+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7c9v | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | E30 F-particle in complex with FcRn | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRUS / Echovirus B / mature / receptor | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationIgG immunoglobulin transcytosis in epithelial cells mediated by FcRn immunoglobulin receptor / IgG binding / beta-2-microglobulin binding / symbiont-mediated suppression of host cytoplasmic pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway via inhibition of RIG-I activity / early endosome lumen / Nef mediated downregulation of MHC class I complex cell surface expression / DAP12 interactions / picornain 2A / Endosomal/Vacuolar pathway / symbiont-mediated suppression of host mRNA export from nucleus ...IgG immunoglobulin transcytosis in epithelial cells mediated by FcRn immunoglobulin receptor / IgG binding / beta-2-microglobulin binding / symbiont-mediated suppression of host cytoplasmic pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway via inhibition of RIG-I activity / early endosome lumen / Nef mediated downregulation of MHC class I complex cell surface expression / DAP12 interactions / picornain 2A / Endosomal/Vacuolar pathway / symbiont-mediated suppression of host mRNA export from nucleus / Antigen Presentation: Folding, assembly and peptide loading of class I MHC / symbiont genome entry into host cell via pore formation in plasma membrane / picornain 3C / negative regulation of iron ion transport / T cell mediated cytotoxicity / cellular response to iron(III) ion / negative regulation of forebrain neuron differentiation / antigen processing and presentation of exogenous protein antigen via MHC class Ib, TAP-dependent / T=pseudo3 icosahedral viral capsid / ER to Golgi transport vesicle membrane / peptide antigen assembly with MHC class I protein complex / transferrin transport / regulation of iron ion transport / regulation of erythrocyte differentiation / negative regulation of receptor-mediated endocytosis / HFE-transferrin receptor complex / response to molecule of bacterial origin / MHC class I peptide loading complex / cellular response to iron ion / positive regulation of T cell cytokine production / antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I / MHC class I protein complex / host cell cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / peptide antigen assembly with MHC class II protein complex / negative regulation of neurogenesis / positive regulation of receptor-mediated endocytosis / cellular response to nicotine / MHC class II protein complex / positive regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity / multicellular organismal-level iron ion homeostasis / specific granule lumen / peptide antigen binding / antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class II / phagocytic vesicle membrane / positive regulation of immune response / recycling endosome membrane / positive regulation of T cell activation / Interferon gamma signaling / Immunoregulatory interactions between a Lymphoid and a non-Lymphoid cell / negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation / ribonucleoside triphosphate phosphatase activity / viral capsid / Modulation by Mtb of host immune system / sensory perception of smell / positive regulation of cellular senescence / tertiary granule lumen / DAP12 signaling / MHC class II protein complex binding / T cell differentiation in thymus / late endosome membrane / nucleoside-triphosphate phosphatase / negative regulation of neuron projection development / host cell / channel activity / ER-Phagosome pathway / protein refolding / early endosome membrane / monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / amyloid fibril formation / protein homotetramerization / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / learning or memory / DNA replication / RNA helicase activity / endosome membrane / immune response / endocytosis involved in viral entry into host cell / endoplasmic reticulum lumen / Amyloid fiber formation / Golgi membrane / symbiont-mediated suppression of host gene expression / external side of plasma membrane / symbiont-mediated activation of host autophagy / lysosomal membrane / RNA-directed RNA polymerase / focal adhesion / cysteine-type endopeptidase activity / viral RNA genome replication / RNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / Neutrophil degranulation / DNA-templated transcription / virion attachment to host cell / host cell nucleus / SARS-CoV-2 activates/modulates innate and adaptive immune responses / structural molecule activity / endoplasmic reticulum / Golgi apparatus / protein homodimerization activity / proteolysis / extracellular space Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) Echovirus E30 Echovirus E30 | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang, K. / Zhu, L. / Sun, Y. / Li, M. / Zhao, X. / Cui, L. / Zhang, L. / Gao, G. / Zhai, W. / Zhu, F. ...Wang, K. / Zhu, L. / Sun, Y. / Li, M. / Zhao, X. / Cui, L. / Zhang, L. / Gao, G. / Zhai, W. / Zhu, F. / Rao, Z. / Wang, X. | ||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1items China, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020Title: Structures of Echovirus 30 in complex with its receptors inform a rational prediction for enterovirus receptor usage. Authors: Kang Wang / Ling Zhu / Yao Sun / Minhao Li / Xin Zhao / Lunbiao Cui / Li Zhang / George F Gao / Weiwei Zhai / Fengcai Zhu / Zihe Rao / Xiangxi Wang /  Abstract: Receptor usage that determines cell tropism and drives viral classification closely correlates with the virus structure. Enterovirus B (EV-B) consists of several subgroups according to receptor ...Receptor usage that determines cell tropism and drives viral classification closely correlates with the virus structure. Enterovirus B (EV-B) consists of several subgroups according to receptor usage, among which echovirus 30 (E30), a leading causative agent for human aseptic meningitis, utilizes FcRn as an uncoating receptor. However, receptors for many EVs remain unknown. Here we analyzed the atomic structures of E30 mature virion, empty- and A-particles, which reveals serotype-specific epitopes and striking conformational differences between the subgroups within EV-Bs. Of these, the VP1 BC loop markedly distinguishes E30 from other EV-Bs, indicative of a role as a structural marker for EV-B. By obtaining cryo-electron microscopy structures of E30 in complex with its receptor FcRn and CD55 and comparing its homologs, we deciphered the underlying molecular basis for receptor recognition. Together with experimentally derived viral receptor identifications, we developed a structure-based in silico algorithm to inform a rational prediction for EV receptor usage. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7c9v.cif.gz 7c9v.cif.gz | 220.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7c9v.ent.gz pdb7c9v.ent.gz | 174.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7c9v.json.gz 7c9v.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/c9/7c9v https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/c9/7c9v ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/c9/7c9v ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/c9/7c9v | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 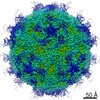 30318MC  7c9sC  7c9tC  7c9uC  7c9wC  7c9xC  7c9yC 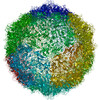 7c9zC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 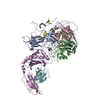
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | x 60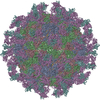
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | x 5
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | x 6
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | 
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | x 60
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Noncrystallographic symmetry (NCS) | NCS oper:
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 UCSF Chimera
UCSF Chimera




 PDBj
PDBj





