[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
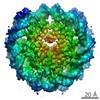
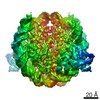
Yorodumi- EMDB-30239: The cryo-EM structure of CENP-A nucleosome in complex with the ph... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-30239 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | The cryo-EM structure of CENP-A nucleosome in complex with the phosphorylated CENP-C | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CENP-A nucleosome / CENP-C / CENP-N / complex / kinetochore / NUCLEAR PROTEIN / CELL CYCLE | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationInterleukin-7 signaling / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / : / HATs acetylate histones / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / : / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication ...Interleukin-7 signaling / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / : / HATs acetylate histones / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / : / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / CENP-A containing chromatin assembly / centromeric DNA binding / protein localization to chromosome, centromeric region / kinetochore assembly / condensed chromosome, centromeric region / detection of maltose stimulus / maltose transport complex / carbohydrate transport / mitotic cytokinesis / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / carbohydrate transmembrane transporter activity / maltose binding / maltose transport / maltodextrin transmembrane transport / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / pericentric heterochromatin / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter complex, substrate-binding subunit-containing / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter complex / telomere organization / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Meiotic synapsis / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / cell chemotaxis / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / innate immune response in mucosa / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / Defective pyroptosis / Negative Regulation of CDH1 Gene Transcription / HDACs deacetylate histones / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / lipopolysaccharide binding / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / HDMs demethylate histones / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / kinetochore / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Meiotic recombination / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / Metalloprotease DUBs / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / RMTs methylate histone arginines / HCMV Early Events / structural constituent of chromatin / UCH proteinases / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / nucleosome assembly / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / antibacterial humoral response / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / outer membrane-bounded periplasmic space / HATs acetylate histones Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) | ||||||||||||
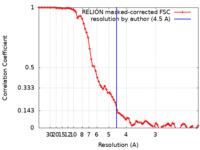
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.5 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ariyoshi M / Makino F | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 3 items Japan, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2021 Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2021Title: Cryo-EM structure of the CENP-A nucleosome in complex with phosphorylated CENP-C. Authors: Mariko Ariyoshi / Fumiaki Makino / Reito Watanabe / Reiko Nakagawa / Takayuki Kato / Keiichi Namba / Yasuhiro Arimura / Risa Fujita / Hitoshi Kurumizaka / Ei-Ichi Okumura / Masatoshi Hara / Tatsuo Fukagawa /  Abstract: The CENP-A nucleosome is a key structure for kinetochore assembly. Once the CENP-A nucleosome is established in the centromere, additional proteins recognize the CENP-A nucleosome to form a ...The CENP-A nucleosome is a key structure for kinetochore assembly. Once the CENP-A nucleosome is established in the centromere, additional proteins recognize the CENP-A nucleosome to form a kinetochore. CENP-C and CENP-N are CENP-A binding proteins. We previously demonstrated that vertebrate CENP-C binding to the CENP-A nucleosome is regulated by CDK1-mediated CENP-C phosphorylation. However, it is still unknown how the phosphorylation of CENP-C regulates its binding to CENP-A. It is also not completely understood how and whether CENP-C and CENP-N act together on the CENP-A nucleosome. Here, using cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) in combination with biochemical approaches, we reveal a stable CENP-A nucleosome-binding mode of CENP-C through unique regions. The chicken CENP-C structure bound to the CENP-A nucleosome is stabilized by an intramolecular link through the phosphorylated CENP-C residue. The stable CENP-A-CENP-C complex excludes CENP-N from the CENP-A nucleosome. These findings provide mechanistic insights into the dynamic kinetochore assembly regulated by CDK1-mediated CENP-C phosphorylation. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_30239.map.gz emd_30239.map.gz | 34 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-30239-v30.xml emd-30239-v30.xml emd-30239.xml emd-30239.xml | 26.8 KB 26.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_30239_fsc.xml emd_30239_fsc.xml | 7.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_30239.png emd_30239.png | 32.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-30239.cif.gz emd-30239.cif.gz | 7.6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30239 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30239 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30239 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30239 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7by0MC 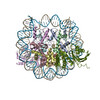 7bxtC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10565 (Title: The cryo-EM structure of the CENP-A nucleosome in complex with the phosphorylated CENP-C: CENP-A nucleosome in complex with phosphorylated CENP-C C-terminal domain (601-864) and CENP-N N-terminal domain (1-211) EMPIAR-10565 (Title: The cryo-EM structure of the CENP-A nucleosome in complex with the phosphorylated CENP-C: CENP-A nucleosome in complex with phosphorylated CENP-C C-terminal domain (601-864) and CENP-N N-terminal domain (1-211)Data size: 1.6 TB Data #1: CENP-A nucleosome in complex with phosphorylated CENP-C C-terminal domain (601-864) and CENP-N N-terminal domain (1-211) [micrographs - multiframe]) |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_30239.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 36.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_30239.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 36.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : CENP-A nucleosome in complex with CENP-C C-terminal and CNEP-N N-...
+Supramolecule #1: CENP-A nucleosome in complex with CENP-C C-terminal and CNEP-N N-...
+Supramolecule #2: Histone H3,Histone H3-like centromeric protein A
+Supramolecule #3: Histone H4
+Supramolecule #4: Histone H2A type 1-B/E
+Supramolecule #5: Histone H2B type 1-J
+Supramolecule #6: DNA (145-mer)
+Supramolecule #7: Maltodextrin-binding protein,LINKER PEPTIDE,CENP-C
+Macromolecule #1: Histone H3.2,Histone H3-like centromeric protein A
+Macromolecule #2: Histone H4
+Macromolecule #3: Histone H2A type 1-B/E
+Macromolecule #4: Histone H2B type 1-J
+Macromolecule #7: Maltose Binding Protein tag, linker,CENP-C
+Macromolecule #5: DNA (145-MER)
+Macromolecule #6: DNA (145-MER)
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.5 mg/mL | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R0.6/1 / Material: MOLYBDENUM / Mesh: 200 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY ARRAY / Support film - Film thickness: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 10 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | JEOL CRYO ARM 200 |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Min: 80.0 K / Max: 80.0 K |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 3838 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 3710 pixel / Digitization - Frames/image: 1-50 / Number grids imaged: 5 / Number real images: 5346 / Average exposure time: 10.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 1.2 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 150.0 µm / Calibrated defocus max: -7.0 µm / Calibrated defocus min: -0.5 µm / Calibrated magnification: 45454 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 1.4 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 50000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: JEOL CRYOSPECPORTER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



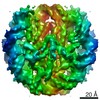
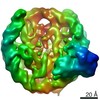
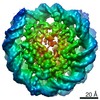
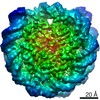
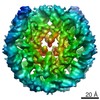
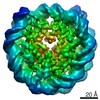
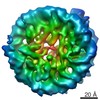
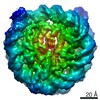
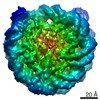
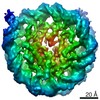
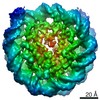
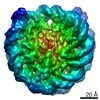











 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)