle lumen / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / peptide binding / protein folding chaperone / positive regulation of endothelial cell migration / acrosomal vesicle / protein export from nucleus / positive regulation of phagocytosis / response to endoplasmic reticulum stress / early endosome lumen / Nef mediated downregulation of MHC class I complex cell surface expression / DAP12 interactions / Endosomal/Vacuolar pathway / protein maturation / Antigen Presentation: Folding, assembly and peptide loading of class I MHC / T cell mediated cytotoxicity / lumenal side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane / negative regulation of iron ion transport / cellular response to iron(III) ion / negative regulation of forebrain neuron differentiation / antigen processing and presentation of exogenous protein antigen via MHC class Ib, TAP-dependent / regulation of iron ion transport / ER to Golgi transport vesicle membrane / peptide antigen assembly with MHC class I protein complex / regulation of erythrocyte differentiation / transferrin transport / response to molecule of bacterial origin Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.73 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Domnick, A. / Susac, L. / Trowitzsch, S. / Thomas, C. / Tampe, R. | |||||||||
| Funding support | European Union, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Molecular basis of MHC I quality control in the peptide loading complex. Authors: Alexander Domnick / Christian Winter / Lukas Sušac / Leon Hennecke / Mario Hensen / Nicole Zitzmann / Simon Trowitzsch / Christoph Thomas / Robert Tampé /   Abstract: Major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC I) molecules are central to adaptive immunity. Their assembly, epitope selection, and antigen presentation are controlled by the MHC I glycan through a ...Major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC I) molecules are central to adaptive immunity. Their assembly, epitope selection, and antigen presentation are controlled by the MHC I glycan through a sophisticated network of chaperones and modifying enzymes. However, the mechanistic integration of the corresponding processes remains poorly understood. Here, we determine the multi-chaperone-client interaction network of the peptide loading complex (PLC) and report the PLC editing module structure by cryogenic electron microscopy at 3.7 Å resolution. Combined with epitope-proofreading studies of the PLC in near-native lipid environment, these data show that peptide-receptive MHC I molecules are stabilized by multivalent chaperone interactions including the calreticulin-engulfed mono-glucosylated MHC I glycan, which only becomes accessible for processing by α-glucosidase II upon loading of optimal epitopes. Our work reveals allosteric coupling between peptide-MHC I assembly and glycan processing. This inter-process communication defines the onset of an adaptive immune response and provides a prototypical example of the tightly coordinated events in endoplasmic reticulum quality control. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7qpd.cif.gz 7qpd.cif.gz | 280.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7qpd.ent.gz pdb7qpd.ent.gz | 214.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7qpd.json.gz 7qpd.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qp/7qpd https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qp/7qpd ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qp/7qpd ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qp/7qpd | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  14119MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 5 types, 5 molecules BTEMC
| #1: Protein | Mass: 11748.160 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P61769 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P61769 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 45761.184 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O15533 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O15533 |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 54341.102 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P30101, protein disulfide-isomerase Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P30101, protein disulfide-isomerase |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 38363.535 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P04439 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P04439 |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 46523.211 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P27797 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P27797 |
-Sugars , 2 types, 2 molecules
| #6: Polysaccharide | beta-D-mannopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta- ...beta-D-mannopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source |
|---|---|
| #7: Polysaccharide | alpha-D-glucopyranose-(1-3)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D- ...alpha-D-glucopyranose-(1-3)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-3)-beta-D-mannopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose Type: oligosaccharide / Mass: 1235.105 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: editing module of peptide-loading complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#5 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 68 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Details: Patch CTF / Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.73 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 97952 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj









